
STRATEGIC PLANNING, ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE, ANALYSIS OF ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE IN STRATEGIC CHANGE MANAGEMENT MEDIATION IN STATE INTELLIGENCE AGENCY
Dani Nugraha 1 ![]()
![]() ,
Dadan Umar Daihani 2, Kusnadi 3
,
Dadan Umar Daihani 2, Kusnadi 3
1, 2, 3 Faculty of Economics, University Trisakti Jakarta, Indonesia
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
The purpose of
this study is to realize the legal, administrative and physical order of
State Property in the State Intelligence Agency towards effective, efficient,
optimal, and accountable management of State Property, as well as
transparency, strategies and important steps are needed to realize change. In
supporting the policy-making process related to State Property, it is
necessary to fulfill basic information in the form of current and actual
goods data by carrying out updates through periodic inventory of State
Property. The research design and method used in this research is hypothesis
testing. This research is a quantitative non-experimental, using a
questionnaire given to 98 respondents. This research was conducted at the
Logistics Bureau of the State Intelligence Agency. Data analysis using SPSS
and PLS.3.20 software with multivariate Structural Equation Model (SEM)
analysis method.The results of this study indicate that: Strategic Planning
and Organizational Culture on Strategic Change Management are positive and
significant. The influence of Strategic Change Management on Organizational
Performance is positive and significant. The influence of Strategic Change
Management mediating Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture on
Organizational Performance is positive and significant. It means that the
higher/positive mediation of Strategic Change Management on Strategic
Planning and Organizational Culture, the higher/positive Organizational
Performance. The theoretical
implication of Strategic Change Management as mediating to Strategic Planning
and Organizational Culture able to improve Organizational Performance, by
improving Strategic Change Management through increasing its dimensions will
be able to improve the Organizational Performance of the State Intelligence
Agency. |
|||
|
Received 15 March 2022 Accepted 15 April 2022 Published 30 April 2022 Corresponding Author Dani
Nugraha, dn485008@gmail.com DOI 10.29121/granthaalayah.v10.i4.2022.4568 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2022 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the license
CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download, reuse,
re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work must
be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Strategic Planning, Organizational
Culture, Strategic Change Management, Organizational Performance |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
Human resources have a major role in every organizational activity, including the State Intelligence Agency. Although supported by facilities and infrastructure as well as excessive sources of funds, without the support of competent human resources, organizational activities at the State Intelligence Agency will not run well and optimally. This shows that human resources are a key factor that must be considered with all its potential. Because human resources will determine the successful implementation of organizational activities wherever they are. Each organization or agency is established to achieve the goals to be achieved in accordance with its vision and mission. To achieve this goal, good cooperation is needed. The success of a company cannot be separated from the best abilities given by its members or employees. The establishment of harmonious cooperation between human resources within an agency or organization, can affect the performance of the agency.
To realize the Vision of the State Intelligence Agency, strategic steps must be formulated that must be carried out jointly by all elements in the organization, in the form of a mission statement. Vision and mission are the core that become written guidelines in a management system by describing what conditions are to be achieved, what must be implemented, prioritized and prioritized and become the basis of all programs or activities of the organizational unit as the implementer. This means that the implementation of activities in every line in the organization must refer to the vision and mission guidelines. The thing that becomes the focus in achieving the State Intelligence Agency is, of course, how the mission can be carried out quickly, measurably and its progress can be monitored. So that it can become an intelligence organization that has strong resources and is also well coordinated and able to synergize with every part of the organization.
The abundance of human resources that exist today requires thinking carefully, namely how to utilize human resources optimally. One of the national problems faced by the Indonesian people today is the handling of the low quality of human resources. The large number of human resources, if used effectively and efficiently, will be beneficial to support the pace of sustainable national development. In order for the community to have reliable human resources, quality education is needed, the provision of various social facilities, adequate employment opportunities. Weaknesses in the provision of these facilities will cause social unrest which will have an impact on community security. Currently, the ability of human resources is still low, both in terms of their intellectual abilities and technical skills Bourland-davis et al. (2017); Sinambela (2019).
The quality of human resources will be fulfilled if job satisfaction as an element that affects performance can be created perfectly. Discussing job satisfaction will not be separated from the factors that can affect one's job satisfaction. So that employee satisfaction is always consistent, at least an agency must always pay attention to the environment in which the employee carries out his duties, for example colleagues, leaders, work atmosphere and other things that can affect a person's ability to carry out their duties. The problem of culture itself is an essential thing for an organization or institution, because it will always be related to the life that exists within the company. Organizational culture is a philosophy, ideology, values, assumptions, beliefs, expectations, attitudes and norms that are shared and binding in a particular community. Specifically, the culture in the organization will be determined by the working conditions of the team, leadership and organizational characteristics as well as the applicable administrative processes Lewis (2018).
The research gap found the placement of the Strategic Change Management variable in the management of state property in the logistics bureau of the State Intelligence Agency as a mediator variable, which mediates the Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture factors on Organizational Performance. This can be seen in the research: Hess and Flatten (2019) with the title Strategic Flexibility in Turbulent Times: Impact of CEO's Willingness and Permission to Change.
Strategic Planning, according to Wolf and Floyd (2017) is the process of selecting organizational goals; determination of strategies, policies and strategic programs needed for these objectives; and establishing the methods needed to ensure that strategies and policies are implemented. This is in line with the opinion of Bryson (2015) that planning is a type of decision making for the specific future that managers want for their organization. Strategic Planning, is the key to success that affects organizational performance, because strategy is an overall plan that explains the competitive position of a company.
Strategic Planning is the process of selecting organizational goals, determining strategies, policies and strategic programs to achieve these goals; and establishing methods to ensure that strategies and policies are implemented. Strategic Planning is the key to success that affects organizational performance, because strategy is an overall plan that explains the competitive position of a company.
Novelty or novelty in this research is Strategic Planning and Strategic Policy, namely strengthening changes that will occur in the Management of State Property Logistics Bureau of the State Intelligence Agency. In addition to the strategic change management factor, in this study, Strategic Planning also wants to see its impact on organizational performance. Hess and Flatten (2019) found that Strategic Planning can create a new approach to continuous improvement that leads to an increase in organizational performance. Despite the broad consensus on the positive relationship between Strategic Planning and Organizational Performance, understanding organizational learning remains elusive and there appears to be little agreement on the accepted theory of organizational learning Wolf and Floyd (2017).
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Strategic change management is critical to the development, growth, success and survival of any organization operating in an ever-changing environment. Nevertheless, there seems to be a clear consensus among researchers and practitioners alike that most organizational change initiatives fail. Several studies have found that 70 percent of change efforts are unproductive. A study highlights that 90 percent of change programs have failed if there was no change in the organization Nuhu et al. (2016).
Strategic change management is one of the most dynamic fields in many research areas such as strategic management and corporate turnaround. Strategic change management has been recognized as one of the main sources of organizational performance improvement Nguyen et al. (2019). There are at least two main perspectives on the use of strategic change management in the literature. One view of strategic change management has focused on how organizations reverse poor performance through the use of strategic change management.
Another view of strategic change management has focused on how to maintain or improve organizational performance. This view recognizes that organizations can maintain and improve performance with consistent and persistent use of strategic change management and focus on aligning organizational strategy, structure, and ideology with ongoing change Shermin (2017). Therefore, the decline in performance may be a consequence of organizational stagnation that occurs over several periods, leading to the alignment of organizational strategy, structure, and ideology with the demands of a dynamic and changing operating environment Hensmans (2019); Vitolla et al. (2017).
The opinion that the two perspectives can be seen as two sides of the same coin, namely the organization has focused on strategic change management as a means to improve organizational performance. The only major difference between the two perspectives may depend on the timing of the use of Strategic change management with the former focusing on times when the organization is underperforming, while the latter focuses on continuing to implement Strategic change management to maintain and improve organizational performance. Shermin (2017); Hess and Flatten (2019)
One of the most important things in strategic change management is involving people in the change process. But change in an organization cannot be achieved without the support of employees and management, as both parties must feel that they are part of the change process. It must be remembered that not every change process is a success, a large proportion of organizations fail in this process. The fact that all people in leadership positions are better at directing more attention to positively influencing people for the cultivation and development of human resources taking into account these issues raised by various models and management systems of the modern world. This will lead to the existence of positive feedback that will support management decisions, set priorities, change policies in the medium and long term and thus will improve organizational performance Hensmans (2019).
This study tries to develop theories about Information Technology Capabilities which is carried out to see how Information Technology Capabilities help human resources so that it will improve organizational performance, several theories about Strategic Planning, which are carried out for organizational strategic planning are contained in several studies from Barron and Chou (2017); Esfahani et al. (2018); Dlamini et al. (2019); Al-Dhaafri and Alosani (2020).
Organizational Culture also depends on the human aspect where some previous and recent studies that have become references are according to several experts including, Zhou et al. (2018); Rebelo and Gomes (2019); Jain (2019) Radford et al. (2020);M. Muzamil Naqshband (2020).
Strategic Change Management is a process of organizational change, has different phases. Change has become a vital organ of every organization's life. Some previous research references are,Vitolla et al. (2017); Guiette and Vandenbempt (2018); Hirst (2019); Hensmans (2019); Tichy (2020); Bordum (2020); Järvi and Khoreva (2020).
Organizational Performance according to Antony and Bhattacharyya (2018); Oyewobi et al. (2019); Tarifa-Fernández et al. (2019) The potential success of an organization depends to a large extent on performance, which is related to its ability to effectively implement strategies to achieve organizational goals. Baird et al. (2019); Chen et al. (2020).
Classical organizational theory has mentioned several approaches regarding the organization as an entity with a coalition implying the existence of several (competing) group cultures. Kumar and Sharma (2018) describes organizations as political entities, in which there are various groups or coalitions whose purpose is to lobby and to direct the attention of organizations towards their own personal interests and specific goals. Tarifa et al. (2019) further state that intergroup conflict can arise from differences in achieving goals or differences in the perception of reality. The paper Ibrahim et al. (2015) mentions cultural understandings such as performance in time frames and forms of social relations between organizational units which are seen to be contrasting both empirically and normatively. Ratten and Ferreira (2016) describe organizations as internal interest groups, or constituencies, that claim on the organization. An organizational constituency is any group within the organization whose members have an identifiable common interest that they are trying to promote. Such constituencies may be demarcated by department or hierarchies or, more generally, by groups of members who have different values and interests. Obviously, if certain groups have different goals and interpretative systems it is quite possible they will all develop a common set of understandings and assumptions. which can then be described as organizational culture, although it does not specifically refer to organizational culture, he states that to understand organizational behavior, the unit of analysis must be the basic sub-unit that makes up an organization. Following a systems framework, organizational behavior can be seen as the result of interactions between subunits within the organization.
It appears that organizational culture is best conceptualized as a very different phenomenon. Unfortunately, this approach has been neglected by most organizational culture researchers. Yunis et al. (2017) focuses on subcultures and their formation in organizations. They define an organizational subculture as a subset of organizational members who interact regularly with each other, identify themselves as distinct groups within the organization, share a set of problems that are generally defined as problems of all, and routinely take action on the basis of a unique collective understanding. for groups. Researchers argue that there are several subcultures within organizations, each with its own agenda and perspective.
3. METHODOLOGY
This study uses a survey technique, a deductive approach and is quantitative in nature Rahi (2017). The deductive approach aims to test the theory through collecting data from respondents and then applying it and observing it with statistical tests. The quantitative method focuses on collecting data according to the problem and the number of populations and data analysis. This research Wang et al. (2018) is a testing hypothesis that aims to explain the nature of the relationship between two or more variables Cooper and Schindler (2014). In this study also tested the hypothesis of the influence of Strategic Planning Al-Dhaafri and Alosani (2020) Organizational Culture Kumar and Sharma (2018) on Organizational Performance Dlamini et al. (2019) mediated by Strategic Change Management Hess and Flatten (2019) This research is a survey research, (Saad Laraqui 2018), where by collecting information from or about individuals who will be described, compared, or explained about knowledge of attitudes and behavior.
The research was conducted in the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency. The method of collecting and determining the sample is used purpose sampling. The method used with certain criteria is in accordance with the needs in the study. Hair et al. (2019); Voler Hoffman. (2015). The object to be used in the study, according to Arikuntoro, is that the population is an object that is all used in research. If someone who wants to examine all the characteristics and elements in a research area and that research includes population research.According to Hair et al. (2019) population is an area of generalization in which it consists of characters or qualities that have been determined by researchers to be studied and then drawn conclusions.
Based on the method of collecting data obtained through a questionnaire, the questionnaire items were designed based on the Likert scale with an ordinal measurement scale. Likert scale is a measurement interval scale used to measure attitudes, opinions and perceptions of a person or group of people about social phenomena. Likert scale is used to measure attitudes, opinions, and perceptions of a person or group of people about social phenomena. Researchers have determined specific social phenomena, hereinafter referred to as research variables. On the Likert scale, the variables to be measured are translated into variable indicators. Then the indicator is used as a starting point for compiling instrument items which can be in the form of statements or questions, both favorable (positive) and unfavorable (negative) Pranatawijaya et al. (2019).
Data collection techniques in research with quantitative methods are given to instruments that have been tested for the validity and reliability of each variable to be examined to the sample. Questionnaires were given to border area personnel with different echelon rank stratifications and officers who had been sampled. The quantitative method using a closed questionnaire (closed/structured questionnaire) will be distributed to the sample. Questionnaires are given if they have analyzed previous data on secondary data obtained from previous references/reports. Furthermore, to give a value to the answers given by respondents to the questions asked, a certain value weight is given, Pranatawijaya et al. (2019).
The sample in this study is non-probability sampling is a sampling technique that does not provide equal opportunities or opportunities for each element or member of the population to be selected as a sample. Primary data collection in this study was carried out through a survey process. The survey was conducted using a questionnaire instrument.
Based on the formulas and tables of Krejcie and Morgan with a population of 120 to 130, the minimum number of samples for the population is 92 to 97. The questionnaires were distributed as many as 120 respondents, namely; Director, Head of Bureau, Kabinda, Kabag, Kasubdit at the Logistics Bureau of the State Intelligence Agency. The number of samples in this study that were successfully obtained were 98 respondents, using primary data and direct questionnaire distribution. The population in this study were, Director, Head of Bureau, Kabinda, Head of Sub-Directorate of the Logistics Bureau at the State Intelligence Agency. Methods of collection and determination The sample is used for purpose sampling. The method used with certain criteria is in accordance with the needs in the study Hair et al. (2015); Voler Hoffman. (2015).
4. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This study uses several methods of data collection, namely: questionnaires, interviews and documentation studies. Characteristics data, Director, Head of Bureau, Kabinda, Head of Sub-Directorate, who work in the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency as a Decision Making Officer. The demographic data of the respondents from the questionnaire will be presented in descriptive statistics. The results of the questionnaire data and documentation studies will be tested using PLS-SEM Hair et al (2019).
Test results for descriptive statistics for each indicator were also carried out. All variables will be measured by numbers that have been tested. Each variable will be measured based on its dimensions and all supporting indicators.
Variables measured from Strategic Planning are measured by 2 (two) dimensions of 6 (six) statement indicators. Organizational Culture Variables. Measured by 3 (three) dimensions of 9 (nine) statement indicators. Strategic Change Management Variables. Measured by 4 (four) dimensions of 8 (eight) statement indicators. Organizational Performance variable, measured by 3 (three) dimensions of 9 (nine) statement indicators.
Evaluation of the measurement model or outer model begins by testing the convergent validity (convergent validity) and discriminant validity (discriminant validity). The PLS Algorithm validity measurement model in Figure 1
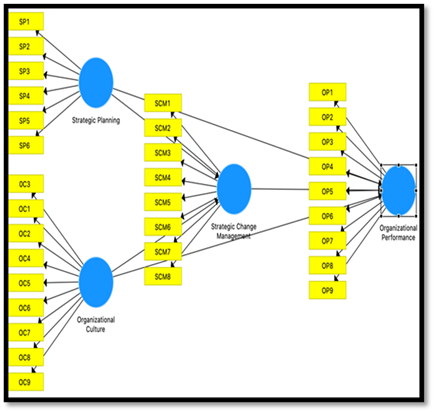
|
Figure 1 PLS
Algorithm Processed Display Source: Processed
data (2022) |
The loading factor value for each indicator from the data processing results must be more than 0.5 and the average extracted variance (AVE) value must be more than 0.5 to assess convergent validity. Measurement model for the validity of Strategic Change Management.
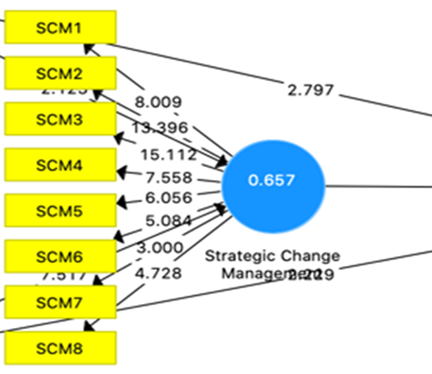
|
Figure 2 Display of the results of the PLS Algorithm Strategic Change
Management Source: Processed
data (2022) |
Evaluation of the structural model starts from the feasibility test of the model by looking at the R-square. The results of the model's feasibility test (Goodness of Fit Model) are shown in Table 1.
|
Table 1 Goodness of Fit Model . Test Results |
||
|
Variabel |
R-Square |
Adjusted Square |
|
Strategic Change
Management |
0.657 |
0.65 |
|
Organizational
Performance |
0.81 |
0.804 |
|
Source: Processed data (2022) |
|
|
Based on Table 1 Strategic Change Management has a mediating model which shows where the adjusted R-Square 0.650 value Strategic Change Management is able to be a link to Organizational Performance. This figure is able to explain the Strategic Planning variable, Organizational Culture is able to explain Strategic Change Management by 65.0%. The R-square value for Strategic Change Management of 0.657 indicates a strong model because it is more than 0.5. Organizational Performance variable can be explained by Strategic Change Management by 65.7%.
The value of effect size f ² for the Strategic Planning variable is 0.435, meaning that the Strategic Planning variable has a strong influence as well and Organizational Culture of 0.349 has a strong influence at the structural level. The strength of the effect size f² which is large can be accepted in studies with small samples, indicating the value of the effect size f² is more than 0.2 which identifies a strong influence at the structural level.
The results of testing the hypothesis of the influence of each variable are as follows:
H1. Strategic Planning has a T-Statistic value of 2.123 > 1.96 and a P-Value of 0.000 < 0.050. This figure shows that Strategic Planning has a significant positive influence on Strategic Change Management.
H2. Organizational Culutre has a T-Statistic value of 7.517 > 1.96 and a P-Value of 0.000 < 0.050. This figure shows that Organizational Performance has a significant positive effect on Strategic Change Management.
H3. Strategic Planning has a T-Statistic value of 2.797 > 1.96 and a P-Value of 0.005 < 0.050. This figure shows that Strategic Planning has a significant positive effect on Organizational Performance.
H4. Organizational Culutre has a T-Statistic value of 2.229 > 1.96 and a P-Value of 0.000 < 0.050. This figure shows that Organizational Culture has a significant positive effect on Organizational Performance.
H5. Strategic Change Management has a T-Statistic value of 5.404 > 1.96 and a P-Value of 0.000 < 0.050. This figure shows that Strategic Change Management has a significant positive effect on Organizational Performance.
H6. Strategic Planning has a T-Statistic value of 2.022 > 1.96 and a P-Value of 0.000 < 0.050. This figure shows that Strategic Planning has a positive effect on Organizational Performance mediated by Strategic Change Management.
H7. Organizational Culture has a T-Statistic value of 4.339 > 1.96 and a P-Value of 0.000 < 0.050. This figure shows that Organizational Culture has a positive effect on Organizational Performance mediated by Strategic Change Management.
5. CONCLUSION
The results of this study provide a conclusion that in general, Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture are variables that affect Strategic Changes Management as a mediating variable. Likewise Strategic Changes Management has a good influence on Organizational Performance, as well as Strategic Changes Management variables as a mediation on Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture variables have a strong influence on Organizational Performance of the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency, this will provide a positive impact on the performance of the Logistics Section for the Management of State Property, the State Intelligence Agency. There needs to be maximum handling if the State Intelligence Agency gets better, especially in improving the quality of Human Resources as well as improving organizational infrastructure, so that in dealing with change, they will be more prepared and keep up with the times and increasingly advanced technology. The conclusions of the variables in this study are as follows:
Strategic Planning has a significant positive effect on Strategic Change Management, the meaning of this positive influence is that the accepted change plan gives a positive reaction to changes in the human resource organization. Al-Dhaafri and Alosani (2020), Increased changes should be made by increasing the dimensions of the organization of resources in the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency.
Organizational Culture has a positive effect on Strategic Change Management. This illustrates that the purpose of organizational culture through human resources is to meet the standards expected for the progress of the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency so that defense is carried out, especially in responding to all organizational changes from related officials. with other resources. Schuldt and Gomes (2020).
Strategic Planning, has a significant positive effect on Organizational Performance, the meaning of this positive influence is that the accepted change plan gives a positive reaction to changes in the organization of human resources. Muthusamy (2019). Increased changes should be made by increasing the dimensions of the organization of resources in the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency.
Organizational Culture has a positive effect on Organizational Performance, this positive effect gives the conclusion that Organizational Culture is able to show a good culture on organizational performance, which is the goal of the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency in producing quality resources, as well as good abilities so that the direction of quality must meet the dimensions that are the reference for the quality of the performance of the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency, this is still the main task if the State Intelligence Agency wants to continue to be a quality organization. Schuldt and Gomes (2020)
Strategic Change Management has a positive effect on Organizational Performance, a significant positive effect on Organizational Performance, this illustrates that organizational and performance changes greatly affect the performance of the Logistics Section of the State-Owned Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency. The maximum policy is the extent to which the benefits of an outcome are felt in accordance with what is expected. So that Strategic Change Management is a strong variable affecting organizational performance, it can be seen from how all parties involved work together to increase the maximum value for the needs and desires of the State Intelligence Agency. Hess and Flatten (2019)
Strategic Planning is influenced by Organizational Performance which is strongly mediated by Strategic Change Management, this shows that with a strong organizational change plan in mediating human resource planning carried out by the State Intelligence Agency, it can increase the influence on performance in the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency. . Good organizational performance will have a maximum impact on the progress of the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency in each section, in taking a policy of readiness for change can create the performance of the State Intelligence Agency. Al-Dhaafri and Alosani (2020)
Organizational Culture, on Organizational Performance which is positively mediated by Strategic Change Management, this shows that this illustrates that organizational culture has a strong influence on organizational performance, then Strategic Change Management as mediation is expected to increase the influence of culture on the performance of the Logistics Section of State Property Management State Intelligence Agency. If changes to organizational culture are able to provide good resource changes, it will also bring good quality to an organization that maximally develops all aspects for the advancement of national defense. Muthusamy (2019); Schuldt and Gomes (2020)
Based on the results of the research conducted, the theoretical implications related to the development of planning theory, change, culture and organizational performance from Strategic Change Management, Strategic Planning Organizational Culture to the State Intelligence Agency are as follows:
Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture The results of this study strengthen the positive and significant influence of Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture on Strategic Change Management and Organizational Performance of the State Intelligence Agency in line with previous research.
Strategic Change Management as mediating for Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture is very strong in improving organizational performance, especially in the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency.
The results of the study conclude that improving Strategic Change Management through increasing its dimensions will be able to improve the performance of the Logistics Section of State Property Management of the State Intelligence Agency, and can increase the trust and loyalty of related parties. Improvement and development of the quality of human resources must first, pay attention to policies and changes. Development and synergy in work will provide a good indication of the performance of the State Intelligence Agency.
REFERENCES
Al-Dhaafri, H., & Alosani, M. (2020). Closing the strategic planning and
implementation gap through excellence in the public sector: empirical
investigation using SEM. Measuring Business Excellence, 24(4),
553–573. https://doi.org/10.1108/MBE-12-2019-0128
Antony, J. P., & Bhattacharyya, S. (2018). Measuring organizational performance and
organizational excellence of SMEs – Part 1: A conceptual framework. Measuring
Business Excellence, 14(2), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1108/13683041011047812
Baird, K., Su, S., & Munir, R. (2019). Levers of control, management innovation and
organisational performance. Pacific Accounting Review, 31(3),
358–375. https://doi.org/10.1108/PAR-03-2018-0027
Barron, K., & Chou, S. Y. (2017). Toward a spirituality mode of firm
sustainability strategic planning processes. Society and Business Review,
12(1), 46–62. https://doi.org/10.1108/sbr-01-2016-0008
Bordum, A. (2020). The strategic balance in a change management
perspective. Society and Business Review, 5(3), 245–258. https://doi.org/10.1108/17465681011079473
Bourland-davis, P. G., Graham, B. L., & Graham, B.
L. (2017). Corporate Social
Responsibility, Sustainability, and Ethical Public Relations. Corporate
Social Responsibility, Sustainability, and Ethical Public Relations. https://doi.org/10.1108/9781787145856
Bryson, J. M. (2015). Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit
Organizations. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral
Sciences: Second Edition. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.74043-8
Chen, M. Y. C., Lam, L. W., & Zhu, J. N. Y. (2020). Should companies invest in human resource
development practices? The role of intellectual capital and organizational
performance improvements. Personnel Review. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-04-2019-0179
Cooper, D. R., & Schindler, P. S. (2014). Business research methods (12th ed.).
McGraw-Hill.https://www.worldcat.org/title/business-research-methods/oclc/821067127
Dlamini, N., Mazenda, A., Masiya, T., & Nhede, N.
T. (2019). Challenges to
strategic planning in public institutions. International Journal of Public
Leadership, 16(1), 109–124. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijpl-10-2019-0062
Esfahani, P., Mosadeghrad, A. M., & Akbarisari,
A. (2018). The success of
strategic planning in health care organizations of Iran. International
Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance, 31(6), 563–574. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHCQA-08-2017-0145
Guiette, A., & Vandenbempt, K. (2018). Dynamic of Change Strategic Environments.
https://doi.org/10.1108/s1744-211720140000007018
Hair, J. F., Celsi, M., Money, A. H., Samouel, P.,
& Page, M. J. (2015). Essentials
of business research methods (3rd ed.). Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9781315704562/essentials-business-research-methods-joseph-hair-jr-mary-wolfinbarger-arthur-money-phillip-samouel-michael-page
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., &
Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to
use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. In European Business Review.
https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-11-2018-0203
Hensmans, M. (2019). The Trojan horse mechanism and reciprocal
sense-giving to urgent strategic change. In Journal of Organizational Change
Management (Vol. 28, Issue 6). https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-06-2015-0084
Hess, J., & Flatten, T. (2019). Strategic Responsiveness and Adaptive
Organizations: New Research Frontiers in International Strategic Management. Strategic
Responsiveness and Adaptive Organizations: New Research Frontiers in
International Strategic Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/9781789730111
Hirst, A. (2019). Journal of Organizational Change Management. Journal
of Organizational Change Management Iss Work Study Property Management, 24(3),
767–788. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/09534811111175742%5Cnhttp://dx.doi.org/10.1108/%5Cnhttp://
Ibrahim, T. M., & Muritala, T. A. (2015). Does Government Policies Improve Business
Performance ? Evidence from Nigeria. Journal of Studies in Social
Sciences, 11(2), 143–159. https://infinitypress.info/index.php/jsss/article/view/1107
Jain, A. K. (2019).
Volunteerism and organisational culture: Relationship to organizational
commitment and citizenship behaviors in India. Cross Cultural Management,
22(1), 116–144. https://doi.org/10.1108/CCM-11-2013-0167
Järvi, K., & Khoreva, V. (2020). The role of talent management in strategic
change. Employee Relations, 42(1), 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-02-2018-0064
Kumar, N., & Sharma, D. D. (2018). The role of organisational culture in the
internationalisation of new ventures. International Marketing Review, 35(5),
806–832. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-09-2014-0299
Lewis, D. (2018). Culture and Organization. In Non-Governmental
Organizations, Management and Development. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203591185-8
Liu, L., Qu, W., & Haman, J. (2018). Product market competition, state-ownership,
corporate governance and firm performance. Asian Review of Accounting, 26(1),
62–83. https://doi.org/10.1108/ARA-05-2017-0080
M. Muzamil Naqshband,
et al. (2020).
Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration Organizational culture profile
of Malaysian high-tech industries Organizational culture profile of Malaysian
high-tech industries. Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration
Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration Iss Journal of Knowledge
Management Iss Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration, 7(1),
34–55. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274074023_Organizational_culture_profile_of_Malaysian_high-tech_industries
Muthusamy, S. K. (2019). Power of positive words: communication, cognition,
and organizational transformation. Journal of Organizational Change
Management, 32(1), 103–122. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-05-2018-0140
Nguyen, V. T., Siengthai, S., Swierczek, F.,
& Bamel, U. K. (2019).
The effects of organizational culture and commitment on employee innovation:
evidence from Vietnam’s IT industry. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 13(4),
719–742. https://doi.org/10.1108/JABS-09-2018-0253
Nuhu, N. A., Baird, K., & Appuhami, R. (2016). The association between the use of
management accounting practices with organizational change and organizational
performance. Advances in Management Accounting, 26, 67–98. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1474-787120150000026003
Oyewobi, L. O., Oke, A. E., Adeneye, T. D., &
Jimoh, R. A. (2019).
Influence of organizational commitment on work–life balance and organizational
performance of female construction professionals. Engineering, Construction
and Architectural Management, 26(10), 2243–2263. https://doi.org/10.1108/ECAM-07-2018-0277
Pranatawijaya, V. H., Widiatry, W., Priskila,
R., & Putra, P. B. A. A. (2019). Penerapan Skala Likert dan Skala Dikotomi Pada Kuesioner Online. Jurnal
Sains Dan Informatika. https://doi.org/10.34128/jsi.v5i2.185
Prof. Dr.Voler Hoffman. (2015). Strategic Management. 0–55.
Quinn, R. E., & Cameron, K. S. (2019). Positive organizational scholarship and
agents of change. Research in Organizational Change and Development, 27,
31–57. https://doi.org/10.1108/S0897-301620190000027004
Radford, G. P., Radford, M. L., Lingel, J., Library,
T., & Foucault, M. (2020).
Relationships between employee commitment and organizational cultures.
Rahi, S. (2017).
Research design and methods: A systematic review of research paradigms,
sampling issues and instruments development. International Journal of
Economics & Management Sciences, 6(2), 1–5. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d957/e1a07a961a572ce70f7d5845cb423ac8f0be.pdf
Ratten, V., & Ferreira, J. (2016). Global talent management and corporate
entrepreneurship strategy. International Business and Management, 32,
151–165. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1876-066X20160000032006
Rebelo, T., & Gomes, A. D. (2019). Is organizational learning culture a good
bet?: An analysis of its impact on organizational profitability and customer
satisfaction. Academia Revista Latinoamericana de Administracion, 30(3),
328–343. https://doi.org/10.1108/ARLA-10-2015-0275
Schuldt, K. S., & Gomes, G. (2020). Influence of organizational culture on the
environments of innovation and organizational performance. Gestao e Producao.
https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-530x4571-20
Shermin, V. (2017). Disrupting governance with blockchains and smart
contracts. Strategic Change. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsc.2150
Sinambela, L. P. (Prof. D. (2019). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia. In PT.Bumi
Aksara.
Sugiyono, A. (2015). Cara Mudah Belajar SPSS & LISREL (A.
Bandung (ed.); First Edit). AlFABETA. http://library.usd.ac.id/web/index.php?pilih=search&p=1&q=0000126375&go=Detail
Tarifa-Fernández, J., de-Burgos-Jimenez, J.,
& Cespedes-Lorente, J. (2019). Absorptive capacity as a confounder of the process of supply chain
integration. Business Process Management Journal, 25(7),
1587–1611. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-12-2017-0340
Tichy, N. (2020). The essentials of strategic change management. Journal
of Business Strategy, 3(4), 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb038990
Vitolla, F., Rubino, M., & Garzoni, A. (2017). The integration of CSR into strategic
management: a dynamic approach based on social management philosophy. Corporate
Governance (Bingley), 17(1), 89–116. https://doi.org/10.1108/CG-03-2016-0064
Wang, T. C., Tang, T. W., & Cheng, J. S. (2018). Art-oriented model of hotel service
innovation. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management,
30(1), 160–177. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-02-2016-0059
Wolf, C., & Floyd, S. W. (2017). Strategic Planning Research: Toward a
Theory-Driven Agenda. Journal of Management. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206313478185
Yi Chia. (2015). The Relationship Between Relational Assets and Competitive
Advantage of Foreign Bank In China’s Industry : From the Pespective Of
Strategic Alliances. In First Edition (pp. 100–109). https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-relationship-between-relational-assets-and-of-Chia/ff4b4634674295ece7d92b25d8fef42cc9280d28
Yunis, M., El-Kassar, A. N., & Tarhini, A. (2017). Impact of ICT-based innovations on
organizational performance: The role of corporate entrepreneurship. Journal
of Enterprise Information Management, 30(1), 122–141. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-01-2016-0040
Zhou, C., Hu, N., Wu, J., & Gu, J. (2018). A new scale to measure cross-organizational cultural intelligence: Initial development and validation. Chinese Management Studies, 12(3), 658–679. https://doi.org/10.1108/CMS-10-2017-0309
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2022. All Rights Reserved.