
Original Article
The comprehensive theory of relativity and The effect of force
|
1 Department of Basic
Science, Air Force University of Engineering, Xi’an 710051, China |
|
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
As is well known, real motion has two characteristics: uniform speed and variable speed. The changes in speed and curvature of spatial position are related to the effects of force. Therefore, this article studies the relativistic expression of speed changes, investigates the effects of force on variable speed, deformation, and position, so established the theory of comprehensive relativity and the theory of force effect, thus solving the computational difficulty of curvature tensor. Keywords: Special Theory of Relativity, General
Theory of Relativity, Variable Speed Theory of Relativity, Comprehensive
Theory of Relativity, The Effect of Force |
||
1. INTRODUCTION
The existing
expressions of special relativity and general relativity are clear. Special
relativity only applies to average velocity, General relativity mainly
describes universal gravitation. Many production and living conditions in
reality are variable speed, The change in speed is the effect of force. So now
based on associated with variable speed, it is necessary to derive the
comprehensive theory of relativity and the theory of the Effects of force.
In this paper, according
to the fundamental principles of Einstein's theory of relativity Einstein et al. (1935), Einstein (1908), Furthermore the effect of variable speed on
spatial displacement is proposed, So the expression of comprehensive relativity
was derived. Have also studied the various effects of force, the force effects
of variable speed, variable energy, abnormal state, and variable position are
expressed, the study of these mechanical problems is related to the previously
proposed theory of power dynamics Ma (2023).
In the
expression of this theory: (![]() ) describes the three dimensions vector, (
) describes the three dimensions vector, (![]() ) described the four-dimensional vector,(
) described the four-dimensional vector,(![]() ) described tensors, (
) described tensors, (![]() ) Describe direction (
) Describe direction (![]() )
Reverse expression of the time component of a 4-dimensional vector. (
)
Reverse expression of the time component of a 4-dimensional vector. (![]() ) Describe the mutual displacement of spatial
and temporal components in four-dimensional vectors, (
) Describe the mutual displacement of spatial
and temporal components in four-dimensional vectors, (![]() ) described the average value of the physical
quantity. The program representatives of Equations and Formula are represented
by <i>.
) described the average value of the physical
quantity. The program representatives of Equations and Formula are represented
by <i>.
2. The comprehensive theory of
relativity
Many physical
quantities vary depending on position and velocity, The derivation of
relativity requires the comprehensive introduction of the effects of position
and velocity.
2.1. The expression of comprehensive
relativity
Under conditions
of varying speed, the change in position is related to the characteristics of
speed, The formula for comprehensive relativity is expressed as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
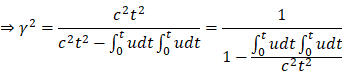
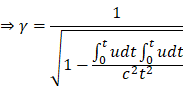
2.2. Simplified expression of the
publication of comprehensive relativity theory
According to the
characteristics of average speed and variable speed in displacement expression,
Introduce variable speed values (![]() ) related to displacement, The simplified
expression of relativity is as follows:
) related to displacement, The simplified
expression of relativity is as follows:
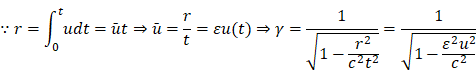
![]()
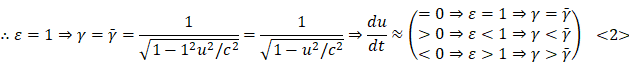
![]()
![]()
2.3. Energy expression based on
comprehensive relativity theory
According to the
effect of force on momentum, Force transfers energy in space, Force also has
energy transfer in time and object states, so it can always be the combined
effect of state reversed four-dimensional force (![]() ) and four-dimensional position (
) and four-dimensional position (![]() ), The expression of energy is as follows:
), The expression of energy is as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
2.4. Relative changes about physical
quantities
The calculation
principle of the relative reference frame variation of physical quantities: The
physical quantity must be a four-dimensional vector, The fourth component of a
four-dimensional vector must be variable due to velocity. According to the principle of power
transmission through interaction, Interaction generates power (![]() ), The interactive effect changes the
four-dimensional component (
), The interactive effect changes the
four-dimensional component (![]() ) of the original physical quantity, The rate
of change of the four-dimensional component is expressed as (
) of the original physical quantity, The rate
of change of the four-dimensional component is expressed as (![]() ), So the relative changes in the components
of four-dimensional component must be expressed according to the principle of
conservation (
), So the relative changes in the components
of four-dimensional component must be expressed according to the principle of
conservation (![]() ), The physical quantities (
), The physical quantities (![]() ) about the old coordinate system (
) about the old coordinate system (![]() ) generate new physical quantities (
) generate new physical quantities (![]() ) about the new coordinate system (
) about the new coordinate system (![]() ) due to the transfer of power, Express as
follows:
) due to the transfer of power, Express as
follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The expression of
the motion state based on the speed (![]() ) is a motion of the new coordinate system (
) is a motion of the new coordinate system (![]() ) relative to the old coordinate system (
) relative to the old coordinate system (![]() ):
):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The expression of
the motion state based on the speed (![]() ) is a motion of the old coordinate system (
) is a motion of the old coordinate system (![]() ) relative to the new coordinate system (
) relative to the new coordinate system (![]() ):
):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
2.5. Expressing the relative changes of
physical quantities based on tensors
According to the
characteristics of the calculation, the relative changes in physical quantities
can be introduced into tensor expressions.
The relative
variation of the fourth component has characteristics(![]() ), The derivation based on tensor expression
is as follows:
), The derivation based on tensor expression
is as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
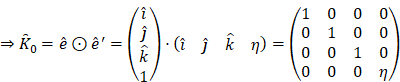
The tensor (![]() )
expression based on the speed (
)
expression based on the speed (![]() )
is a motion of the new coordinate system (
)
is a motion of the new coordinate system (![]() )
relative to the old coordinate system (
)
relative to the old coordinate system (![]() ):
):
![]()
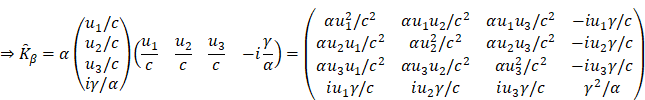
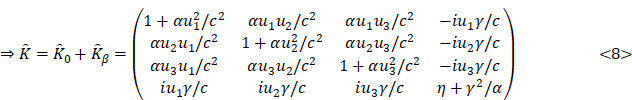
tensor (![]() )
expression based on the speed (
)
expression based on the speed (![]() )
is a motion of the new coordinate system (
)
is a motion of the new coordinate system (![]() )
relative to the old coordinate system (
)
relative to the old coordinate system (![]() ):
):
![]()
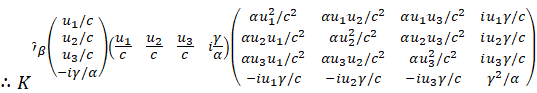
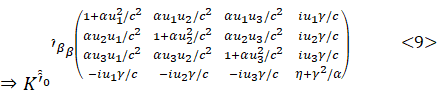
Calculation of relativistic quantities based
on tensor expression:
![]()
![]()
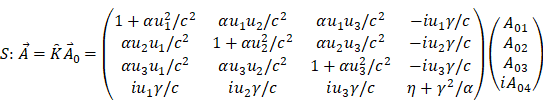
![]()
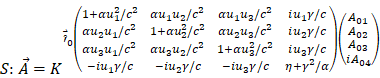
2.6. Time and spatial variations based
on the theory of comprehensive relativity
Spatial Variation
according to the theory of relativity:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
According to
formula <11>, Time Variation according to the theory of relativity:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Characteristics of
Time variation:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
2.7. The calculation method of
Differential of relativistic coefficients
The
differentiation method of relativistic coefficients (![]() ) should be calculated according to the
characteristics of the application.
) should be calculated according to the
characteristics of the application.
According to the
specific process of speed change, the differentiation method of relativistic
coefficients is as follows:
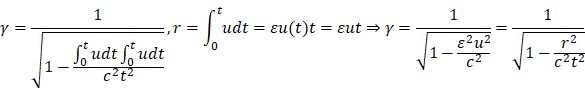
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In the general
calculation of kinetic energy, the differential method of relativistic
coefficients needs to be as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The differential
expression comparison between velocity variation and kinetic energy derivation
has the following characteristics:
![]()
![]()
![]()
3. The relativistic expression of the
effect of force
3.1. The expression of real force based
on field source
The
real force (![]() ) is a combination (
) is a combination (![]() ) of basic force (
) of basic force (![]() ) and
newborn force (
) and
newborn force (![]() ).
).
Basic force (![]() ) from Source creation is expressed by three physical quantities: Field
strength (
) from Source creation is expressed by three physical quantities: Field
strength (![]() ),
Field source (
),
Field source (![]() ),
and Force load (
),
and Force load (![]() ):
):
![]()
![]()
According to the theory of power flow and variation Ma (2023), Calculate the
principle by movement and change of power (![]() )
generated by Basic force (
)
generated by Basic force (![]() ),
So it generated newborn force (
),
So it generated newborn force (![]() ),
This is related to the velocity (
),
This is related to the velocity (![]() )
of the field source (
)
of the field source (![]() )
and the energy (
)
and the energy (![]() )
of the force load (
)
of the force load (![]() ),
Express as follows:
),
Express as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In the calculation
of newborn force, it is necessary to make calculation expressions according to
the characteristics in sequence:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
3.2. Relative force expression based on
frame of reference
The
four-dimensional vector expression of force (![]() ):
):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Firstly, assume that the reference frame (![]() )
is stationary, the velocity of the force load relative to the reference frame
is (
)
is stationary, the velocity of the force load relative to the reference frame
is (![]() ), The real force can be derived from the
expression of momentum:
), The real force can be derived from the
expression of momentum:
![]()
![]()
![]()
frame (![]() )
relative to the static reference frame (
)
relative to the static reference frame (![]() )
is (
)
is (![]() ),
The momentum (
),
The momentum (![]() )
expression of the reference frame, So the expression of the momentum relative
to the reference frame (
)
expression of the reference frame, So the expression of the momentum relative
to the reference frame (![]() ) is as follows:
) is as follows:
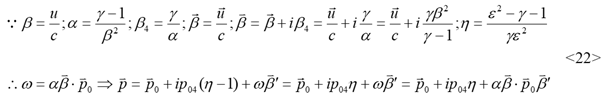
The time based on
the static reference frame (![]() )
is (
)
is (![]() ),
The time based on the new reference frame (
),
The time based on the new reference frame (![]() )
is (
)
is (![]() ),
So the force (
),
So the force (![]() )
expression relative to the reference frame (
)
expression relative to the reference frame (![]() ) is as follows:
) is as follows:
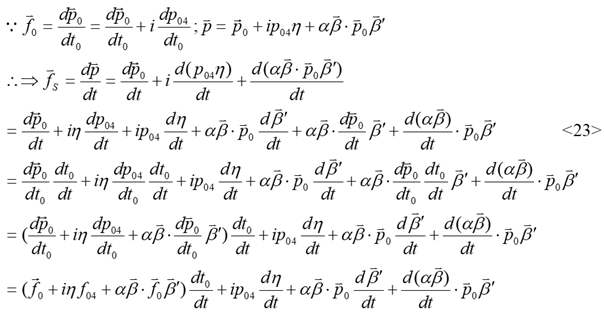
The variation force
(![]() )
of true force (
)
of true force (![]() )
in relativity theory, Generate Class suitability force (
)
in relativity theory, Generate Class suitability force (![]() ) in the new reference frame as well, Express
as follows:
) in the new reference frame as well, Express
as follows:
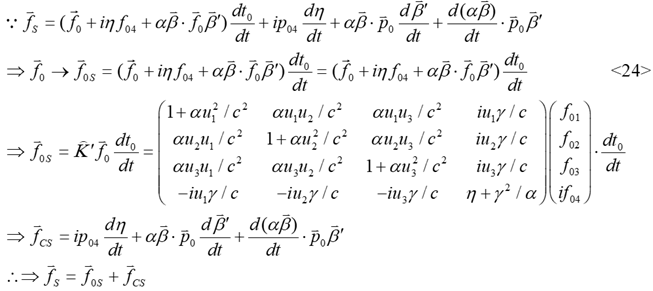
According to the
above expression, If the speed (![]() ) is the static reference frame (
) is the static reference frame (![]() ) relative to the reference frame (
) relative to the reference frame (![]() ), The force expression
relative to the
reference frame (
), The force expression
relative to the
reference frame (![]() ) is as follows:
) is as follows:
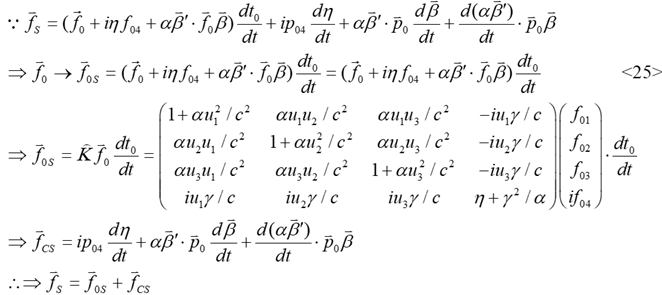
3.3. The energy effect of force
The comprehensive effect of force (![]() )
is expressed in derivation based on the force effect of momentum (
)
is expressed in derivation based on the force effect of momentum (![]() ),
The expression of acceleration (
),
The expression of acceleration (![]() ) is also related to
force:
) is also related to
force:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The expression of the total energy (![]() )
effect of force and the derivation of the total energy position (
)
effect of force and the derivation of the total energy position (![]() ):
):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In the action of
force, the object receiving force undergoes a change in energy in its state, So
the change in state energy is the relative change (![]() ) between total energy and kinetic energy, The expression of abnormal
energy (
) between total energy and kinetic energy, The expression of abnormal
energy (![]() ) is as follows:
) is as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Kinetic energy
(![]() )
is the effect of velocity, so there is a correlation between kinetic energy and
the average relative coefficient (
)
is the effect of velocity, so there is a correlation between kinetic energy and
the average relative coefficient (![]() ), The force effect of kinetic energy is
expressed as follows:
), The force effect of kinetic energy is
expressed as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
According to the
above expression, the effect of force on energy is divided into three
categories:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
4. The effect of force on space
The basic
principle of spatiotemporal special effects: Time and space are fundamentally
flat, If there is a change, it is essentially the effect of force, so we need
to derive the effect of force on space fundamentally.
4.1. The mechanical expression of differential space
A flat space forms a curvature based on the action of
force, The position of the bend needs to be expressed according to
differentiation, Firstly, assume the physical vector (![]() ),
This vector is a function (
),
This vector is a function (![]() )
of a physical quantity (
)
of a physical quantity (![]() ),
It means introducing smaller multiple differential quantities (
),
It means introducing smaller multiple differential quantities (![]() )
to express commonly used differential quantities (
)
to express commonly used differential quantities (![]() ),
Calculate the true constant (
),
Calculate the true constant (![]() )
of (
)
of (![]() ), Express the profound differentiation of
physical vectors as follows:
), Express the profound differentiation of
physical vectors as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Differential
expression of Vectors (![]() )
and Scalars (
)
and Scalars (![]() ) of spatial positions:
) of spatial positions:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The change in
spatial position is the effect of force (![]() ),
The force effect of space curve (
),
The force effect of space curve (![]() ) is is expressed as
follows:
) is is expressed as
follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
4.2. The action of force makes moving objects feel the curvature of space
The action of force causes a change in the differential of
position, The variation(![]() )
of the differential position of force action is the variation(
)
of the differential position of force action is the variation(![]() )
between the true position(
)
between the true position(![]() )
and the uniform velocity position(
)
and the uniform velocity position(![]() ), Derive as follows:
), Derive as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Experience of curvature(![]() )
and curvature radius(
)
and curvature radius(![]() )
in space Can be experienced, This is fundamentally the effect of force(
)
in space Can be experienced, This is fundamentally the effect of force(![]() ),
The curvature radius(
),
The curvature radius(![]() )
based on the force effect is as follows:
)
based on the force effect is as follows:
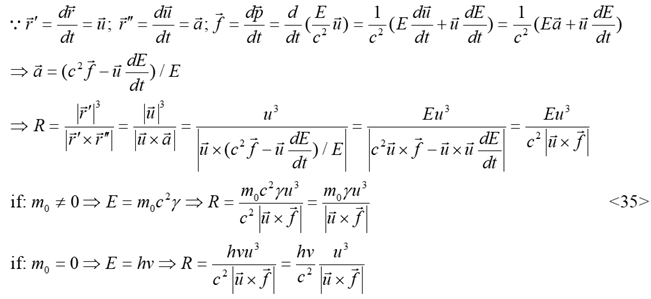
It is necessary to apply curvature vector (![]() )
in reality, The curvature vector can be derived based on the effect of force (
)
in reality, The curvature vector can be derived based on the effect of force (![]() ),
Derive as follows:
),
Derive as follows:
![]()
![]()
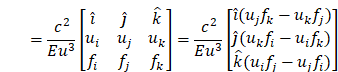
4.3. The effect of universal gravitation on the action of a mass bearing load
Expression of the
Universal Gravitational Characteristics basic force (![]() ) Accepted by a Mass Load:
) Accepted by a Mass Load:
![]()
![]()
![]()
According to the
theory of power flow, The expression of the newborn force (![]() ) of universal gravitation of mass under load:
) of universal gravitation of mass under load:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
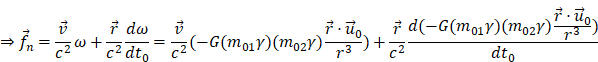
![]()
The total gravitational force (![]() )
of the force load (
)
of the force load (![]() )
relative to the gravitational field source (
)
relative to the gravitational field source (![]() )
is expressed as follows: Simplified expression of new forces (
)
is expressed as follows: Simplified expression of new forces (![]() ),
The curvature vector(
),
The curvature vector(![]() )
expressed according to formula <36>:
)
expressed according to formula <36>:
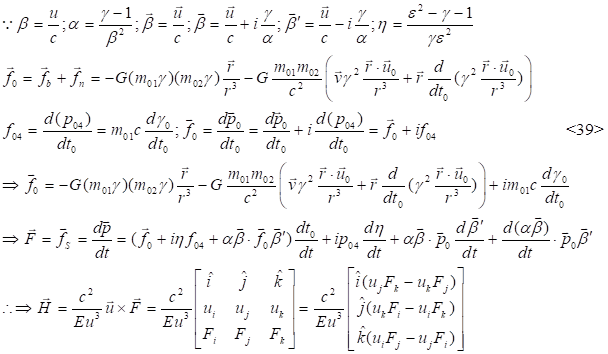
4.4. Expression of Universal Gravitation Accepting a Force Load with Zero Mass
Photons have no
mass, Using photons as an example to calculate universal gravitation, Proving
the state changes of photons in gravitational space:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
4.5. Simplified derivation of general relativity
The innovation of
general relativity is profound, The expression based on tensors is also very
comprehensive, The difficulty of this theory in practical applications lies in
the derivation of the curvature tensor (![]() )
, The root of curvature is the effect of force (
)
, The root of curvature is the effect of force (![]() ) on motion speed(
) on motion speed(![]() ), So the curvature tensor is defined as
follows:
), So the curvature tensor is defined as
follows:
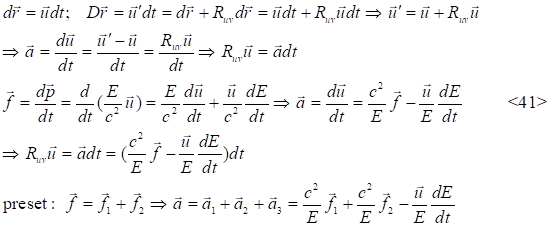
The force (![]() )
and speed(
)
and speed(![]() )
in expression are already known, The interaction effect between these two
vectors and tensors is expressed as follows:
)
in expression are already known, The interaction effect between these two
vectors and tensors is expressed as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
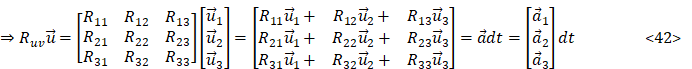
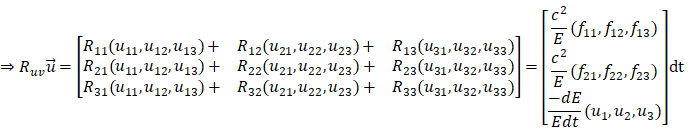
Force and speed must already be known, based on the expression characteristics of vectors and scalars, the curvature tensor can be derived precisely:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
5. Summary
As is well known,
real motion has two characteristics: uniform speed and variable speed. The
changes in speed and the curvature of spatial position are related to the
effects of force. Therefore, this article establishes a comprehensive theory of
relativity and the effects of force. If these two theories are true, they can
be effectively applied in reality. According to the fundamental principles of
scientific research, these two theories need to be validated through
experiments.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Einstein, A. (1908). Über Das Relativitätsprinzip Und Die Aus Demselben Gezogenen Folgerungen. Jahrbuch der Radioaktivität und Elektronik, 4, 411–462.
Einstein, A., Podolsky, B., and Rosen, N. (1935). Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality be Considered Complete? Physical Review, 47, 777–780. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.47.777
Ma, H. (2023). A New Physics Theory About the Kinetic Force Mechanism of Energy Flow. International Journal of Research - GRANTHAALAYAH, 11(1), 115–127. https://doi.org/10.29121/granthaalayah.v11.i1.2023.4988
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2025. All Rights Reserved.