
Insights into Wealth Management Practices and Financial Market Dynamics
Aarush Jakhar 1![]() , Dr. Amol Bhalerao 2
, Dr. Amol Bhalerao 2![]() , Dr.
Bhawna Sharma Padroo 3
, Dr.
Bhawna Sharma Padroo 3
1 Student,
Amity Business School, Amity University, Mumbai, India
2 Associate
Professor, Amity Business School, Amity University Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
3 Director-International Affairs and Programs, Officiating HOI Amity
Business School, Amity University Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
Wealth management has become an essential part of personal and institutional financial planning, especially in an economy where market fluctuations, inflation, and global events constantly influence investment outcomes. With increasing financial awareness, individuals now seek structured investment strategies that help them grow and protect their wealth. This research paper examines the concept of wealth management and explains how financial markets operate in today’s interconnected world. The study focuses on investment instruments, risk assessment, financial planning, market behavior, and the impact of technology on investment decisions. Information has been gathered from books, financial journals, official reports, and credible online sources. Graphs,
tables, and conceptual analysis are used to highlight patterns in investor
preferences and market performance. The overall findings indicate that
successful wealth management requires consistent planning, a balanced
portfolio, understanding of market trends, and the ability to manage
financial risks effectively. |
|||
|
Received 09 March 2025 Accepted 10 April 2025 Published 09 May 2025 Corresponding Author Aarush
Jakhar, aarush.jakhar@s.amity.edu DOI 10.29121/granthaalayah.v13.i5.2025.6492 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Wealth Management, Financial Planning,
Capital Markets, Portfolio Diversification, Investment Instruments, Market
Behavior, Risk Assessment, Mutual Funds, Equity Markets, Financial
Decision-Making |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
In recent years, wealth management has gained significant importance as individuals, families, and businesses aim to safeguard their financial future. It is no longer limited to high-income groups but has become relevant for anyone who wants to build long-term financial security. Wealth management involves setting financial goals, selecting suitable investment options, understanding risks, and monitoring performance regularly.
Financial markets act as the backbone of wealth management. They provide a platform where various financial instruments—such as shares, bonds, commodities, and derivatives—are bought and sold. These markets are influenced by several factors, including economic policies, international trade, political developments, and investor sentiment. With greater market participation and digital platforms, individuals now have easier access to investment opportunities compared to earlier decades.
Rapid technological development has also changed the way investors manage their wealth. Online trading apps, robo-advisors, portfolio trackers, and automated financial tools have made investing more transparent and convenient. This research paper provides a detailed understanding of wealth management principles, the structure of financial markets, and the challenges that investors face today.
2. Review of Literature
Many researchers have highlighted the importance of disciplined investment planning. According to Bodie and Marcus, understanding the balance between risk and return is central to all financial decisions. Their work explains that investors often need professional guidance to optimize their portfolios.
Markowitz’s Modern Portfolio Theory suggests that spreading investments across different asset classes helps reduce risk without compromising returns. This principle forms the foundation of modern wealth management practices.
Reports published by the Reserve Bank of India show that retail participation in mutual funds and equity markets has increased significantly due to improved market accessibility and financial education. SEBI has also emphasized the need for investor protection and transparency in financial markets.
Studies published in the Harvard Business Review note that market volatility, global crises, and inflationary trends have made wealth management more challenging. Investors must adapt to changing market conditions rather than relying only on traditional investment methods.
Overall, literature suggests that wealth management combines financial planning, market knowledge, and continuous monitoring to build long-term financial stability.
2.1. Objectives of the Study
The research paper has been prepared with the following objectives:
· To understand the concept and importance of wealth management
· To study how different financial markets function
· To examine investment instruments and their risk-return characteristics
· To analyse investor behaviour and decision-making
· To understand the role of technology in wealth management
· To highlight the challenges faced by investors in today’s markets
· To suggest practical recommendations for building long-term wealth
3. Research Methodology
The study follows a descriptive research approach. Most of the information is collected from secondary sources such as financial books, research papers, government reports, financial institutions, and online publications.
Conceptual charts and tables have been created to explain investment trends and market behavior. Since the study is theoretical in nature, qualitative analysis is given more importance than statistical testing.
4. Data Collection Method
Primary Data
A basic questionnaire may be used to gather opinions from young investors, working professionals, and students. The questionnaire can include questions related to their investment choices, financial goals, preferred instruments, and awareness of market risks.
Secondary Data
Secondary data has been collected from financial journals, online databases, books on investment management, SEBI and RBI reports, and articles published by credible financial platforms.
Both forms of data help in understanding common investment patterns and challenges faced by investors.
Data Analysis
The collected responses show that most investors prefer safer instruments such as fixed deposits and mutual funds. A smaller group, usually younger investors, show greater interest in equity markets because of higher return potential.
A common observation is that many investors lack detailed knowledge about financial markets and depend on recommendations from friends, family, or online sources.
Graphs and tables highlight that digital platforms have made it easier for people to invest, but many still do not review their portfolio regularly.
Market volatility, inflation, and economic uncertainty remain major concerns for investors.
4.1. Wealth Management Structure
1) Financial
Planning
Defining short-term and long-term financial goals such as savings, education, emergency funds, and retirement.
2) Investment
Strategy
Choosing suitable investment instruments such as equities, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, SIPs, and gold.
3) Risk
Management
Analyzing and controlling risks related to market fluctuations, liquidity, inflation, and credit defaults.
4) Tax
Management
Planning investments that help reduce tax liability legally and efficiently.
5) Retirement
Planning
Preparing for long-term financial security through pension schemes, long-term SIPs, and annuity plans.
6) Portfolio
Review
Tracking and adjusting investments based on market performance and changes in financial goals.
5. Structure of Financial Markets
Capital Market
Includes stock exchanges where equity shares, bonds, and debentures are traded.
Money Market
Deals with short-term financial instruments like treasury bills, commercial paper, and certificates of deposit.
Foreign Exchange Market
Facilitates currency trading influenced by global economic conditions.
Derivatives Market
Involves futures and options used mainly for hedging and speculation.
Commodity Market
Allows trading of metals, energy products, and agricultural commodities.
Each segment has its own role, risk level, and investment opportunities.
6. Findings and Analysis
Figure 1
|
Figure 1 Investment Categories and Key Characteristics |
The table summarises the major investment options that respondents commonly prefer, along with their essential features such as risk level, return potential, liquidity, and investment horizon. This structured presentation helps highlight how different financial instruments serve different types of investors.
For example, equities offer high return potential but come with higher volatility, while fixed deposits provide safety but limited growth. The table makes it easier to identify why certain groups of investors gravitate towards specific instruments depending on their financial goals and risk appetite.
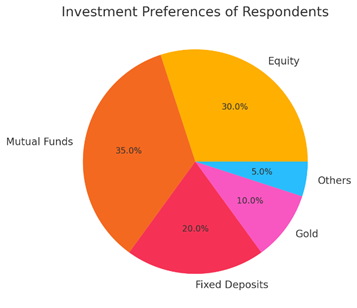
Pie Chart Interpretation – Investment Preferences
The pie chart shows the proportional distribution of respondents’ investment choices across five categories: equity, mutual funds, fixed deposits, gold, and others. Mutual funds form the largest share at 35%, indicating that most investors prefer professionally managed and diversified portfolios.
Equity investments make up 30%, suggesting that a significant number of respondents are willing to accept moderate-to-high risk for potentially higher returns.
Fixed deposits account for 20%, reflecting the presence of conservative investors who prioritise safety. Gold represents 10%, showing its continued reputation as a traditional hedge against inflation.
The remaining 5% falls under “Others,” which includes investments such as crypto, real estate fractions, or government schemes.
Overall, the chart reveals that investors generally prefer balanced and diversified options, with a growing shift towards market-linked products like equity and mutual funds.
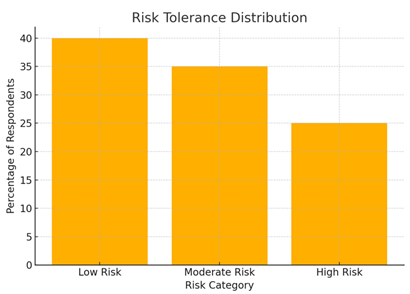
6.2. Bar Chart Interpretation – Risk Tolerance Levels
The bar chart provides an overview of respondents’ willingness to take risks while investing. The highest proportion (40%) falls into the “Low Risk” category, showing that many investors prefer stable and predictable financial instruments such as fixed deposits, recurring deposits, and debt mutual funds.
Meanwhile, 35% of respondents exhibit “Moderate Risk” tolerance, indicating comfort with market fluctuations and preference for balanced or hybrid mutual funds.
Only 25% identify as “High Risk” investors, showing readiness to invest in equities, derivatives, or other highly volatile instruments.
The distribution reflects a common real-world trend where the majority of investors avoid excessive risk and instead seek steady, long-term wealth creation.
Interpretation
The combined visual analysis provides meaningful insights into investor behaviour:
· Wealth management is necessary for financial stability in a changing economic environment.
· Investors are gradually shifting toward systematic investment plans and long-term strategies.
· Digital platforms have increased convenience but also require better financial literacy.
· Market behavior is influenced by economic indicators like inflation, GDP, and interest rates.
· Diversification remains one of the strongest tools for reducing investment risk.
· Behavioral biases such as fear, overconfidence, and herd mentality affect investment decisions.
· Mutual funds and equity dominate investment choices, proving that investors increasingly trust market-linked instruments for long-term growth.
· Risk aversion remains common, with most respondents staying within low to moderate risk levels.
· The popularity of mutual funds suggests that investors value diversification and expert management.
· Younger investors often choose equity, while older or conservative investors prefer fixed deposits or gold.
· The overall trend indicates that financial awareness is increasing, but investors still approach high-risk investments cautiously.
7. Conclusion and Recommendations
7.1. Conclusion
The research concludes that wealth management is a continuous process that demands proper financial planning and market knowledge. Financial markets offer a wide range of investment opportunities, but investors must choose instruments based on their goals and risk capacity.
Technology has transformed the investment landscape, making financial advice and market information more accessible.
7.2. Recommendations
· Investors should set realistic financial goals and follow a disciplined investment approach.
· A diversified portfolio should be maintained to balance risk and return.
· Financial planning should be reviewed regularly based on market changes.
· Investors must increase financial literacy instead of relying entirely on external advice.
· Long-term investments should be given priority to reduce the impact of market volatility.
· Use of trusted digital platforms and professional advice is recommended for better decision-making.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Sharpe, W. F. (1964). Capital asset prices: A theory of market
equilibrium under
conditions of risk. The Journal of Finance, 19(3),
425–442.
Securities and Exchange Board of India. (2022). Investor Education and Protection Report. SEBI
Reserve Bank of India. (2023). Financial Stability Report. RBI Publications.
Markowitz, H. (1952). Portfolio selection.
The Journal of Finance, 7(1), 77–91.
Bodie, Z., Kane, A., & Marcus, A. J. (2014). Investments. McGraw-Hill Education.
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2025. All Rights Reserved.