|
|
|
|
Article Type: Research Article
Article Citation: Dr. Gurnam Singh, and Dr. Deepak Kumar
Shrivastava. (2020). ASSESSMENT AND INFRASTRUCTURE OF DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARY
SYSTEM IN KOTA REGION (RAJASTHAN). International Journal of Research
-GRANTHAALAYAH, 8(5), 38-50. https://doi.org/10.29121/granthaalayah.v8.i5.2020.52
Received Date: 03 May 2020
Accepted Date: 19 May 2020
Keywords:
Social Capital
Public Libraries
Trust
Integration
Community Cohesion
ABSTRACT
The public libraries play very important role in fostering the intellectual development of society at large. They support both formal and non-formal education systems of our society. They are considered as People’s University and serve as a center for self-education and lifelong learning. They are considered to be an intellectual power house which strives to fulfill and meet the educational needs of the public through varied resources and services Presented Research Paper reveals that Rajasthan State are need urgent attention on the District Public libraries for lack of staff and insufficient budget. It’s great achievement that in 2006, Library legislation passed in Rajasthan but not seems their major effects till today. I think Rajasthan needs advocacy to run the Public libraries. In Rajasthan, maximum libraries are facing the problem of book losses and no regular basis stock verification done. Hope after reviewing this study Govt. of Rajasthan will observe the pros and cons.
1. INTRODUCTION
Public library is a Public institution, established with charge of care of collection of book and duty of accessible those who use them and task of convincing every reader without cast, creed, age, sex or etc. infect, Intellectuals of particular city can be judge by enrollment of them in Public library because it’s a lifelong learning institution and cultural hub of knowledge.
“A Public library is a library that is
accessible by the general Public and is generally funded from Public sources,
such as taxes”.
Public libraries in India is not much more appreciated by Govt. and NGO’s also before 21stcentury and specially if we see the scenario of North Indian libraries than we will get unseated because South India is more and more powerful in comparison to other regions of India. Reasons may be many. In North India Rajasthan and Punjab both are the state mostly depends on agriculture and now both are fast growing state in India. So the question is that how the more or less same nature state is driving their libraries in current scenario. Public Library in current environment becomes the community hub and providing more or more services to the community.
The Public library is an institution for the people, of
people, and by the people. It is for all, without the distinction of cast,
creed, color and Public library has to play a crucial role in modern society in
meeting many of its social needs like communication, education, recreation and
socio-cultural development. This role is more curial in developing countries
like India where societal change are faster than elsewhere and the people need
to be better informed in order to be successfully involved in the process of
change and development. For the Public library to play this role effectively it
must be established on a statuary foundation. At least this has been the
universal consensus with regard to be the Public library. Establishment of the
Raja Ram Mohan Roy library Foundation has given an impetus to the development
of Public libraries. The foundation seeks to assist State Government in the
establishment of rural libraries. Thus, in comparison with the condition on the
eve of independence; the present conditions in India are more conductive to
Public library development.
1.1. SERVICES OF PUBLIC LIBRARY
· Service of books and other library material.
· Reference Service.
· Inter library loan.
· Newspapers.
· Journals and Magazines service.
· Photocopy Printing and Scanning Service.
· Help in searching in search of library books and other documents for readers.
· Reservation of Books for readers.
· Current Awareness services (CAS).
· Online Public Access Catalogue (OPAC).
· Internet / Wi-Fi Service.
· Provide Audio-Video Materials.
· Bibliographic Services.
· Physically Catalogue.
· Books Fare and Exhibition.
· Cultural Activities in library.
Beyond all these services many new services has been provided in North Indian libraries like in Govt. Divisional Public Library Kota provides –
1) Tele Health Awareness Services by the assistance of IPLM
2) Class on Screen Services for IIT JEE
3) Voice Donation Program
4) Library Services for Marginalized People
5) Library Services for Prisoners’
6) Animal Clinic Services
7) Research Assistance Services.
2. ABOUT RAJASTHAN AND RAJASTHAN DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARIES SENARIO
Rajasthan is the largest State of the republic of India in terms of area. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert, which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with Pakistan. The region borders Pakistan to the west, Gujarat to the southwest, Madhya Pradesh to the southeast, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana to the northeast and Punjab to the North. Rajasthan was formed on 30 March, 1949, when all erstwhile princely States merged in to India. The only difference between erstwhile Rajputana and Rajasthan is the certain portion Governed directly by the British Government, in the province of Ajmer-Merwara, were include. Portions lying geographically outside of Rajputana and belonging to Tonk state were given to Madhya Pradesh.
2.1. THE PRESENT RAJASTHAN HAS
Table 1: Demographic Scenario of North West Region of Rajasthan
|
1 |
Total area: |
3,42,236 Km Square |
|
2 |
Region: |
North- West |
|
3 |
Capital: |
Jaipur |
|
4 |
Total Population: |
7,47,91,568 (in 2016) |
|
5 |
Literacy Rate: |
Male: 79.19%, Female: 52.12% (2011) |
|
6 |
Area: |
3,42,236 Km Square |
|
7 |
Sex Ratio: |
1000 Male, 926 Females |
|
8 |
Languages: |
Hindi, English |
|
9 |
Lok Sabha: |
25 |
|
10 |
Rajya Sabha: |
10 |
|
11 |
Legislator Assembly: |
200 |
|
12 |
District: |
33 |
|
13 |
Division: |
07 |
2.2. PRESENT PUBLIC LIBRARIES SCENARIO IN RAJASTHAN
Public library system of Rajasthan is performing well after passing library legislation Act in year 2006, although started working in 2001, when the Government of Rajasthan established the separate department of public libraries in merging with pre-established “Bhasha Vibhag” and finally now department is working as “Department of Language and Library Science”. Now the Public libraries are owned department and rest are on the basis of department from Govt. Rajasthan department of education. After passing the act Directorate of Language and library move towards automation and started to feeling details of books in library Software’s designed by Rajcomp for Public libraries. In Rajasthan at present there is 1 (One) State Central library, 7 Divisional libraries, 33-District libraries, 6-Tehsil libraries and 276- Panchayat Samiti libraries.
Table 2: Types of Libraries available in Rajasthan
|
S. No. |
Types of Libraries available in Rajasthan |
No. of Libraries |
|
1 |
Govt. Central State Public Library |
01 |
|
2 |
Govt. Divisional Public Libraries |
07 |
|
3 |
Govt. District Public Libraries |
33 |
|
4 |
Govt. Tehsil Public Libraries |
06 |
|
5 |
Govt. Panchayat Samiti Libraries (Part -Time) |
276 |
|
|
Total No of Libraries |
323 |
All the Public libraries of Rajasthan governed by directorate ‘Department of language and library’ Govt. of Rajasthan. This directorate manages the finance, infrastructure and services to concern library.
All the State, Divisional and District Public libraries governed by directorate while all Panchayat Samiti libraries funded by directorate but libraries are provided by department of education. So we can say two type of library handling by directorate.
Full Time Libraries: 47
Part Time Libraries: 276
Full time means open to all according to time from Governed by directorate while part time means before school time library and after school time library.
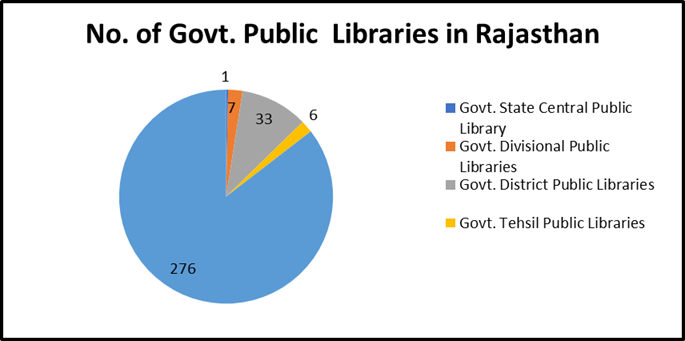
Figure 1: Government Public Libraries in Rajasthan
2.3. KOTA REGION
On the Rajasthan, the present study concentrates on Govt. Divisional Public library Kota and all Govt. District Public libraries of the Kota Region. The library names are under:
Table 3: Establishment Year Description of Public Libraries
|
S.NO. |
NAME OF THE LIBRARY |
YEAR OF ESTABLISHMENT |
|
1 |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
1956 |
|
2 |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi (Kota) |
2008 |
|
3 |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
1956 |
|
4 |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
1956 |
|
5 |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
1956 |
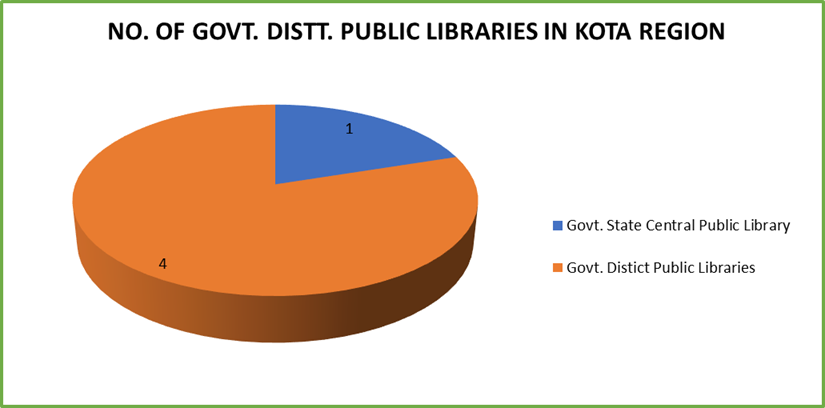
Figure 2: No. Of Govt. Distt. Public Libraries In Kota Region
2.4. IMPORTANCE OF THE PROPOSED RESEARCH
The focus of the present study is on the District Public libraries of Rajasthan. For this purpose the Govt. District Public libraries of Kota Region (Rajasthan) have been taken up. The primary objective of this study is to find out the strength and weakness of this system. Finding of this study can be applied to improve the govt. District Public library systems of Rajasthan. This research with the important in creating awareness about the Govt. District Public libraries of Rajasthan.
3. PREVIOUS STUDIES
Literature review is an important component of any research work. Literature pertained to this research study has been derived from different information sources such as textbook, journals (CD-ROMs, online and print) and reference sources etc. with the aim of putting the study in proper prospective. In order to achieve this effectively, the information related to topic on “Assessment and infrastructure of Public library system in Kota region Rajasthan” the review is focus in the following manner: The concept of development and assessment of Public Library System.
Smith (1984) has reviewed the involvement of the public libraries in literacy education. The public libraries in U.S.A. were selected for his study. The important findings of the study revealed that 1) public libraries in urban and sub-urban communities are involved more in literacy education than libraries in rural communities, 2) public libraries located in large communities and serving demographically heterogeneous areas p[provide more literacy education services than libraries is smaller and homogeneous communities, 3) larger libraries have more literacy education programmes than smaller libraries, 4) public libraries that have a wide range of non-print materials and equipment are more active in literacy education than libraries with limited non-print resources, 5) more libraries that involved in literacy education provide in-service training to their staff than libraries which do not provide these services and 6) the main barriers to the literacy education are the low profile of public libraries in the community, staffing patterns, and lack of staff expertise.
HaniffUddin (2000) has emphasized the importance of establishing rural libraries in each and every village of Bangladesh. They are: 1) To sensitize the people to better health, water supply and sanitation, 2) To find out government policy, 3) To provide better crops, 4) To prevent and control environmental pollution, 5) To provide text books and teaching aids, 6) To provide sport facilities, and 7) To prevent and control social problems. The study explored the inter linkages between libraries and rural development and also highlighted some rural aspects of the country.
Thomas (2001) has studied the state of application of IT in the public library field in India, their future plans and the problems they face in this process. The findings of the study revealed that 8℅ of the libraries computerized are two state central libraries, two district libraries and a voluntary organization library. They are T.S Central state library, Chandigarh; H.K.M. State Library, Bhubaneswar; District central Library, Coimbatore; City central Library, south zone, Bangalore; and Ramakrishna mission Vivekananda Library, Bhubaneswar. Only 28℅ libraries were planning to automate. The major problem the library encountered was with regard to updating of databases and correctness of entries.
Proctor, R. A. (2001) reported on the public library work force project, a two year U.K study funded by the library and Information commission which looked at employer’s needs and the Department of Library and Information studies curriculum, career choices for newly qualified and qualifying librarians, recruitment and selection issues and the retention of professional staff. It also covered training and development. The survey achieved 84 percent response from public library authorities. The results are that the recruitment, development and leadership issues in particular need to be urgently addressed in this sector.
Raju (1990) has attempted an evaluative study of the working of Andhra Pradesh public Libraries Act, 1960 and its contribution towards the development of public services in the state. The evaluation of this Act and public library services in Andhra Pradesh revealed that the state public Library system failed to provide an effective public library service. The library cess is not effectively collected and remitted by the local administrator and thus planning and phasing of services are in the face of uncertainty. Financial constraints remain the major bottleneck in universalizing free public library service in the state. The government gives no due importance to the improvement of library system in the state. The study led to the conclusion that only an Imaginative leadership in the state can save the situation from ending in a catastrophe.
Laxman Rao and Ratna Rao (1997) have conducted a study on the role of public libraries in national and social movements in Andhra Pradesh during the pre-independence period. The social movements were against caste system, evils of drinking, widow marriages, women’s education etc. The various national movements were independence movement and such others. The findings of the study indicated that the role played by the libraries in these movements helped to redefine the purpose and function of libraries.
Venkata Ramana and Vinod Kumar (1997) have emphasized the importance of a need-based planning for public library automation in their study report and indicated the following important facts to develop and execute effective plans to implement the library information storage and retrieval process in public libraries: 1) It requires the financial support from funding agencies, talent, education, creativity, determination, management and above all vision on the part of the library professional and other support staff and 2) The professionals should get themselves trained and take the lead in operating the systems.
Deshpande (2000) has studied the importance of public libraries in developing countries and has pointed out the salient characteristics of a public library and grass root services. the services which can be offered to the public are detailed in the study, which are educating the illiterates, providing information Services for women, giving children's service, conducting adult education classes, providing information on social evils, giving information service to the farmers, creating science temper, and providing information services to the disadvantaged.
Padmamma et al. (2001) has assessed children's views on public library through a survey of child users of Chickmanagalore City Central library, Karnataka. The study revealed the perceptions of child users on the existing facilities, services, and resources as: almost all of the respondents feel good about collection of books, magazine and newspapers; but they the library does not provide the user services like new arrival services, inter-library loan, paper clipping service, reference service, overnight issue and book exhibition and the children and concludes we the statement that the user satisfaction should be the ultimate objective of the library.
Shrivastava, D.K. (2008) has studied the public library system in Rajasthan to figure out the implementation of information technology. The study revealed that ICT knowledge of library staff working in Public Libraries is very low, which has become hindrance in 10 automation Public Libraries in Rajasthan. It was suggested that government should provide facility for imparting technological skills of the library staff.
4. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The survey method is being adopted to conduct the research for the present study. Survey method is generally conducted in the field of librarianship. It is useful to know the exact facts and figures about a system. The questionnaire will be prepared for librarian.
4.1. Questionnaire for Librarian (Library Survey)
For this purpose, the research scholar intends to visit the Govt. District Public Library understudy of Kota Region in Rajasthan. For the collection of data, questionnaires would be designed for the Librarians. A Structured questionnaire with multiple choices and open-ended question, designed according to objectives, would be handed over to each librarian. Primary data would be collected through the questionnaire containing the various questions related to the district Public Library system i.e. Library collection, reading room facility, book selection procedure, circulation system, Library finance, Library automation and Library infrastructure etc. For secondary data extensive use annual reports, Library Journals, e-newsletter, national and international publications would be made.
4.2. SCOPE OF THE STUDY: LIMITATIONS
The present study required lot of field work and survey to know the existing status of assessment and infrastructure of Public libraries system in the Govt. District Public libraries of Kota Region Rajasthan. Since the definition of Public Library includes all the large and small libraries that provide library service to the public is not possible for the investigator to cover all the libraries in each city and village of Rajasthan. The present study only concentrates on the assessment and infrastructure of Govt. Divisional Public Library Kota (Rajasthan), all Govt. District Public libraries Kota Division Rajasthan:
Table 4: List of Govt. District Public Libraries in Kota Region (Raj)
|
S. No. |
NAME OF THE LIBRARY |
|
1. |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
|
2. |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi (Kota) |
|
3. |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
|
4. |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
|
5. |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
4.3. PROCEDURE OF DATA COLLECTION
The data for the present study was collected by personally visiting all the libraries included in the study. Information regarding system, services and ongoing scenario as well as the expected future plans of the Public Libraries in Rajasthan was collected through the personal observations, web-sites and questionnaire meant for Librarians and discussions with the Librarian and other professional staff.
5. STATE OF ARTS OF THE SELECTED PUBLIC LIBRARIES OBSERBED
This is the study which is based on the study of Govt.
District Public libraries of Kota Region (Rajasthan). In Kota Region there is a
1(one) Govt. Divisional Public Library situated in Kota and 4 (Four) Govt.
District Public libraries along with 24 Panchayat Samiti Public libraries. Here I am trying to showcasing the all brief
details about the concern studied libraries and their infrastructure so easily
we can trace the things exhaustively.
5.1. GOVERNMENT DIVISIONAL PUBLIC LIBRARY KOTA (RAJASTHAN)
Table 5: Govt. Divisional Public Library Kota (Rajasthan) at a Glance
|
Administered By |
State Government |
|
Total No. of Reg. Members |
1425 |
|
Collection |
Books-72150 |
|
Newspapers-11 |
|
|
Magazines-55 |
|
|
Audio/Video-2248 |
|
|
E-Books |
|
|
Area of Library |
1008 Square feet |
|
Period of Loan for Books |
2 Books, for 14 Days |
|
Classification of Scheme |
DDC, 23ed. |
|
Catalogue Code |
AACR-II |
|
Building Status |
Own Building |
|
Timing of the library |
11.00 AM to 7.00 PM Remain closed on Tuesday, Second Saturday of the month and all gazzeted holidays. |
|
Services |
Circulation, Reservation of Books, E-resources, slides, Photo Copied, Scanning, OPAC, Departmental Website inter Library loan, Library catalogue, CAS, Workshop and activities, Books exhibition, Cultural program, Internet Access, Disabled friendly library. |
|
Facility for Users |
Seating Arrangement Drinking Water, Parking. |
5.2. GOVERNMENT DISTRICT
PUBLIC LIBRARY RAMGANJMANDI, KOTA (RAJASTHAN)
Table 6: Govt. District Public Library Ramganjmandi (Kota, Rajasthan) At a Glance
|
Administered By |
State Government |
|
Total No. of Registered Members |
64 |
|
Collection |
Books-15445 |
|
Newspapers-05 |
|
|
Magazines-11 |
|
|
Audio/Video-Nil |
|
|
Area of Library |
1200 Square feet |
|
Period of Loan for Books |
1 Books, for 14 Days |
|
Classification of Scheme |
DDC |
|
Catalogue Code |
AACR-II |
|
Building Status |
Rented Building |
|
Timing of the library |
11.00 AM to 7.00 PM Remain closed on Tuesday, Second Saturday of the month and all gazzeted holidays. |
|
Services |
Circulation, Reservation of Books, Reference of Books Inter Library loan, Library catalogue. |
|
Facility for Users |
Seating Arrangement, Drinking Water, Parking. |
5.3. GOVERNMENT DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARY JHALAWAR (RAJASTHAN):
Table 7: Govt. District Public Library Jhalawar (Rajasthan) At a Glance
|
Administered By |
State Government |
|
Total No. of Registered Members |
425 |
|
Collection |
Books-46690 |
|
Newspapers-12 |
|
|
Magazines-9 |
|
|
Audio/Video-0 |
|
|
Area of Library |
5000 Square feet |
|
Period of Loan for Books |
1 Books, for 14 Days |
|
Classification of Scheme |
DDC |
|
Catalogue Code |
AACR-II |
|
Building Status |
Own Building |
|
Timing of the library |
11.00 AM to 7.00 PM Remain closed on Tuesday, Second Saturday of the month and all gazzeted holidays. |
|
Services |
Circulation, Reservation of Books, E-resources, Inter Library loan, Library catalogue, Books exhibition, Internet Access. |
|
Facility for Users |
Seating Arrangement Drinking Water, Parking. |
5.4. GOVERNMENT DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARY BARAN (RAJASTHAN)
Table 8: Govt. District Public Library Baran (Rajasthan) at a glance
|
Administered By |
State Government |
|
Total No. of Registered Members |
160 |
|
Collection |
Books-26486 |
|
Newspapers-15 |
|
|
Magazines-16 |
|
|
Area of Library |
6000 Square feet |
|
Period of Loan for Books |
2 Books, for 14 Days |
|
Classification of Scheme |
CC |
|
Catalogue Code |
CCC |
|
Building Status |
Own Building |
|
Timing of the library |
11.00 AM to 7.00 PM Remain closed on Tuesday, Second Saturday of the month and all gazzeted holidays. |
|
Services |
Circulation of Books, Inter Library loan, Reservation of Books, Reference service Library Catalogue, workshop and activities Books exhibition, cultural competition. |
|
Facility for Users |
Seating Arrangement Drinking Water, Parking, Public meeting Room. |
5.5. GOVERNMENT DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARY BUNDI (RAJASTHAN)
Table 9: Govt. District Public Library Bundi (Rajasthan) at a glance
|
Administered By |
State Government |
|
Total No. of Registered Members |
298 |
|
Collection |
Books-48061 |
|
Newspapers-7 |
|
|
Magazines-44 |
|
|
Area of Library |
4800 Square feet |
|
Period of Loan for Books |
2 Books, for 14 Days |
|
Classification of Scheme |
No |
|
Catalogue Code |
No |
|
Building Status |
Own Building |
|
Timing of the library |
11.00 AM to 7.00 PM Remain closed on Tuesday, Second Saturday of the month and all gazzeted holidays. |
|
Services |
Circulation of Books, Inter Library loan, Reference Services and Internet access. |
|
Facility for Users |
Seating Arrangement Drinking Water, Parking, Public meeting Room. |
5.6. BUDGET OF
PUBLIC LIBRARIES OF KOTA REGION (RAJASTHAN), 2013-2016
Table 10: Budget of Public Libraries of Kota Region (Rajasthan),
2013-2016
|
Sr. No. |
Name of The Library |
Budget |
Budget |
Budget |
|
1. |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
98,90,000 |
37,15,000, |
47,05,000 |
|
2. |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi |
8,36,000 |
8,91,000 |
9,31,000 |
|
3. |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
19,31,000 |
19,86,000 |
20,46,000 |
|
4. |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
14,51,000 |
14,92,000 |
15,66,000 |
|
5. |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
13,31,000 |
13,96,000 |
14,46,000 |
5.7. DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARIES SYSTEM OF KOTA REGION (RAJASTHAN)
Table 11: District Public Libraries System of Kota Region (Rajasthan)
|
S. No. |
Name of The Library |
Years of Establishment |
Registered Members |
Collection of Books |
Administrated by |
Staff |
|
|
Professional |
Non-Professional |
||||||
|
1. |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
1956 |
1425 |
72,150 |
State Govt. |
3 |
8 |
|
2. |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi |
2008 |
64 |
15,455 |
State Govt. |
2 |
Nil. |
|
3. |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
1913 |
425 |
46,690 |
State Govt. |
1 |
3 |
|
4. |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
1996 |
160 |
26,486 |
State Govt. |
1 |
2 |
|
5. |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
1956 |
298 |
48,061 |
State Govt. |
1 |
2 |
5.8. PUBLIC LIBRARIES SYSTEM OF KOTA REGION (RAJASTHAN)
Table 12: Public Libraries System of Kota Region (Rajasthan)
|
S. No. |
Name of The Library |
Library Timing |
Security/ Membership Fees in Rs. |
Purchase of Books |
Scheme of Classification used |
Classified catalogue |
|
1. |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
11.00 AM. To 7.00 PM Tuesday, Second Sat. and All Gazzeted Holidays is Closed |
Membership Fees=100 Security=1000 Child & BPL= Free |
RRRLF and Committee Members |
DDC |
ACR-II |
|
2. |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi |
---do--- |
Membership Fees=50 No Security |
---do--- |
DDC |
AACR-II |
|
3. |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
---do--- |
Membership Fees=50 Child =20 No Security |
---do--- |
DDC |
AACR-II |
|
4. |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
---do--- |
Membership Fees=20 No Security |
---do--- |
CCC |
CC |
|
5. |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
---do--- |
Membership Fees=50 Child =20 No Security |
---do--- |
No |
No |
5.9. SERVICES PROVIDE IN GOVT. DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARIES OF KOTA
REGION (RAJASTHAN)
Table 13: Services Provide in Govt. District Public Libraries of Kota Region (Rajasthan)
|
S. No. |
Name of The Library |
Circulation |
Inter Library Loan |
Reference Services |
Reservation of Books |
Library Catalogue Physically |
OPAC |
Internet Access/ WI -Fi |
Computers |
Scanning |
Photocopy |
Current Awareness Service (CAS) |
|
1. |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
2. |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
3. |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
4. |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
5. |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
5.10. INFRASTRUCTURE OF GOVT. DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARIES OF KOTA
REGION (RAJ.)
Table 14: Infrastructure of Govt. District Public Libraries of Kota Region
|
S. No. |
Name of The Library |
Own Library Building/Rented |
Air-Conditioning |
Seating Arrangement |
Parking |
Public Meeting Room |
Drinking Water |
|
1. |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
Yes |
N0 |
60 |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
2. |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi |
Rented |
N0 |
10 |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
3. |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
Yes |
N0 |
75 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
4. |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
Yes |
N0 |
20 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
5. |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
Yes |
N0 |
100 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
5.11. AUTOMATION
STATUS IN GOVT. DISTRICT PUBLIC LIBRARIES OF KOTA REGION (RAJASTHAN)
Table 15: Automation Status in Govt. District Public Libraries of Kota Region
|
S. No |
Name of The Library |
Library Software |
Computerized Circulation |
Online Public Access Catalogue |
Web-Site |
|
1. |
Govt. Divisional Public Library, Kota |
E-Library |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
2. |
Govt. District Public Library, Ramganjmandi |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
3. |
Govt. District Public Library, Jhalawar |
E-Pustkalya |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
4. |
Govt. District Public Library, Baran |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
5. |
Govt. District Public Library, Bundi |
No |
No |
No |
No |
6. FINDINGS
1) Maximum District Public libraries are confining only the routine task of collecting, organizing the reading materials and are providing circulation services, reference services etc. but are facing many problems like lack of qualified professional staff, insufficient financial support and infrastructure etc.
2) Except for the divisional Public library Kota, the number of registered members in the rest of the District library is very low.
3) In the few District Public Libraries have computerized library system and rest of the district Public libraries computers, library software, scanning, photocopy in negligible.
4) Most of the District Public Libraries have its own buildings. There is a good arrangement for readers sit and parking.
7.
CONCLUSION
After
the understanding of overall all analysis and findings, I reached on this
conclusion that the Rajasthan State are need urgent attention on the District Public
libraries for lack of staff and insufficient budget. It’s great achievement
that in 2006, Library legislation passed in Rajasthan but not seems their major
effects till today. I think Rajasthan needs advocacy to run the Public
libraries. In Rajasthan, maximum libraries are facing the problem of book
losses and no regular basis stock verification done. Hope after reviewing this
study Govt. of Rajasthan will observe the pros and cons.
SOURCES OF FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
REFERENCES
[1] Research Methodology Practice (1988) P. Philominathan – Shri A.V.V.M. Pushpam College – Poondi –Thanjavar
[2] Kothari, C.R. (2004) Research Methodology Method $ Technique, New Delhi: New Age International (P) Ltd.
[3] Research Methodology (1990) Methods & Techniques 2ed, Kothari C. R. – Vishwa Prakashan – New Delhi.
[4] Gopal M. A. (2001). An Introduction to Research Procedure in Social Sciences –Asia Publishing House - Bombay
[5] Shokeen, Ashu. (1993). “Organizational Commitment and Work Motivation as Predictors of Work Performance an Academic and Special Libraries: A Comparative Study.” Ph.D. diss. Jiwaji University, Gwalior.
[6] Morrison, Donald F. (1990). Multivariate Statistical Methods. New York: McGraw-Hill.
[7] Rubenstein, Amy S. (1986). An item-level analysis of questionnaire type measures of intellectual curiosity. Cornell University Ph. D. thesis.
[8] Chopra B.S., et.al. (2005). “Leadership for the Indian Managers, A human relation approach”, The Times research foundation.
[9]
Chatterjee N.N. (2006). “Management of Personal
in Indian enterprises: Concept, Practices and emerging trends”, Allied book
agency, Calcutta.
[10] Best libraries in the world:
Wikipedia 2005 (Sources)
[11] Census of India search detail” (http://www.census India. gov.in/pca/ search
details.aspx? id=113235).
Census idia.gov. In retrieved 10 may, 2015.
[12] Central Secretariat library”
Ministry of culture, Govt. of India. Accessed May, 2017. http://www.csl.nic.in.
[13] Central Secretariat Library”
Ministry of culture, Govt. of India. Accessed August 9, 2017.
http://www.csl.nic.in/.
[14] Connemara Public library: Http://www.connemara Publiclibrarychennai.com
[15] Delhi Public Library: www.dpl.gov.in
(http://www.dpl.gov.in/)
[16] Delhi Public library”
Ministry of culture, govt. of India. Accessed March 24, 2017.
Dpl.gov.in/index.php/mission-statement.
[17] District Census Bundi 2011” (http://www.census 2011.co.in/ district.php)
[18] District Census Kota 2011”
(http://www.census
kota2011.co.in/ district.php)
[19] http.//wwmariekecortogliing.com/header/Jaipur-party/general
information-about-Rajasthan.
[20] http://www.education.rajasthan.gov.in/content/raj/education/department-of-language-and-library/hi/home0.html#. (Accessed Date: 29th
April, 2018)
[21] Https//in Wikipedia. Org
wiki/S.R. Ranganathan.
[22] Library network: http://www.wbpublibnet.gov.in.
[23] National Library of India; nationallibrary.gov.in (http://www.national
library.gov.in/)
[24] Rajasthan: www.rajasthan.gov.in
[25] Sinha Library: http://www.sinha library.gov.in/)
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2020. All Rights Reserved.


