
THE ROLE OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT IN ENHANCING OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY AND BUSINESS GROWTH
1 Sr.
Lecturer, Technical Education Department Sardar Vallabh Bhai Polytechnic
College, Bhopal (MP), India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
This study
looked at how financial management can help a business run more smoothly and
grow. Using a mixed-methods approach, the study used both quantitative and
qualitative analysis to find patterns in financial management practices and
look at how they affect organizational performance in more subtle ways. A
quasi-experimental design was employed to evaluate causal relationships in
practical business environments without random assignment. The study
population comprised formally organized business enterprises, featuring a
sample of 90 respondents, including owners, accountants, and managers, chosen
through stratified purposive and random sampling to guarantee
representativeness. Structured questionnaires with closed-ended questions
were used to collect primary data, which made it easy and consistent to
gather data. We used descriptive statistics to summarize and show the
results, find patterns, and help people make smart choices. The results show
how important good financial management is for making operations run more
smoothly and helping businesses grow in a way that lasts. |
|||
|
Received 15 September 2022 Accepted 21 October 2022 Published 30 November 2022 Corresponding Author Dr.
Preeti Maheshwari, mdrpreeti@gmail.com DOI10.29121/granthaalayah.v10.i11.2022.6596 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2022 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Management, Business, Financial, Cash,
Cost |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
Financial management is very important for the long-term success and sustainability of any business because it gives structure and discipline to planning, allocating, controlling, and using financial resources in a way that maximizes value creation. Financial management is the most important part of making decisions in an organization. It makes sure that limited resources are used well to support day-to-day operations while also working toward long-term growth goals. By doing thorough financial planning and budgeting, businesses can figure out what their future financial needs will be, set realistic performance goals, and coordinate activities across departments. This cuts down on uncertainty and makes everything run more smoothly. Management can set spending priorities, cut out unnecessary costs, and make sure that money is spent on things that will improve processes, adopt new technologies, train employees, and expand capacity by making a good budget. Cost control and cost management, which are important parts of financial management, help make operations more efficient by finding problems in production, procurement, logistics, and administrative processes. Organizations can find waste, cut down on operational bottlenecks, and use resources better without giving up quality or customer satisfaction by looking at cost structures and using methods like variance analysis, standard costing, and activity-based costing.
Managing working capital well helps operations run smoothly by keeping the right balance between cash flow and profit. This means that the business has enough cash on hand to meet short-term obligations without investing too much in inventories or receivables, which could tie up valuable funds. Good management of cash flows, inventories, accounts receivable, and accounts payable reduces operational problems, improves relationships with suppliers and customers, and makes the company more able to quickly adapt to changes in demand or market conditions. Financial management is also very important for business growth because it helps make strategic investment and financing decisions that will affect the organization's future direction. Financial managers use strict capital budgeting and investment appraisal methods like net present value, internal rate of return, and profitability index to look at possible projects and figure out if they are worth the risk and how they will help create long-term value. This disciplined approach makes sure that growth plans, whether they involve new products, entering new markets, mergers and acquisitions, or building new infrastructure, are in line with the company's strategic goals and financial resources. Financial management helps businesses grow in a controlled and profitable way by choosing investments that will make money over the long term. This is better than trying to grow too quickly, which could put a strain on resources or raise financial risk. Also, good financial management makes it easier to get money from outside sources by keeping accurate financial records, clear reporting systems, and strong financial performance, which makes investors, lenders, and other stakeholders trust you more.
This credibility makes it easier for the organization to get money for growth opportunities when they come up, and it lowers the cost of capital. Performance measurement and financial analysis help both operational efficiency and growth even more by giving management timely and useful information to evaluate productivity, profitability, and financial health. Organizations can keep an eye on their operational results, find any differences between planned performance and actual performance, and take corrective action quickly by using financial ratios, trend analysis, and performance indicators. This creates a culture of accountability and continuous improvement. Strategic financial management also includes risk management in decisions about operations and growth. This means finding possible financial risks like changes in interest rates, exchange rates, commodity prices, and credit conditions, and coming up with ways to lessen their effects.
This proactive approach to risk management keeps the organization's finances stable while giving it the confidence to go after growth opportunities. In today's business world, financial management depends more and more on digital technologies, automation, and data analytics to make things more accurate, efficient, and responsive. Financial information systems make accounting easier, speed up reporting, and help managers make decisions in real time. This lets managers quickly find inefficiencies and change their plans to fit the needs of the market. Ultimately, financial management goes beyond just keeping track of records and costs. It becomes a strategic partner in the success of the organization by making sure that operations are run efficiently, resources are used wisely, risks are handled well, and growth opportunities are pursued in a way that is good for the long term. Financial management lays a strong foundation for improved operational efficiency and long-term business growth by combining financial discipline with strategic vision and operational execution. This helps businesses stay competitive, adaptable, and focused on value in a global economy that is becoming more complicated and dynamic.
2. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
The success or failure of a small firm hinges on its financial management. The effect of financial management strategies on the prosperity of small businesses is the focus of this research. The purpose of this study was to collect information on the financial management methods and company success stories of one hundred small business owners. To determine which financial management techniques were associated with company performance, regression analysis was used to examine the data. The findings show that budgeting, cash flow management, and financial forecasting are some of the most important financial management strategies for small businesses. Profitability and expansion are more likely to occur in companies with solid financial management procedures. These results demonstrate how critical sound financial management techniques are to the prosperity of small businesses. In order to make educated choices, stay out of financial jams, and maintain long-term success, business owners should make financial management a top priority. A better chance of success exists for small firms that use good financial management procedures. If they want their companies to succeed, company owners should work on their financial management strategies.
Company performance has immense significance in the commercial realm. Strategy, financial management, human resource management, and the business climate are a few of the elements that impact a company's success. The long-term health and expansion of every company depends on its financial management. Discussing effective financial management solutions to boost company success is the driving force behind this research. This research employed a descriptive analytical technique based on secondary data culled from a variety of sources, including scholarly publications, novels, and financial records from different companies. The research concludes that in today's complicated and competitive business world, good financial management is crucial to a company's success. With the correct approach to financial management, businesses may better anticipate and distribute resources, control risks, and seize opportunities.
Hajeri and Nobanee (2021) When it comes to the overarching purpose of financial management, it lays out the rules for the distribution of duties between an organization's general and financial resources. Modern approaches to financial management have evolved substantially, which is assisting modern businesses in making better use of their financial resources. One of the main advantages is that it helps businesses find the most profitable financial models, which increases their profit margins compared to the previous one. Here are only a few of the many objectives of financial management: Efficiency in operations was enhanced. Taken into account the dependable availability of cash. Maximising profits over the long run. The management of capital resources is done correctly.
Mihajlovic et al. (2020) The growth of businesses and the expansion of national economies are both influenced by sound financial management. Due to the interconnected nature of financial matters with management, technology, resources, staff, etc., financial management has a unique position within the management system. The ability to pivot is a must for the contemporary financial manager in the face of ever-shifting market circumstances. Both the enterprise's and the economy's performance are critical to its capacity to get funding and effectively manage its resources. Maximising stock value via decision-making that increases business value is, hence, the principal objective of financial management.
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
1) Research
Approach
The research employed a mixed-methods framework, integrating quantitative analysis to discern trends in financial management practices and qualitative analysis to investigate their complex effects.
2) Research
Design
A quasi-experimental design was utilized to investigate causal relationships in authentic business environments without the implementation of random assignment.
3) Population
and Sample
The population comprised formally organized business entities, with respondents consisting of owners, accountants, and managers. To make sure the sample was representative, 90 people were chosen using stratified purposive and random sampling.
4) Data
Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to show and summarize data, find patterns, and help people make decisions. Statistical software was used to make tables and charts that were clear and correct.
4. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATIONS
Table 1
|
Table 1 Gender of the Respondents |
||
|
Particular |
Frequency |
Percentage% |
|
Male |
45 |
50.0% |
|
Female |
45 |
50.0% |
|
Total |
90 |
100 |
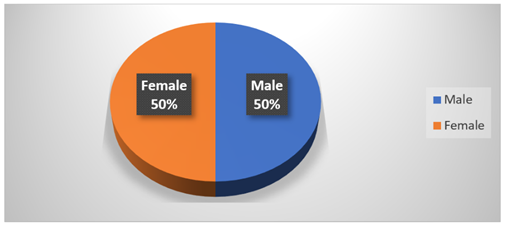
Figure 1
|
Figure 1 Gender of the Respondents |
Table 1 shows how many men and women answered the question. The results show that the respondents are evenly split between men and women, with each group making up 50.0% of the total. This balanced representation indicates that the study effectively captured viewpoints from both genders without favoritism towards either group.
Table 2
|
Table 2 Age of the Respondents |
||
|
Particular |
Frequency |
Percentage% |
|
20 – 29 |
24 |
26.7% |
|
30 – 39 |
30 |
33.3% |
|
40 – 49 |
22 |
24.4% |
|
50 - 59 |
14 |
15.6% |
|
Total |
90 |
100 |
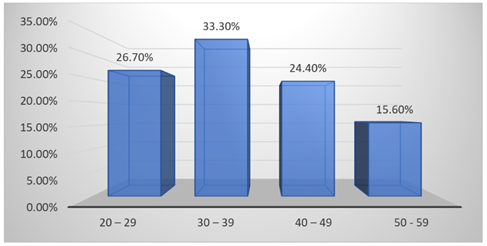
Figure 2
|
Figure 2 Age of the Respondents |
The age distribution of the respondents is shown in Table 2. The majority of respondents, 33.3%, are between the ages of 30 and 39, which means that most of them are in their early middle age. Next are people between the ages of 20 and 29 (26.7%), which shows that younger adults are very involved. The age group of 40 to 49 years makes up 24.4% of the total, while the age group of 50 to 59 years makes up the smallest percentage at 15.6%. Overall, the data show that most of the people who answered are in the age range where they can work.
Table 3
|
Table 3 Annual Income Turnover (Income Level) Of Participants |
||
|
Income Range |
Frequency |
Percent (%) |
|
10,000,000 – 39,000,000 |
18 |
20 |
|
40,000,000 – 69,000,000 |
26 |
28.9 |
|
70,000,000 – 99,000,000 |
20 |
22.2 |
|
100,000,000 – 150,000,000 |
16 |
17.8 |
|
150,000,000 and above |
10 |
11.1 |
|
Total |
90 |
100% |
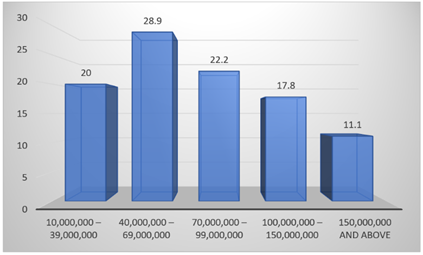
Figure 3
|
Figure 3 Annual Income Turnover (Income Level) of Participants |
The annual income turnover of the people who took part is shown in Table 3. 28.9% of respondents have an income between 40,000,000 and 69,000,000, which is the highest percentage. This means that most of the people who answered the survey have a moderate income. Next are those who make between 70,000,000 and 99,000,000 (22.2%) and those who make between 10,000,000 and 39,000,000 (20.0%). Seventeen percent of participants make between 100,000,000 and 150,000,000 a year, while eleven percent make 150,000,000 or more a year. Overall, the results show that most of the people who took part make between low and medium amounts of money each year.
Table 4
|
Table 4 Financial Management Practices Employed |
||
|
Financial Management Practice |
Frequency |
Percent (%) |
|
Record keeping management practices |
28 |
31.1% |
|
Cash management practices |
24 |
26.7% |
|
Capital financing practices |
20 |
22.2% |
|
Financial reporting practice and analysis |
18 |
20.0% |
|
Total |
90 |
100.0 |
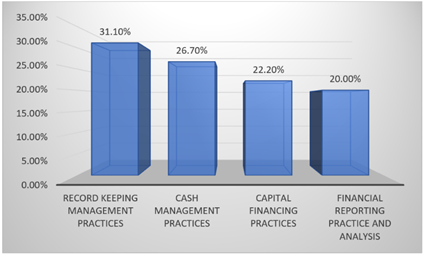
Figure 4
|
Figure 4 Financial Management Practices Employed |
Table 4 shows how the people who answered the survey manage their money. The results show that 31.1% of the respondents use record keeping management practices the most. This means that most of the people who answered said that keeping good financial records is important. 26.7% of people said that cash management practices were very important, which shows how important it is to keep track of cash coming in and going out. 22.2% of people use capital financing practices, while only 20.0% use financial reporting practices and analysis.
The results show that most people use basic financial management techniques, but fewer people use more advanced ones like financial reporting and analysis.
Table 5
|
Table 5 Contribution of Financial Management Practices on Business Growth |
|||
|
Outcome |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Mean |
|
Improved management efficiency |
1 |
5 |
3.7 |
|
Attract more capital |
1 |
5 |
3.6 |
|
Increased availability of capital |
1 |
5 |
3.6 |
|
Increased operational margin |
2 |
5 |
3.5 |
|
Increased risk management |
1 |
4 |
2.9 |
Table 5 shows how the people who answered thought that financial management practices helped their businesses grow. The results show that the mean score for improved management efficiency was the highest (3.7), which means that good financial management practices make business operations much more effective. The next two things, attracting more capital and making capital more available, both have a mean score of 3.6. This means that good financial management helps people get money and grow their capital.
Also, the average operational margin went up to 3.5, which is a good sign for profitability. The lowest mean score (2.9) for increased risk management, on the other hand, suggests that respondents think that financial management practices have a moderate effect on managing business risks. Overall, the results show that good financial management can help a business grow a lot, especially by making it more efficient and easier to get money.
5. CONCLUSION
This study emphasizes the crucial function of financial management in improving operational efficiency and fostering business growth, underpinned by a systematic and well-organized research methodology. The study utilized both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies, enabling the identification of measurable trends and comprehensive insights into the impact of financial management practices on organizational performance. The quasi-experimental research design, utilized in authentic business contexts, enhanced the reliability of the results by facilitating significant comparisons in the absence of random assignment. By focusing on formally structured businesses and getting answers from business owners, managers, and accountants, the data was sure to show real-world, experience-based views. Stratified, purposive, and random sampling methods made the sample more representative, and structured questionnaires used to collect primary data gave accurate and useful information. Descriptive data analysis made it easier to understand and present results, which helped people draw informed conclusions. Overall, the research methodology was a solid basis for showing that good financial management practices are very important for running a business well, using resources wisely, and keeping the business growing. This shows how important it is to make good financial decisions for the success of the organization.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Ćurčić, M., Kostić, R., and Arapović, T. (2018). Planning and Control as a Function of Company Management. Oditor, 4(1), 94-103. https://doi.org/10.5937/Oditor1801094C
Dwangu, A. M., and Mahlangu, V. P. (2021). Accountability in the Financial Management Practices of School Principals. International Journal of Educational Management, 35(7), 1504-1524. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEM-06-2021-0243
Erambo, G. E., Mulwa, J. M., Aketch, J. R., Sangoro, O., and Muchibi, W. M. (2016). Financial Management Practices and Firm Performance Among Micro and Small Enterprises in Busia Town, Kenya. International Journal of Management and Commerce Innovations, 4(2), 303-310.
Gopalan, C. (2016). The Impact of Rapid Change in Educational Technology on Teaching in Higher Education. HAPS Educator, 20(4), 85-90. https://doi.org/10.21692/haps.2016.037
Hajeri, H., and Nobanee, H. (2021). The Goal of Financial Management and Operational Efficiency.
Khalid, S., and Sarker, A. E. (2017). Financial Management Innovations in the United Arab Emirates: Rationales, Trends and Outcomes. Asian Education and Development Studies, 8, 405-415. https://doi.org/10.1108/AEDS-07-2018-0121
Lekić, N., Savić, G., Knežević, S., and Mitrović, A. (2018). The Efficiency Analysis in Small Wineries in the Republic of Serbia. Ekonomika Poljoprivrede, 65(4), 1529-1544. https://doi.org/10.5937/ekoPolj1804529L
Mihajlovic, M., Tadin, D., and Gordić, B. (2020). The Role of Financial Management in the Company. Tehnika, 75(4), 498-503. https://doi.org/10.5937/tehnika2004498M
Todorović, M. (2011). Psychology and Financial Management: Behavioral Corporate finance. Business Economics, 4(1), 275-287. https://doi.org/10.5937/ekopre1106275T
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2022. All Rights Reserved.