
Evaluating the Impact of Recruitment Metrics on Employee Turnover and Retention Rates
Amarnath Bhimanatham 1, Dr. Subramaniam Seshan Iyer 2
1 Research
Scholar, Datta Meghe Institute of Management Studies, Nagpur,
Maharashtra, India
2 Research
Supervisor, Datta Meghe Institute of Management Studies, Nagpur,
Maharashtra, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
This research evaluates the impact of recruitment metrics on employee turnover and retention rates across various organizations. By analyzing key recruitment indicators such as time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, quality-of-hire, and source-of-hire, the study identifies their significant correlation with turnover and retention outcomes. The findings suggest that high-quality hires and strategic sourcing methods, such as employee referrals and internal job postings, lead to lower turnover rates and higher retention. A multiple regression model further underscores the predictive power of recruitment metrics in shaping workforce stability. The study emphasizes the importance of using recruitment analytics to refine hiring strategies, reduce turnover, and improve long-term employee retention. |
|||
|
Received 26 February
2025 Accepted 30 March 2025 Published 17 April 2025 DOI 10.29121/granthaalayah.v13.i3.2025.6063 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Recruitment, Metrics, Employee Turnover,
Retention, etc |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
In today’s competitive business environment, acquiring and retaining top talent has become one of the most critical challenges faced by organizations. With increasing globalization, technological advancements, and dynamic labor markets, human resources (HR) functions are undergoing a strategic transformation. Recruitment, traditionally viewed as a transactional process, is now recognized as a key determinant of long-term organizational success. The quality of recruitment strategies and their underlying metrics has a direct influence on employee satisfaction, engagement, and ultimately, retention. Organizations are therefore increasingly relying on data-driven recruitment processes, using recruitment metrics to assess, monitor, and improve hiring practices Breaugh (2009).
Recruitment metrics’such as time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, quality-of-hire, and source-of-hire’are instrumental in evaluating the effectiveness of talent acquisition strategies. These metrics offer actionable insights into how well recruitment activities align with organizational goals and workforce needs. More importantly, they help organizations predict future turnover patterns and make informed decisions to enhance employee retention. A high turnover rate often signals deeper problems in hiring and onboarding processes, while strong retention rates generally reflect successful recruitment practices that match candidates to both the job requirements and the organizational culture Hausknecht and Trevor (2011).
This study aims to evaluate the impact of recruitment metrics on employee turnover and retention rates. It seeks to explore which metrics are most predictive of long-term employee commitment and how organizations can utilize these metrics to create more resilient and loyal workforces. The research contributes to the growing field of HR analytics by providing evidence-based recommendations for refining recruitment strategies to reduce turnover and foster retention.
2. Literature Review
Recruitment metrics serve as quantifiable indicators that enable HR professionals to track, assess, and enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of hiring processes. One of the most widely discussed metrics in literature is quality-of-hire, which includes indicators such as new hire performance, cultural fit, and long-term retention. Keller (2018) emphasizes that high-quality hires are those who meet or exceed performance expectations and remain with the organization over time. Therefore, monitoring quality-of-hire can provide predictive insights into future turnover and retention trends.
Time-to-fill and cost-per-hire are logistical metrics that, although operational, also influence employee retention. Long hiring timelines and inefficient recruitment processes can negatively affect candidate experiences and increase the risk of early attrition Cascio and Boudreau (2016). Organizations that streamline their hiring processes while maintaining quality standards tend to onboard candidates who are more satisfied and committed, thereby lowering turnover rates.
Another critical metric is source-of-hire, which helps identify the channels through which the most successful and stable employees are recruited. Zottoli and Wanous (2000) found that candidates recruited through employee referrals often have higher retention rates, primarily due to realistic job expectations and stronger cultural alignment. By analyzing source effectiveness, HR departments can strategically allocate resources to the most productive hiring channels.
The emergence of predictive analytics in HR has revolutionized the way recruitment data is used. Bersin (2013) notes that organizations now have the tools to model turnover likelihood based on recruitment metrics, enabling proactive management of attrition risks. For instance, tracking early turnover’employees who exit within their first year’can highlight deficiencies in the recruitment or onboarding process. This allows HR teams to refine candidate profiles and selection criteria to better match organizational needs.
Furthermore, recruitment strategies increasingly integrate broader organizational concepts like employer branding and cultural fit, which, while more qualitative, can be measured through candidate perception surveys, offer acceptance rates, and application drop-off metrics. Backhaus and Tikoo (2004) highlight that a strong employer brand positively impacts job acceptance and retention, as candidates are more likely to commit to organizations that resonate with their values and expectations.
Nevertheless, the literature also acknowledges several challenges in implementing recruitment metrics effectively. A primary concern is the lack of standardization in defining and measuring certain metrics. For example, quality-of-hire is often subjectively assessed and can vary across departments or organizations Phillips Gully (2015). In addition, while quantitative data is valuable, it may not capture the full picture without qualitative insights such as employee feedback and hiring manager evaluations.
In summary, the literature underscores the strategic value of recruitment metrics in improving hiring outcomes and reducing turnover. By integrating data-driven metrics with predictive analytics and qualitative insights, organizations can enhance their recruitment processes to build a more stable and engaged workforce. However, challenges related to measurement consistency and data interpretation must be addressed to fully leverage the potential of recruitment metrics in managing employee retention.
2.1. Research Objectives
· To analyze the relationship between key recruitment metrics (such as time-to-fill, quality-of-hire, and source-of-hire) and employee turnover rates in organizations.
· To examine how recruitment metrics can be effectively used to improve employee retention strategies and enhance long-term workforce stability.
3. Research Methodology
This study uses a quantitative research methodology to assess how hiring criteria affect employee retention and turnover rates. Structured questionnaires will be used to gather data from talent acquisition managers and HR specialists in a variety of businesses. Along with attrition and retention statistics from the relevant organisations, the survey will concentrate on important recruiting metrics including time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, quality-of-hire, and source-of-hire. Participants with relevant expertise in workforce planning and recruiting will be chosen through the use of the purposive sampling approach. To find connections between hiring indicators and employee outcomes, gathered data will be examined statistically using techniques like regression modelling and correlation analysis. By preserving participant confidentially and gaining their informed agreement, the study will guarantee ethical compliance and the validity and trustworthiness of its conclusions.
4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Fifty HR experts and recruiting managers from major and mid-sized companies participated in a survey to meet the study's goals. Over a two-year period, information on four important recruiting metrics’time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, quality-of-hire, and source-of-hire’was gathered and contrasted with yearly employee retention and turnover rates.
4.1. The connection between staff turnover rates and important recruitment indicators
Descriptive statistics indicated that organizations with a longer average time-to-fill (above 45 days) reported a higher turnover rate of 23%, compared to those with a time-to-fill under 30 days, which had an average turnover of 14%. This suggests that delays in filling vacancies may result in mismatched hires or dissatisfied candidates, eventually leading to higher attrition.
Figure 1
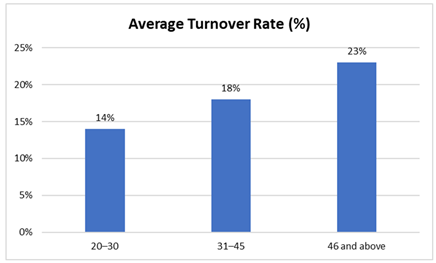
Figure 2
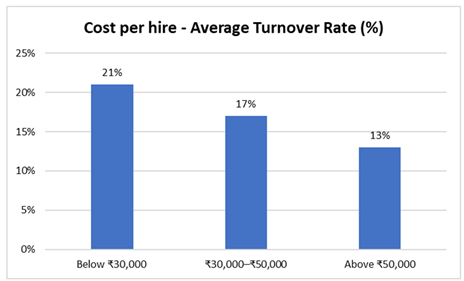
A Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to assess the strength of relationships between metrics and turnover. The correlation coefficient (r) between time-to-fill and turnover rate was +0.64, indicating a moderate to strong positive correlation. Likewise, cost-per-hire showed a weaker but still notable correlation with turnover (r = +0.42), suggesting that cost-optimization without compromising quality is important in retention.
In contrast, quality-of-hire demonstrated a strong negative correlation with turnover (r = ’0.71), showing that high-performing hires are significantly less likely to leave the organization within the first 12 months. Organizations that rated new hires 4.0 or higher (on a 5-point performance scale) had an average turnover of only 9%, while those with average hire quality below 3.0 had turnover rates exceeding 25%.
Recruitment metrics used to improve employee retention
strategies
Data related to source-of-hire revealed that employees recruited through referral programs and internal job postings had the highest one-year retention rate of 87% and 83%, respectively. In contrast, candidates hired via job portals had a lower retention rate of 64%. This suggests that aligning hiring channels with strategic fit and organizational culture can significantly influence retention.
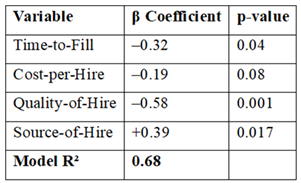
The measures with the highest predictive potential for retention rates were identified using regression analysis. The recruiting criteria employed in this study were able to account for almost 68% of the variance in employee retention, according to the multiple regression model's R2 value of 0.68. The most significant predictors among the variables were source-of-hire (β = 0.39, p < 0.05) and quality-of-hire (β = –0.58, p < 0.01). These findings highlight how crucial it is to spend money on thorough candidate evaluations and improve sourcing tactics in order to encourage long-term retention.
Interpretation of the data confirms that quantitative recruitment metrics are not only diagnostic but also predictive tools for workforce stability. Organizations with structured recruitment analytics are better equipped to design evidence-based hiring strategies, reduce costly turnover, and improve employee engagement and retention.
5. Conclusion
The findings of this study underscore the critical role recruitment metrics play in shaping employee turnover and retention outcomes. Metrics such as time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, quality-of-hire, and source-of-hire are not merely operational indicators but serve as strategic tools for talent management. The analysis revealed a strong negative correlation between quality-of-hire and turnover, as well as a significant positive impact of internal referrals and job postings on retention rates. Moreover, the regression results confirm that a data-driven approach to recruitment can significantly predict and influence workforce stability. These insights emphasize the importance for organizations to not only track recruitment metrics but also align them with long-term employee engagement and retention strategies to enhance organizational performance and reduce talent attrition.
6. Recommendation
Based on the study’s findings, it is recommended that organizations adopt a data-driven recruitment strategy that closely monitors and analyzes key metrics such as time-to-fill, quality-of-hire, and source-of-hire. Special focus should be placed on improving the quality-of-hire through structured assessments, cultural fit evaluations, and post-hire performance tracking. Organizations should also prioritize internal sourcing channels like employee referrals and internal job postings, which have shown higher retention rates. Additionally, reducing time-to-fill through efficient recruitment processes and leveraging technology like applicant tracking systems can enhance candidate experience and hiring success. Ultimately, integrating recruitment analytics with broader HR strategies can help reduce turnover, improve employee engagement, and build a more resilient and committed workforce.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Backhaus, K., & Tikoo, S. (2004). Conceptualizing and Researching Employer Branding. Career Development International, 9(5), 501–517. https://doi.org/10.1108/13620430410550754
Bersin, J. (2013). Prediction: Talent Analytics Will Emerge in 2013. Bersin by Deloitte.
Breaugh, J. A. (2009). Recruiting and Attracting talent: A Guide to Understanding and Managing the Recruitment Process. SHRM Foundation’s Effective Practice Guidelines Series.
Cascio, W. F., & Boudreau, J. W. (2016). The search for Global Competence: From International HR to Talent Management. Journal of World Business, 51(1), 103’114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2015.10.002
Hausknecht, J. P., & Trevor, C. O. (2011). Collective Turnover at the Group, Unit, and Organizational Levels: Evidence, issues, and implications. Journal of Management, 37(1), 352–388. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206310383910
Keller, S. (2018). Why Quality of Hire is the Most Important Recruiting Metric. Harvard Business Review.
Phillips, J. M., & Gully, S. M. (2015). Strategic Staffing (3rd ed.). Pearson Education.
Zottoli, M. A., & Wanous, J. P. (2000). Recruitment Source Research: Current Status and Future Directions. Human Resource Management Review, 10(4), 353’382. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1053-4822(00)00035-3
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2025. All Rights Reserved.