DEVELOPING A MODEL FOR PROMOTING ASSET BASED COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT (ABCD) IN NIGERIA
Abstract
Asset based community development (ABCD) is a shift and direct contrast to the conversional need-based community development (NBD). It focuses on community asset as useful tool to stir up the development of a community. It is concerned with what is available in the community that could be used to development as against dependence on outsiders or expert for development. The different types of asset in communities were enumerated. The benefits and criticisms against the approach were also highlighted. A model to guide the application of the approach was designed. The paper is of the view that every development intervention in the nation should have its root on asset-based development approach.
Keywords
Model, Community Development, Promoting
INTRODUCTION
Early days of development practice witnessed development interventions that saw the recipients as poor and needy. This concept permeated into almost all forms of development
In the field of Community Development, the case is not different. Hence the United States international co-operation administration of (1956) in (Hanachor, 2013) presented community development as “a method by which national government reaches out to people at the village level and help item use local initiative and resource to achieve increased production and higher standard of living” The picture in the minds of development practitioners during this period is to bring development to the people.
This ideal is the brain behind the top-down development approach which has been criticized for lack of involvement and local content, lack of empowerment and sustainability, which often result to abandonment, of development project or programs.
Another phase in development continuum of our communities is the Need Based Development (NBD). Community development practitioner in this phase lay emphases on the identification of needs of communities and responding to the need will, in their understanding result to development.
This approach, though resourceful, but still does not allow or make room for local initiative. The intervention agencies still take control of the projects or programmes with little or no room for community members to participate.
These and many other reasons led to the evolving of Asset Based Community Development (ABCD). Asset based community development is a shift and direct contrast to the conversional need-based community development (NBD). Instead of looking at the community to see the needs to respond to, it is concerned with what is available in the community that could be used to develop it. An asset is a special kind of resources that an individual, organization or entire community can use to reduce or prevent poverty and in justice. It could be a stock that could be drawn up and build upon. Asset based community development operates with community resources and assets within the community and mobilizes individuals, associations and institutions to come together to reason and develop their potentials.
In asset-based development approach, quality time is spent in identifying the asset of individual, associations and institutions within the community, and work together to build on the identified assets of all that are within. Asset based community development begins with the recognition of all uncovered and recognized assets in the community, thereby creating local economic opportunities. Each community has peculiar skills that can be directed toward community development. Asset based community development approach categorizes asset inventory into five groups or categories: Individuals, Associations, Institutions, Place based and Connections or relationships.
Category A-Individuals: ABCD assumes that everybody in the community has asset and gifts to be recognized and identified.
Category B-Associations: Associations are small informal groups like chub’s or volunteer groups. When people come together, they discover each other’s gift and assets. In asset-based community development associations are useful channels to community mobilization.
Category C-Institutions: Institutions are organized paid professionals’ groups having recognized structure, such as government agency, schools and private businesses. They form resources and asset to the community.
Category D-Place based asset: People decide to be in a place because of what they see or feel about the place. A place is a Centre of natural resources, hence the attraction or choice of a place. Land, buildings heritage and green spaces are assets to community, and could be used to develop the community
Category E-Connection or Relationship: Asset based community development emphasizes on building relationship within community members. When people interact and share ideals, they create connections which are very vital asset to the community. ABCD recognizes the value of this asset as it builds relationships to increase social capital network of the community. Nel (2017) looking at asset based approaches and need based found that asset based approaches tend to build relationship between community members, while need based approaches tend to focus more on the relationship between organizations and community.
POTENCY AND THE BENEFITS OF ASSET BASED COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT
-
The identification of skills gifts resources and knowledge (assets) which exist in the community is the bases of asset-based community development approach. This process eliminates the problem associated with executing projects against the desires of community members.
-
The use of local associations as vehicles through which community assets and skills are identified and matched with little or no support from outside solidifies their power, effectiveness and entitlement as against. the relationship and connection that exist with technical experts in the case of other approaches.
-
The ABCD approach to community development is in line with the principles and practice of participatory approach to development. It solicits for total participation from community members, and emphasizes on the contribution of their talent, resources and skills which are readily available.
-
In asset-based community development, leaders involve others as active members of the community, not just recipients of service which is common in other approaches.
-
Asset based community development assist community members to realize their potentials for above the contributions of outside intervention agents.
-
ABCD approach encourages sustainable community development by building and strengthening the capacity of community members.
-
Asset based community development results to power distribution between the outside expert and community members as against the power and control domination by experts inherent in other approaches. Criticisms against asset-based community development.
Despite the sported advantages of asset-based community development, there are still challenges and criticisms against the practice, the following are some of the agreements against ABCD.
-
Lack of popularity: The approach is yet new in some parts of the globe. A good number of development practitioners are yet to adopt the approach as it seem to go contrary to what they already know. New ideals are not easily accepted without proofs. This forms a challenge and criticism against ABCD.
-
Over reliance on the workability of ABCD has been criticized by many development practitioners. The critics maintain that the approach is naïve, only concentrating on identifying asset in the community and mobilizing resources for community issues without a focus on the problems
-
The ABCD has been criticized for not specifying clearly the power, privilege and influence in community work.
-
Over dependence on local resources is another criticism against ABCD approach. It is believed that the approach do not take advantage of regional and global resources’ available to the community due to its focus on local resources.
This paper is of the view that no one approach to community development will appear to be best. Combination of approaches will yield more positive outcome. Combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches, need based and asset-based community development approach, though in the present realities, the asset based approach should be the bases and the beginning of all community development interventions.
ASSET BASED DEVELOPMENT MODEL
A model is a representation of a physical object, usually in miniature form used to explain the working of a real-world event or system.
Asset based community development model explains the process and relationship between the various stages involved in the development circle.
It begins with goal setting to evaluation.
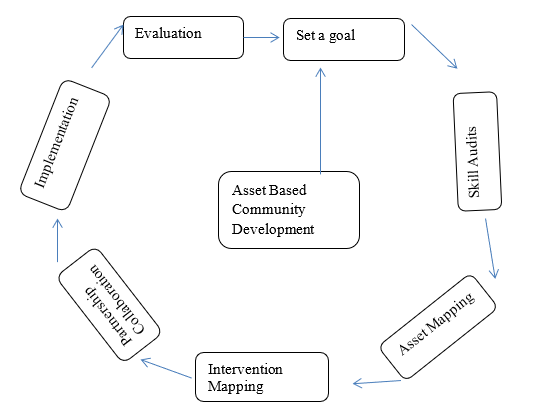
Goal setting: Every development work in the community has a goal to achieve. Development practitioner set goals which become the change target or expectations. Goal setting as a practice is not only common to community developers. Business organization and government agencies set goals. Goals give direction to action. In community development, it is the goals set that will direct the community action in direction to achieve the goals. Goal setting in asset-based development is important because it is the goal that will determine the skill and knowledge that will be required for the execution of the development initiative.
Skill auditing : In asset-based development, after setting of goals the next thing to do is skill auditing. This is the identification of all available skills and resources present in the community. Skill audit could be done either through visual survey or physical assessment.
Asse t mapp ing: Asset mapping is the visual representation of all assets present in a community. Asset mapping is usually drawn to show the different kinds of asset in a geographic location and their relationship. A geographical assets map is presented on colours, codes or icons to represent their location.
Inte rvention ma pping: In asset-based community development (ABCD), organizations are useful asset and channel through which community mobilization is achieved. Intervention mapping in this model is a method of identifying the various activities of organizations and groups in the development of a given community. Intervention mapping is the process of harmonizing the different activities of organizations within the community to avoid duplication and wastage. Intervention mapping is a form of community organization which according to (Hanachor & (, 2019) brings together all development activities of a community, expressing which organizations is carrying out which work in the community. It is a type of activity inventory which helps to prevent clash of interest in community work.
Partnership and collaboration: Asset based community development (ABCD) recognizes the experiences of individuals, groups, communities and organizations within a community. The usefulness of these asset or resources lies in their relationship which propels the transfer of knowledge within the community. According to (Alan, Sillitoe, & &pottier, 2004) , knowledge partnership is the relationship in which individuals, groups and organizations share their knowledge in order to create innovative solutions, brining different kinds of knowledge into dialogue. Knowledge partnering brings together development actors into partnership where they can share what they know and learn from each other. When development actors understand themselves and share knowledge, they prevent development conflicts and clash. This is one of the merits of asset-based community development, since it builds on the relationship with all actors in the development of communities.
Knowledge partnering proposes that development is a social process and that meaningful knowledge sharing is capable of producing new ideas which will result to new resource mobilization for positive change.
Knowledge partnering is based on three care principles: that development is a social process, that everyone knowledge matters, and that bringing different kinds of knowledge together can catalyze new solutions to development issues (Hiruy & Eversole, 2013) . These principles are in line with the focus of Asset based community development model.
Implementation: simply put implementation is the articulation and enforcement of all planned activities towards the direction of the achievement of set goals. In development process, when goals are sets and every machinery is put in place in the direction of the goal or objective implementation is merely the consummation of all planned activities that will bring about the achievement of the goal.
Evaluation: This is the last stage of ABCD model. Evaluation is a fact-finding exercise aimed at verifying the outcome of an event or process
It is an assessment carried out to know if a particular process has been accomplished in line with its intent. In Asset based community development, evaluation is the last in the model circle or chain.
The process is such that the outcome of the evaluation will either be that the expected change is achieved or that new set of goal will emerge following the outcome of the evaluation.
Evaluation result serves as a feedback or guide to development practitioners
CONCLUSION
Social and economic change had dominated the development agenda of development practitioners since the practice began. Community development practitioners in attempt to bring this development agenda or objective to light, had migrated from one method or approach to the other.
The reminiscence of the practice witnessed the transfer of scientific and expert technology to poor communities to help them develop their community, without the involvement and utilization of the value knowledge and ability of the Local people. This approach, otherwise known as top-down development approach faced many criticisms, hence the quest for a better approach.
The discovery of participatory approach appeared to be a way out of the dead luck of top-down development approach. Though this approach recognized the Local people but it still did not give full control of the affairs of the Community development process to the Community members. The practitioners sometimes turn the community member to spectator of the development process. Irrespective of the fact that the involvement of the community member reflects the acceptable bottom-up approach, the community member is still not seen as the owners of development projects in their communities. Following the experiences from these approaches, development practitioner of the twenty first century are realizing that working with community members and mobilizing them for development is opening a new practice. This kind of practice focuses on communities as the basis for the development and actors not spectators.
The asset-based development approach is community central and recognizes all community members, organizations, institutions, groups and assets and builds on their relation and connection for community development processes. Through building relationships, communities are able to again access to resources and energy that might otherwise remain hidden.
ABCD emphasizes on horizontal community engagement and not vertical (Nel 2017), hence it is undoubtedly going to achieve the much need sustainable community development, given that the community members are chief actors of their development.

