
MOVING TOWARDS DIGITALIZATION: UNVEILING CHALLENGES AND PROSPECTS OF E-MARKETING IN LEAST DEVELOPED ECONOMIES – THE CASE OF YEMEN
Salah Naji Taher Sanad 1![]()
![]() ,
Nawar A. S. AL-Shameri 2
,
Nawar A. S. AL-Shameri 2![]()
![]() ,
Shaima Saleh Mohammed Al-Radai 3
,
Shaima Saleh Mohammed Al-Radai 3![]()
![]()
1 Ph.D.,
Management Studies, University of Kerala, India
2 Institute
of Management in Kerala, University of Kerala, India
3 Department of Economics, University of Kerala, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
This study
aims to shed light on the challenges and potential opportunities for
e-marketing in developing economies with particular
reference to Yemen. Secondary data from relevant reports, research
papers, books, and other Internet resources is used in the study. The current
study indicated that e-marketing in Yemen confronts several challenges,
including poor communication infrastructure, lack of e-marketing knowledge,
limited Internet and social media users, an unstable power supply, lack of
trust, and lack of government incentives. However, there are prospects for
e-marketing to thrive in Yemen, such as the growing youthful population, the
rise in mobile phone users, and the introduction of 4G technology. The study
suggests investing in infrastructure, increasing digital literacy, resolving
security concerns, and active collaboration among businesses, government
entities, and other stakeholders. Implementing these suggestions can improve
e-marketing effectiveness and contribute to the country's economic growth. |
|||
|
Received 20 July 2023 Accepted 21 August 2023 Published 06 September 2023 Corresponding Author Salah
Naji Taher Sanad, salahuadddin99@gmail.com DOI 10.29121/granthaalayah.v11.i8.2023.5273 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2023 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: E-Marketing, Digital Marketing, Business
Strategy, Social Media, Telecommunications,
Challenges, Opportunities, Yemen |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
Information and communications technology (ICT) considerably boosts operational effectiveness and business processes, which raises the company's competitiveness and overall organizational performance Attaran (2003). The global economy is shifting from commodity-based to value-based activity, employment, and wealth. ICT revolutions have transformed companies alongside this global economic upheaval Qashou & Saleh (2018). Internet and technology have long shaped marketing, especially e-marketing Molenaar (2013). E-marketing is the process of promoting a brand online. It combines principles from direct response marketing and indirect marketing to assist businesses in interacting with their target market Sekar & Geetha (2013). E-marketing refers to the use of the Internet and related technologies to generate interactions that promote individual and company goals through the promotion and sale of goods and services Strauss & Frost (2001). Digital media has made the conduct of marketing more effortless than ever before. Managing digital consumer data and electronic customer relationship management systems are two examples of how digital media is utilized to carry out marketing activities Smith & Chaffey (2005).
E-marketing is a growing sector, particularly for businesses in less developed economies with limited resources, weak infrastructure, and intense competition. Such firms cannot afford to take risks, or they may make poor decisions due to inadequate knowledge of e-marketing. As a result, companies require a deeper awareness of E-Marketing challenges and prospects and how this technology may assist them in conducting marketing activities and processes more effectively than traditional methods El-Gohary (2012).
Most of the least developed countries lag behind in terms of employing recent technologies in their business operations, specifically marketing operations. Yemen is one of those countries struggling to implement digital marketing techniques and strategies effectively. Yemen is one of the least developed countries, having been plagued by political unrest for a long time, resulting in poor infrastructure, restricted access to technology, insecurity, high illiteracy, and poverty. All of these obstacles make e-marketing adoption challenging. On the other hand, future possibilities, and chances for adopting e-marketing include the country's expanding population, rising mobile user base, and increased young population growth.
E-marketing in Yemen has received less attention from researchers and practitioners, and a research gap in this field has driven the researchers to conduct this study. Therefore, the current study is conducted to address the following objectives:
1) To identify the challenges facing e-marketing in the context of Yemen.
2) To determine the prospects and potential opportunities for adopting e-marketing in Yemen.
3) To recommend best practices for businesses to enhance their e-marketing efforts in light of the current challenges and opportunities.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
The rapid growth and proliferation of e-marketing can be directly attributed to information and communication technology (ICT) development. Based on their unique perspectives and extensive expertise, specialists have various interpretations of e-marketing significance. Brodie et al. (2007) define it as "the method by which a business communicates with its customers through the use of the internet and other real-time technologies. Strauss & Frost (2001) also described it as "the application of electronic information and tools to the process of creating and facilitating exchanges that meet the needs of individuals and groups.". E-marketing is one of the most common types of contemporary marketing because of the transaction market's role in the creation of new ideas and their practical application Jaas (2022).
According to Jaas (2022), there are many benefits to e-marketing. These include the ability to publish marketing information on websites at a lower cost than the expense of advertising in traditional ways, an increase in the size of the consumer base as a direct result of providing instant and ongoing access, the ability to easily access both new markets and all global marketplaces, and the ability to identify their products without any restrictions based on ethnicity. In addition, it is more accessible to the assistance and guidance offered by specialists.
Businesses must accurately gauge and cater to their consumers' wants and requirements to succeed in e-marketing. Therefore, it is more crucial than ever before to find effective ways and methods to meet such demands, through which technology comes first. True, the world's rapidly evolving technology landscape is influencing the dynamic nature of the digital marketing landscape Kasambu & Sritharan (2020).
Many academics are interested in E-marketing, but the literature on how E-marketing affects marketing results is scant. According to the relevant research findings, there appears to be a discrepancy between E-marketing and marketing outcomes Tsiotsou & Vlachopoulou (2011). Coviello et al. (2006) found no correlation between E-marketing and marketing performance, while Brodie et al. (2007) and Wu et al. (2003) discovered a favorable association. Both monetary and non-monetary measures can be used to assess marketing effectiveness Hacioglu & Gök (2013). Profitability, sales, and capital flow are the most common financial indicators. Non-financial measures such as market share, customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and brand equity may also be used to analyze marketing efficacy Hacioglu & Gök (2013). Every country is at a different point in the evolution of e-marketing.
Salome & Ofunre (2019) argued that even though e-marketing has a wide range of benefits and advantages, Nigeria is facing many issues regarding telecommunication infrastructure, Internet, power supply, and security issues. The study recommends that Nigeria utilize e-marketing and enhance its information technology and security to use e-marketing benefits.
According to UNCTAD's analysis of available statistics, only about one in ten Internet users in the least developed countries (LDCs) make purchases online. This compares to as many as eight in ten Internet users in OECD nations. In this regard, investments in the ICT industry are required, and other metrics that matter for the ICT sector show that Yemen needs to make up. It is being suggested that Yemen encourage mobile network providers to expand their G3 and 4G service offerings in a free market Geneva (2022).
Kaid Zaid & Khan (2019) aimed to identify the principal barriers impeding the adoption of e-marketing practices within Yemeni banks. The study illuminates various technological, environmental, and organizational obstacles that hinder the progress of e-marketing, including deficient infrastructure, limited technical literacy, inadequate internet services, low consumer confidence and awareness regarding e-marketing services, insufficient attention from top management towards e-marketing endeavors, geopolitical instability, and associated security risks, limited availability of payment methods and the associated challenges in obtaining them, substandard responsiveness by banks to customer complaints and requirements, banks' failure to provide accurate and punctual banking services, as well as the high costs incurred in acquiring electronic banking services. Drawing upon the study's findings, the researcher presents crucial recommendations aimed at enhancing the state of e-marketing in Yemen.
Gupta (2020) presented a comprehensive examination of eleven current digital marketing practices and assigned priority to these strategies within the sales funnel, employing the See-Think-Do-Care model. The discourse encompasses an assessment of both the opportunities and challenges associated with implementing digital marketing techniques. The investigation determined that video marketing emerged as the most effective approach for customer attraction, while remarketing proved to be the most impactful technique for encouraging customers to finalize their purchases. The findings of this study contribute to the existing body of literature on online marketing and offer valuable insights for marketers seeking to prioritize their digital marketing strategies.
According to Yasmin et al. (2015), marketers face emerging challenges and prospects. Digital marketing entails the utilization of electronic communication channels by marketers to propagate and endorse their products or services in the market. The principal aim of digital marketing revolves around attracting customers and enabling their active engagement with the brand through digital media platforms. This study focused on elucidating the significance of digital marketing for marketers and consumers. Moreover, the paper comprehensively presents and compares traditional marketing approaches with digital marketing strategies. The research study delineates various manifestations of digital marketing, assesses their effectiveness, and examines their influence on the sales outcomes of firms.
2.1. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE ADOPTION OF E-MARKETING
According to the research of Coviello et al. (2003), conventional marketing methods benefit from the addition of e-marketing. Therefore, the firm's IT-centric culture significantly influences whether or not to perform e-marketing. Technology comes first, then the market capacity comes next Salome & Ofunre (2019). It is being argued that the function of IT in a company affects the way e-marketing is carried out in that company. If IT plays a transformative role, e-marketing can drive the organization's actions. However, E-commerce in Yemen faces major challenges with inadequate financial resources to support investment in the IT industry Bose (2019).
Sheth & Sharma (2005) identified two factors that influence a country's willingness to embrace e-marketing: the state of the country's infrastructure and the maturity of its marketing institutions. Infrastructure development refers to roads, telecommunication, legislative bodies, and good justice systems. On the other side, distribution channels and well-oiled communication systems are examples of what is meant by "marketing institutional development" Salome & Ofunre (2019). Once the country experiences the development of these factors, there will be possible adoption and growth of e-marketing.
3. METHODOLOGY
3.1. RESEARCH DESIGN
This research adopted the descriptive method to point out and describe the challenges and prospects of e-marketing in Yemen.
3.2. DATA SOURCE
Secondary information was gathered from previously published works on e-marketing in least-developed countries, with a special focus on Yemen.
4. DISCUSSION
This section presents an overview of mobile connections, internet users, and social media users in Yemen compared to the country's population. It then discusses the challenges and prospects of E-Marketing in Yemen.
4.1. AN OVERVIEW
Table 1 below shows Yemen's population, mobile connections, internet users, and social media users from 2018 to 2023.
Mobile Connections: Yemeni mobile connections are
predicted to expand despite a modest dip in 2020. With more people using mobile
phones, mobile marketing and advertising have an opportunity.
Population: Yemen's population jumped from 28.58
million in 2018 to 34.07 million in 2023. It indicates that the population is
in an increased trend over the years.
Internet Users: In 2023, Internet users reached 9.1
million, as indicated in Table 1, which indicates that
only 26% of the population has access to the Internet. As compared to the
population, internet users are low in number. Businesses trying to contact
clients online may face the obstacle of the shortage of internet users in the
country.
Table 1
|
Table 1 Population, Mobile Connections, Internet Users, and Social Media Users in Yemen from 2018 to 2023 |
||||||
|
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
|
|
Population |
28.58M |
29.25M |
29.49M |
30.16M |
30.82 M |
34.07M |
|
Mobile Connections |
18.37M |
18.40M |
17.82M |
18.21M |
19.16 M |
19.63M |
|
Internet Users |
7.03M |
7.19M |
7.88M |
8.06 M |
8.24 M |
9.1M |
|
Social Media users |
2.30M |
2.30M |
2.50M |
3.20 M |
3.50 M |
3.05M |
|
Source (www.datareportal.com) |
||||||
Figure 1
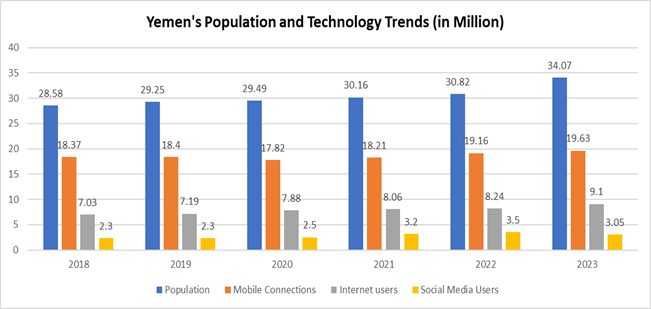
|
Figure 1 Mobile Connections, Internet Users, and Social Media Users Against the
Population in Yemen Source
(www.datareportal.com) |
Social Media Users: Yemen has grown to 3.05 million social media users in 2023. However, just 9% of the population uses social media. It is apparent that businesses may face challenges since social media can be an effective marketing tool, but reaching potential clients may require more tailored tactics. However, Facebook users are relatively high compared to other social media; therefore, businesses may make use of such opportunities.
Table 2
|
Table 2 Social Media Users in Yemen from 2019 to 2023 |
|||||
|
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
Early 2023 |
|
|
Facebook |
2.2M |
2.2M |
2.7M |
2. 85M |
2.5M |
|
Instagram |
410k |
400k |
440k |
657.6k |
619.2k |
|
LinkedIn |
200k |
240k |
270k |
320k |
380k |
|
Twitter |
609k |
998.5k |
385.6k |
599.7k |
858.1k |
|
Source (www.datareportal.com) |
|||||
Figure 2

|
Figure 2 Facebook users in Yemen from 2019-2023 Source
(www.datareportal.com) |
Figure 3

|
Figure 3 Other Social Media Users in Yemen from 2019–2023 Source
(www.datareportal.com) |
With 2.5 million active users in 2023, Facebook retains the greatest user base among the four networks. Businesses now have a big potential to reach a large audience and advertise their products or services through targeted advertising and organic content.
With 619,200 active users in 2023, Instagram's expanding user allows businesses to reach out to a younger demographic of consumers and exploit the platform's visual format to display products or services. Instagram's prominence among younger generations makes it a viable tool for influencer marketing and brand recognition through collaborations with prominent Instagram accounts.
LinkedIn's 380,000 active members in 2023 allow businesses to interact with professionals and market their brand to a more niche audience. LinkedIn's emphasis on professional networking and career development allows businesses to acquire new workers and demonstrate their corporate culture.
Twitter's shifting user base may provide hurdles for e-marketing initiatives, but it nevertheless allows businesses to connect with customers in real-time and join in hot topics and conversations. Twitter may also be used for customer service and reputation management, allowing businesses to reply to customer inquiries and comments promptly.
Generally, the data indicate that each social media network provides distinct e-marketing opportunities, and firms should examine their target demographic and goals when deciding which platform(s) to focus on. Businesses may design efficient e-marketing strategies to reach their intended audience and promote their brand by analyzing each platform's user base and potential reach.
4.2. CHALLENGES OF E-MARKETING IN YEMEN
4.2.1. LOW E-MARKETING EDUCATION
Yemeni businesses lack awareness about e-marketing and its benefits. This can discourage digital marketing investments. Lack of employee expertise hinders e-marketing development due to a lack of skilled staff and poor training. Yemen's computer literacy and technology are still evolving, and some employees worry about making mistakes when using computers, according to Ajami and Mohammadi-Bertiani (2012) and Al-Mamary et al. (2014). Thus, many employees struggle with e-marketing because it requires computer and technology skills.
4.2.2. THE POOR INFRASTRUCTURE OF THE TELECOMMUNICATION INDUSTRY
Yemen's telecoms sector faces big infrastructure challenges. Economic and political turmoil and ongoing war have slowed sector growth. Yemen's telecoms infrastructure is outdated and lacks high-speed Internet and cell networks. Infrastructure shortages have hurt Yemen's mobile sector. Telecommunications companies struggle to provide reliable services due to dropped calls, slow internet rates, and other network issues. Businesses struggle to operate, engage with customers, and conduct web interactions. Poor telecoms infrastructure has hindered international funding, worsening the country's fiscal problems.
4.2.3. SLOW AND EXPENSIVE INTERNET CONNECTION AND LIMITED COVERAGE
Yemen has a limited internet infrastructure, making it difficult for businesses to engage in e-marketing. Slow internet speeds and limited technological access can also hinder digital marketing efforts. Tele Yemen and Yemen Net are the only internet providers, and the government oversees telecoms. Yemen Net is completely government-owned, while Tele Yemen is majority government-owned. It can be said that the Internet in Yemen is monopolized by the government. If private companies are allowed to provide internet services, there could be a higher level of competition, which may result in higher internet quality and lower prices. The current service quality, price, and internet access can impede e-marketing efforts in Yemen. The figure below displays the average price of one gigabyte of mobile data in the Arab world in US dollars.
Figure 4
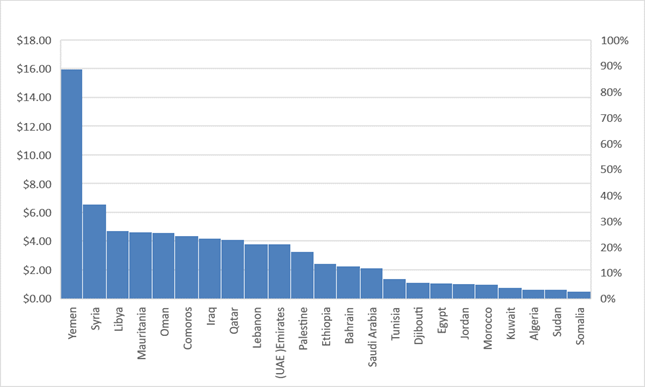
|
Figure 4 Average Price of 1GB of Mobile Data in the Arab World ($/GB, 2019) Source Cable.co.uk,
2020. |
Figure 4 shows that mobile Internet in Yemen is one of the most expensive in the world and the most expensive in the Arab world. Yemen's internet cost is the highest among all Arab countries, with a gigabyte costing about $15.98, as shown in Figure 4. Somalia had the cheapest mobile internet rates among Arab countries, costing about $0.50 per gigabyte on average. The expensive cost of the Internet is one critical challenge for e-marketing to flourish in Yemen.
4.2.4. LIMITED USERS OF THE INTERNET
Yemen's internet user base has reached 9.1 million users by 2023, which indicates that only 26% of the population has online access. This makes online client outreach difficult for firms and businesses in Yemen. If the internet price is reasonable and if it has high speed, the number of expected users may increase, and such an e-marketing challenge may become an opportunity.
4.2.5. UNRELIABLE POWER SUPPLY
In Yemen, an unstable power supply is a major barrier to e-marketing. The equipment required for e-marketing depends mainly on power. The unreliable power supply makes it a great challenge for e-marketing to prosper and flourish in Yemen.
4.2.6. LIMITED USERS OF SOCIAL MEDIA PLATFORMS
Even if the number of social media has been rising over the past years, only 9.0% of the population uses it as per the data at the start of 2023 (Datareportal). While Facebook has millions of users, other social media such as Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter are below a million users each as shown in Table 2.
4.2.7. LACK OF GOVERNMENT INCENTIVES
The government does not promote or set forward any plans for the country's internet network to be expanded and improved. Legislation titled "Law No. 40 of 2006 Regarding Electronic Payments Systems for Financial and Banking Operations" is the sole law that deals with e-payments. The usage of electronic payments and financial transactions in court is acknowledged by this law (Bose, 2019). As has been noted elsewhere Alashwal (2016), Abdullah et al. (2018), Adenobserver (2015), Sabaie (2017), Althawrah (2013), the absence of assistance from the government and regulatory institutions presents a significant obstacle to the digitization of businesses.
4.2.8. LACK OF TRUST
Consumers in Yemen lack trust in digital marketing due to the difficulty of knowing the Source and the difficulty of tracking people in case of cybercrimes. There is currently no cybercrime legislation in place in Yemen. The Penal Code and other applicable legislation address cybercrimes by their general provisions. Yemeni lawyer Ahmad Arman said: The press and publishing legislation, the code of crimes and penalties, and other elements of criminalization and punishment under Yemeni law all fail to provide explicit rules on cybercrime. When presented with instances involving free speech, some courts have utilized broad legal principles. One of the most significant barriers to the widespread adoption of e-marketing is the belief that online transactions are unsafe. Security measures should prevent unauthorized parties from gaining access to or using a user's personal information in any way, including via fraud or hacking. Understanding and addressing security risks is critical if ICT is to be used to offer e-marketing apps.
4.3. PROSPECTS FOR E-MARKETING
4.3.1. GROWING POPULATION
Yemen's population increased from 28.58 million in 2018 to 34.07 million in 2023. There has been a steady increase in the population over the years. Hence, Yemen's population growth has been significant. In recent decades, Yemen, the Arabian Peninsula's second-largest nation, has seen catastrophic population growth. Businesses can utilize such an increase, and e-marketing strategies may be thought of.
4.3.2. THE GROWING NUMBER OF MOBILE USERS
Yemeni mobile phone usage is rising and is likely to continue. The lowering cost of mobile devices, the spread of mobile networks, the population's age, and simplicity of use drive this trend. More than half of the population in early 2023 are using mobile phones, as indicated in Table 1. Yemeni cell phone usage is projected to affect business, education, and entertainment. This can be a great opportunity for businesses to promote their products and services online. If getting an internet connection can be made easy and affordable, it would be expected that the number of internet users may increase to a level closer to the number of mobile phone users, which will be a great opportunity for businesses.
4.3.3. THE INCREASED NUMBER OF FACEBOOK USERS
The number of Yemenis who use Facebook has increased dramatically over the last several years, making it one of the country's most popular social networking platforms. Businesses and organizations can use Yemen's increased Facebook usage for e-marketing. Increased reach with more people using Facebook, businesses and organizations can reach a larger audience, which can help increase brand awareness and attract new customers. Also, targeted their Advertising, Facebook allows businesses and organizations to target their advertising to specific demographics. Companies can utilize this social media platform to promote their products and services and reach a larger audience.
4.3.4. THE INTRODUCTION OF 4G TECHNOLOGY
Fourth-generation cellular technology (4G) has been introduced to Yemen recently, allowing faster data transmission and network efficiency. The launch of 4G technology in Yemen could improve connectivity. The speed and reliability of 4G internet links can help Yemenis acquire information and communicate quickly. It will also ease Internet-dependent E-marketing efforts. Yemen has depended mainly on 2G and 3G over the past year; however, introducing 4G is a great opportunity that could significantly change various industries in Yemen.
4.3.5. YOUNG POPULATION
Figure 5 shows that across most of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, people from 15-29 years of age constitute nearly one-quarter (24%) of the population, compared with 19% across OECD countries. The youth bulge and future demographic projections vary considerably among regions. Yemen has the largest percentage of individuals under 29 at 67%, while Kuwait has the lowest at 38%, indicating that Yemen has the strength of having the largest young population in the region.
The e-marketing industry can benefit from targeting a younger audience due to the larger potential client base it offers. The growing popularity of internet usage and social media platforms has facilitated businesses in their efforts to engage with prospective consumers. The younger generation exhibits greater proficiency and comfort in utilizing technological devices and digital platforms. This suggests they are inclined to employ e-marketing tactics such as social media campaigns, email marketing, and Internet advertising. The prevalence of smartphones has led to a predominant preference among young individuals to utilize mobile devices for internet access and content consumption. E-marketers can leverage this opportunity by creating customized campaigns and engaging with customers via digital platforms.
Figure 5
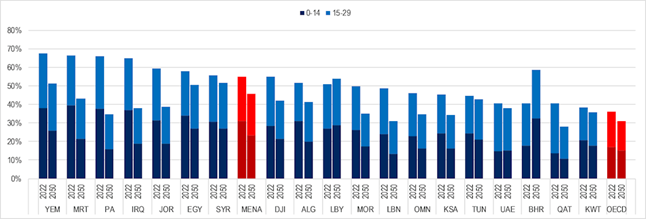
|
Figure 5 Share of Young People as Part of the Total Population, 2022 and 2050 Projections Source OECD Calculations Based on United Nations, Department of
Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2019). World Population
Prospects 2019, Custom Data Acquired Via Website. |
5. CONCLUSION
Marketing has evolved from offline media to the Internet and technology to reach the audience. People live now in the digital era, and strategies and approaches to reaching customers have changed significantly. Such changes have happened more in the developed countries while developing countries are still lagging behind. Yemen is one of those countries which is still very far from business digitalization. E-marketing in Yemen is purely a new concept, and only a few businesses know how to utilize it. It has to be educated, and many developments are yet to take place to use such techniques effectively. Even though there are various challenges on the way of digitalization in Yemen, there are also opportunities and prospects indicators that make adopting the new technology into marketing efforts more possible and required than ever.
6. PRACTICAL IMPLICATIONS
Considering the identified challenges and prospects of e-marketing in Yemen, the study offers practical recommendations and best practices for businesses to enhance their e-marketing efforts.
• The study suggests investing in developing digital infrastructure, such as expanding internet coverage and improving the quality and speed of connections. In addition, the power shortage is to be resolved. This can help businesses overcome connectivity challenges and ensure smoother e-marketing operations.
• The study recommends initiatives to increase digital literacy rates among the population, including training programs and educational campaigns. Businesses may broaden their target population and increase the success of their e-marketing initiatives by improving individuals' digital competencies.
• E-marketing initiatives often raise concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity. The study proposes measures to mitigate these concerns, such as implementing secure payment gateways, encrypting customer data, and raising awareness about online security practices.
• The study emphasizes the importance of collaboration among businesses, government entities, and other relevant stakeholders. By working together, they can address common challenges, share resources, and collectively support the growth of e-marketing in Yemen.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Abdullah, A., Thomas, B., Murphy, L., & Plant, E. (2018). An Investigation of the Benefits and Barriers of E-Business Adoption Activities in Yemeni SMEs. Strategic Change, 27(3), 195-208. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsc.2195.
Adenobserver (2015). Study : Weak Infrastructure in Yemen – an Obstacle to Electronic Commerce.
Ajami, S., and Mohammadi-Bertiani, Z. (2012). Training and its Impact on Hospital Information System (HIS) Success. Journal of Information Technology & Software Engineering, 2(5). https://doi.org/10.4172/2165-7866.1000112.
Alashwal, A. H. A. (2016). Obstacles Facing the Setting up of Virtual Enterprises in the Republic of Yemen : Analytical Study. Journal of Social Studies, 22(4), 169-204.
Al-Mamary, Y. H., Shamsuddin, A., & Nor Aziati, A. H. (2014). Key Factors Enhancing Acceptance of Management Information Systems in Yemeni Companies. Journal of Business and Management Research, 5(1), 108-111.
Althawrah, (2013). 38% of Commercial Organizations Do Not Use E-Commerce.
Attaran, M. (2003). Information Technology and Business Process Redesign. Business Process Management Journal, 9(4), 440-458. https://doi.org/10.1108/14637150310484508.
Bose, U. (2019). ICT, Marketing Technology, and E-Commerce in Unstable Economies (Cases of South Sudan, Syria, Democratic Republic of Congo, Yemen, Somalia). International Journal af all Research Writings, 1(5), 7-14.
Brodie, R. J., Winklhofer, H., Coviello, N. E., & Johnston, W. J. (2007). Is E-Marketing Coming of Age ? An Examination of the Penetration of E-Marketing and Firm Performance. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 21(1), 2–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/dir.20071.
Coviello, N. E., Brodie, R. J., Brookes, R. W., & Palmer, R. A. (2003). Assessing the Role of E-Marketing in Contemporary Marketing Practice. Journal of Marketing Management, 19(7-8), 857-881.
Coviello, N., Winklhofer, H., & Hamilton, K. (2006). Marketing Practices and Performance of Small Service Firms an Examination in the Tourism Accommodation Sector. Journal of Service Research, 9(1), 38–58.
Datareportal “ DIGITAL 2018-2023 : Yemen.” (Accessed March 17, 2023).
El-Gohary, H. (2012). Factors Affecting E-Marketing Adoption and Implementation in Tourism Firms : An Empirical Investigation of Egyptian Small Tourism Organizations. Tourism management, 33(5), 1256-1269.
Geneva (2022). E-Commerce and the Digital Economy in LDCs : At Breaking Point in COVID-19 Times. (Accessed : March 30, 2022).
Gupta, N. (2020). Digital Marketing : Trends, Opportunities, and Challenges. Asian Journal of Management, 11(4), 434-440. https://doi.org/10.5958/2321-5763.2020.00066.9.
Hacioglu, G., & Gök, O. (2013). Marketing Performance Measurement: Marketing Metrics in Turkish Firms. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 14(sup1), S413–S432. https://doi.org/10.3846/16111699.2012.729156.
Jaas, A. (2022). E-Marketing and Its Strategies : Digital Opportunities and Challenges. Open Journal of Business and Management, 10(2), 822-845. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojbm.2022.102046.
Kaid Zaid, M. A., & Khan, M. F. (2019). A Study of Adoption of E-Marketing in Yemeni Banks. International Journal of Management Studies, 2(3), 107-114.
Kasambu, N., & Sritharan, R. (2020). A Study on Problems and Prospects of E-Marketing. Stud. Indian Place Names, 40, 3447-3456.
Molenaar, C. (2013). E-Marketing : Applications of Information Technology and the Internet Within Marketing. Routledge.
Qashou, A., & Saleh, Y. (2018). E-Marketing Implementation in Small and Medium-Sized Restaurants in Palestine. Arab Economic and Business Journal, 13(2), 93-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aebj.2018.07.001.
Sabaie, A. A. (2017). The Status of Electronic Commerce and its Challenges in the Arab World.
Salome, I. O., & Ofunre, I. C. (2019). E-Marketing in Nigeria : Benefits, Challenges and Strategies. Journal of Asian Business Strategy, 9(2), 220-234. https://doi.org/10.18488/journal.1006.2019.92.220.234.
Sekar, M., & Geetha, R. (2013). Challenges and Opportunities of E-Marketing. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management, School of Business Management, Rathnavel Subramanian College of Arts and Science.
Sheth, J. N., & Sharma, A. (2005). International E-Marketing : Opportunities and Issues. International Marketing Review, 22(6), 611-622. https://doi.org/10.1108/02651330510630249.
Smith, P. R., & Chaffey, D. (2005). E-marketing Excellence-at the Heart of E-Business. Oxford : Butterworth Heinemann.
Strauss, J., & Frost, R. (2001). E-marketing (2nd ed.). New Jersey : Prentice Hall.
Strauss, J., & Frost, R. (2001). E-marketing. NJ, USA : Prentice Hall.
Tsiotsou, R. H., & Vlachopoulou, M. (2011). Understanding the Effects of Market Orientation and E-Marketing on Service Performance. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 29(2), 141–155. https://doi.org/10.1108/02634501111117593.
Wu, F., Mahajan, V., & Balasubramanian, S. (2003). An Analysis of E-Business Adoption and its Impact on Business Performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 31(4), 425–447. https://doi.org/10.1177/0092070303255379.
Yasmin, A., Tasneem, S., & Fatema, K. (2015). Effectiveness of Digital Marketing in the Challenging Age : An Empirical Study. International Journal of Management Science and Business Administration, 1(5), 69-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.18775/ijmsba.1849-5664-5419.2014.15.1006.
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2023. All Rights Reserved.