|
|
|
|
Article Type: Research Article
Article Citation: Abrahám A. Embí BS MBA. (2020). INTRODUCING CRYSTALLIZATION BACKWARD
SUCTION TRAPPING LIPIDS AND DEBRIS AS PROPOSED ADDITIONAL FACTOR IN THE GENESIS
OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE. International Journal of Research -GRANTHAALAYAH, 8(9),
215-233. https://doi.org/10.29121/granthaalayah.v8.i9.2020.1174
Received Date: 09 September 2020
Accepted Date: 30 September 2020
Keywords:
Atherosclerosis
Coronary Calcification
Intravascular Lipids
Potassium Ferricyanide
Crystallization Nucleation
Dominant Backward Suction
Lipid Molecule Entrapment
Plaque Progression
ABSTRACT
Coronary artery disease progression involves a slow process of abnormal accumulation of lipid deposits to the inner walls of the arteries followed by an immune system response. It is known that an increase in lipid concentration could trigger cholesterol crystals deposition, thus starting a vicious cycle that could also progress into intra-arterial plaque formation, the hallmark of mature atheromas.
The purpose of this manuscript is to introduce a proposed mechanism for the genesis of coronary artery disease; whereby the actual act of lipids crystallization starts a cycle demonstrated to induce additional crystallization via dehydration. Experiments demonstrate for the first time via images and video-recordings showing that when the onset crystallization occurs near the tissue (≅ 1 mm) a dehydration triggered backward hydrodynamic suction or vacuum ensues with enough force to withdraw lipid molecules from human tissue; these molecules are shown to adhere to the crystals.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Absorption: The transfer of the energy of a wave to matter as the wave passes through it.... if all the energy is lost, the medium is said to be opaque, ie: Crystallization.
Anisotropy: The property of substances to exhibit variations in physical properties along different molecular axes. It is seen in crystals, liquid crystals and, less commonly, in liquids. Analogy would be selecting direction of wood grain when cutting.
BEMR: Acronym for Bioelectromagnetic Radiation.
DBS: Acronym for “Dominant Backward Suction”. The most clinically relevant wave to date filling the coronary arteries. It causes a marked increase in coronary flow velocity observed at the start of diastole. Also observed in vitro at onset of crystallization, for details link to: https://youtu.be/IJgoozrRyrk Or scan QR Code

Electromagnetic Radiation: Defined as how matter typically electrons bound in atoms takes up a photon's energy — and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber. Example is the full absorption of electromagnetic radiation as internal energy by K3Fe.
K3Fe: Short version for Potassium Ferricyanide crystals with formula K3Fe (CN)6. CSA # 13746-66-2.
Macrophage: Large phagocytic cell found in stationary form in the tissues or as a mobile white blood cell.
Nucleation: Nucleation, the initial process that occurs in the formation of a crystal from a solution.
SSP: Acronym for Single Slide Preparation, where a plucked in toto (follicle and shaft) human hair is placed on a glass slide and covered by a solution of diluted K3Fe crystals.
PREAMBLE:
The bridging field of Bioelectromagnetic Radiation is herein presented as a tool for the scientific explanation of the genesis of coronary artery disease.
1. INTRODUCTION
Our manuscript introduces via in vitro experiments the presence of a dominant backward suction
(DBS) occurring during the onset of crystallization of Potassium Ferricyanide
(K3Fe) attracting tissue particles from a human hair follicle or miniorgan [1]
on a glass slide covered by K3Fe in solution. This hydrodynamic DBS
phenomenon had also been detected in vivo
and reported to be present at the start of diastole during diastole as
blood flows into the human coronary arteries [2].
The process of intracoronary lipids crystallization occurs in two major steps,
the first is nucleation also defined as the appearance of a crystalline phase
of a supersaturated solvent; the second is known as crystal growth, which is the increase in the size of particles
and leads to a crystal state [3] Images
and video recordings are introduced demonstrating for the first time via
an in vitro simulation of lipids
crystallization. The data shows via images and video-recordings that when the
onset crystallization occurs near tissue (≅ 1 mm) a dehydration
triggered DBS or vacuum ensues with enough hydrodynamic force to withdraw lipid
molecules from human tissue; these molecules are shown to adhere to the crystals.
2.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. MATERIALS
1) Potassium FerrIcyanide
Crystal. K3Fe (CN)6.
CSA
# 13746-66-2.
2) Hair Follicles plucked via tweezers
from author’s scalp
3) Microscope glass slides: 25x75x1mm
thickness. Pearl Cat. No. 7101
4) Water purity confirmed by hand held
electrical fields detector manufactured by Lishtot
Detection LTD, Israel. For details link to: https://www.lishtot.com/TDP1.html
5) Room relative humidity monitored by
an ACU-RITE sensor model # 01536-RX.
6) Digital Video Microscope Celestron II model # 44341, California, USA.
7) Images downloaded to an Apple
Computer MacBook Pro Photo Application.
2.2. METHODS
2.2.1. PREPARING THE SOLUTION
Commercially
available bottled water was tested for impurities via a handheld electrical fields sensor (Lishtot Sensor).
A solution was prepared by diluting ≅ 2 grams of Potassium Ferricyanide (K3Fe) crystals in 2 ml of the previously
tested for impurities bottled spring water. The solution placed inside a 6-inch
4 mm OD glass tube and withdrawn as needed via pipette.
2.2.2. THE SINGLE SIDE PREPARATION (SSP)
The SSP is
an open-air technique where freshly plucked in
toto human hairs were placed on a clean 25x75x1mm glass slide; and covered
by drops of K3Fe in solution; the liquid was then allowed
to evaporate. Prior to evaporation, the drops were gently touched by a wooden
toothpick and dispersed as to cover the follicle and shaft (Fig.1). After the
hair sample stops drifting and stabilizes, a clean wooden toothpick was used to
gently shepherd the hair sample away from the drop edges. As evaporation
starts, images and video recordings are made and stored.

Figure 1: A: Scalp hair on glass slide
covered by drop of (Potassium Ferricyanide) covering mainly the hair follicle. B:
Same hair. Now the K3Fe drop
surface tension disturbed via wooden toothpick now covering follicle and shaft.
3.
RESULTS
Solute crystallization is
mainly classified as homogeneous (Fig 2 + video) or heterogeneous (Fig 3 +
video) [3] care was taken to show in control experiments
the dynamics via video recordings in both types as the Potassium Ferricyanide
or K3Fe solution
crystalizes. An example of K3Fe homogeneous crystallization
is when no foreign particles are present in the liquid, ie:
Ice formation in clouds. In heterogeneous crystallization, impurities such as
dust particles could trigger a regional temporary nucleation process. In
homogeneous situations, unimpeded crystallization occurs.
3.1. THE FULL
ABSORPTION OF BIOELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION (BEMR) BY K3FE
The crystallography paramagnetic anisotropy of
K3Fe was introduced in 1969 [4] and later demonstrated to fully absorb
electromagnetic radiation [5]. Our experiments document the above mentioned
“full electromagnetic absorption” property of K3Fe, this manifested
in crystals deposition in a semicircular pattern. It occurs within the BEMR
reaches of the hair follicle previously determined to be ≅ 3 mm [6] (Fig 4).
As of recent, human blood tissue has been documented to be a BEMR
emitter; and demonstrated to increase K3Fe crystals adhering to a
hair follicle.
3.2. CONTROL
EXPERIMENTS SHOWING TYPES OF K3FE CRYSTALLIZATION
Homogeneous (Fig. 2)

Figure 2:
Example of unimpeded or “homogeneous” crystallization advance of Potassium
Ferricyanide in solution in the absence of an interfering foreign particle or
opposing magnetic field. Black Arrow: Pointing at forward crystals motion. For
additional detail, please link to:
https://youtu.be/frYJfZWajWs
Or scan QR Code in left upper
corner of image.
Heterogeneous (Fig. 3)
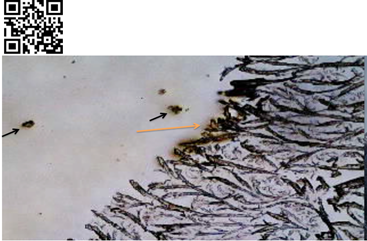
Figure 3:
Example of impeded crystallization advance (heterogeneous). Selected frame
showing foreign unidentified particles triggering crystallization nucleation
and slowing the unimpeded K3Fe crystals
advance. Black Arrows: Foreign particles. Orange Arrow: Nucleation slowing
crystals advance.
For additional details link
to URL https://youtu.be/P7KyQ_5HHOA Or
scan QR Code in left upper corner of image.
3.3. HAIR
FOLLICLES BEMR TRIGGERING DILUTED K3FE NUCLEATION AND CRYSTALLIZATION IN A SEMICIRCULAR PATTERN DELAYING
CRYSTALLIZATION ADVANCE
When the K3Fe is
evaporating and a hair follicle BEMR is detected, nucleation ensues thus
starting an impeded crystallization pattern of crystals formation. This process
slows the crystallization advance (Fig 4 + video). The range of the hair
follicle BEMFs triggering nucleation in K3Fe had been previously determined to be ≅ 3 mm.

Figure 4: Human scalp hair SSP K3Fe showing crystallization
semicircles reflecting human hair bioelectromagnetic waves triggering
nucleation and crystallization.
C:
Heavy crystallization caused by BSW near the follicle, Highlighted
black arrows: Pointing at K3Fe crystals delineating the hair
follicle bioeectromagnetic waves. Red Arrow: (Bottom
right) Pointing at hair follicle magnetic reach as expressed by
crystallization.
For
additional details link to :
https://youtu.be/o1u5mHopdeo
Or
Scan QR Code in right upper corner of figure.
NOTE: In Figure 4 above, the
thicker crystallization highlighted by letter C is due to the Backward Suction
phenomenon attracting tissue particles. This attraction only occurs near the
hair follicle area as shown in (Fig. 5 + video) below.
Example of DBS in Gray Hairs
The example below, clearly
shows a DBS seen during nucleation. This documents the
attraction of two different types of particles from a human miniorgan
(hair follicle), one type was identified via optical microscopy as lipid
molecules; the other theorized to be melanin granules. As a matter of interest
to readers of this manuscript the hair follicle had been found to have “circulatory lipoproteins (LDL and HDL)
present in the capillary loop of the DP (dermal papilla)” [5] or the most distal area of the follicle as
shown in Figure 5 below.
Additionally, hair
follicles are usually covered by sebum, the lipid molecules observed being
withdrawn during crystallization could also be part of secretion from sebaceous
glands. Regardless of the lipid origin a DBS is documented.

Figure 5: Black hair. Selected frame
from video recording showing, F: Follicle. Black Arrows: Crystallization caused
by hair follicle bioelectromagnetic radiation. Highlighted Orange Arrow:
Pointing at lipid particles undergoing backwards motion due to “Backward
Suction” caused by crystallization.
For
details link to URL
https://youtu.be/8jRFBJec06c Or
scan QR Code in left upper corner of image
Recommended to advance video
towards 01:44”
to appreciate stronger suction as crystallization nears follicle.
3.4. DEMONSTRATION OF DBS ATTRACTING LIPID PARTICLES AND UNIDENTIFIED MATERIAL IN GRAY HAIRS
This
is better displayed due to the smaller number of particles attracted in gray
hairs (Figure 6 below).

Figure 6: Gray
hair follicle in K3Fe crystals in solution showing two
distinct particles types. F; Follicle. Black Arrows: Lipid droplets.
Highlighted Orange Arrows: Smaller black particles (possible melanin granules).

Figure 7: Selected
video frame showing granules and lipid droplets attracted by K3Fe
DBS during crystallization. Black Arrow:
Movement direction of lipid droplet. Highlighted Orange Arrows: Movement
direction of unidentified granules.
For additional details link to:
https://youtu.be/f-MGe_mrwr8
Or scan QR Code in left lower
corner of figure.
For specific details move
cursor from 00:50” to 01:06”
stronger
suction as crystallization nears follicle.
3.5. DEMONSTRATION OF DBSW ATTRACTING GREATER NUMBER OF PARTICLES IN BLACK HAIRS

 Figure 8: Black hair follicle showing
increased particles migrating towards the K3Fe crystals. F: Follicle. Black
Arrow: K3Fe crystals. Highlighted Orange Arrow: Pointing at greater number
of particles attracted by DBSW during nucleation.
Figure 8: Black hair follicle showing
increased particles migrating towards the K3Fe crystals. F: Follicle. Black
Arrow: K3Fe crystals. Highlighted Orange Arrow: Pointing at greater number
of particles attracted by DBSW during nucleation.
For
additional details link to URL https://youtu.be/vzbtEukLhBI
Or scan QR Code:
4.
DISCUSSION
The main message herein presented is the introduction of a mechanism
linking a DBS phenomenon during
crystallization attracting particles from human tissue as an additional factor
in intra coronary plaque crystals formation This is supported by similarities in images obtained via
different techniques, such as by optical microscopy from this manuscript as
shown below (Fig 9); and electron microscopy by others as shown in Figure 1
(not shown) in reference [7].
4.1. DEMONSTRATION OF MALLEABLE
LIPID DROPLETS ENTRAPMENT DURING CRYSTALLIZATION.

Figure 9: Black
Hair in SSP K3Fe crystals near follicle. Black Arrow: Left lower
corner. Notice lipid particles trapped by crystals. For additional details,
please link to URL
https://youtu.be/vzbtEukLhBI Or scan QR Code in left upper corner of
image.
4.2. K3FE CRYSTALS IDENTIFIED AS
ANISOTROPIC AND FULLY ABSORBING BIOELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
K3Fe crystals have been identified
as anisotropic and found to fully absorb electromagnetic radiation, such as in
the case of inherent human hair follicle BEMR [8], The first step in crystallization is called
nucleation, the second leads to crystals formation. The emphasis in this
manuscript is placed on the nucleation phase of K3Fe in solution
covering a hair follicle a.k.a. as a miniorgan. The
images obtained show a “back and forth” motion during the water evaporation
(dehydration) leading to the onset of nucleation. Only when nucleation occurred
near the follicle itself (≅ 1 mm) is that a DBS was documented attracting human tissue particles (Fig
10).
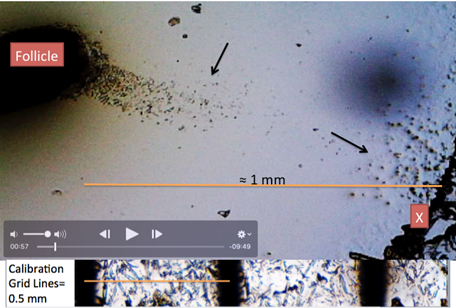
Figure 10: Microphotograph of
video frame at 00:57”. Showing hair follicle in SSP K3Fe. X= K3Fe
nucleation. Black Arrows: Pointing at follicle’s particles attracted by DBS.
Orange Line: Showing approximate distance between follicle and nucleation site.
4.3. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION CAN
BE FULLY ABSORBED USING AN ANISOTROPIC CRYSTAL
K3Fe
crystals have been classified as anisotropic, and as such fully absorbing
incoming electromagnetic radiation. Our experiments show the hair follicle BEMR
triggered K3Fe crystals as result of K3Fe full absorption
of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the hair follicles. This mechanism is
demonstrated in Figures 4,5,6,7,8 and 10 plus video recordings.
5.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
Proposed is a mechanism for
the genesis of coronary artery disease and its progression; involving two
similar tandem events: A primary Dominant Backward Suction (DBS) suctioning
blood tissue and lipids into the coronary arteries during diastole; and a
secondary intra arterial DBS associated with
localized dehydration triggered by the first stage of crystallization or
nucleation attracting and trapping lipids present within ≅ 1 mm of the arterial wall endothelium; this
mechanism is inferred in Figures 9 and 10 plus video-recordings. The lipid
droplets due to their malleability [9] are adhered to the crystals and stay “deformed
but intact”, as if removed from circulation. Supporting the findings is correlation between
hypo hydration and crystallization localized intra-arterial endothelial
function [10], [11]. Additionally, lipids crystals injuring the
inner arterial wall have been proposed to trigger chronic inflammation [12], thus starting a vicious cycle leading towards
coronary artery disease progression
SOURCES OF FUNDING
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author have declared that no competing interests exist.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The author acknowledges the
invaluable guidance from Benjamin Befeler MD in the
drafting of the manuscript.
REFERENCES
[1]
Schneider,
M. R., Schmidt-Ullrich, R., & Paus, R.2009). The hair follicle as a dynamic
miniorgan.
Current biology:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2008.12.005
[2]
Davies,
J. E., Whinnett, Z.
I., Francis, D. P., Manisty, C. H., Aguado-Sierra, J., Willson, K., Foale, R. A., Malik, I. S., Hughes, A. D., Parker, K. H.,
& Mayet, J. (2006). Evidence of a dominant
backward-propagating "suction" wave responsible for diastolic
coronary filling in humans, attenuated in left ventricular hypertrophy.
Circulation, https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.603050
[3]
Nucleation,
Cristallography.The
Editors Encyclopedia Britannica.
[4]
B. N.
Figgis, Malcolm Gerloch,
Ronald Mason, and Ronald Sydney Nyholm the
crystallography and paramagnetic anisotropy of potassium ferricyanide.1969
https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1969.0031
[5]
D. G.
Baranov, J. H. Edgar, Tim Hoffman, Nabil Bassim,
Joshua D. Caldwell. Perfect interferenceless absorption
at infrared frequencies by a van der Waals crystal. DOI:
10.1103/PhysRevB.92.201405
[6]
Abraham
A. Embi
(2018) THE HUMAN HAIR FOLLICLE PULSATING BIOMAGNETIC FIELD REACH AS MEASURED BY
CRYSTALS ACCRETION.” https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1341349.
[7]
Lehti S, Nguyen
SD, Belevich I, Vihinen H, Heikkilä HM, Soliymani R, Käkelä R, Saksi J, Jauhiainen M, Grabowski GA, Kummu
O, Hörkkö S, Baumann M, Lindsberg
PJ, Jokitalo E, Kovanen PT,
Öörni K. Extracellular Lipids Accumulate in Human
Carotid Arteries as Distinct Three-Dimensional Structures and Have
Proinflammatory Properties. (2018). doi:
10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Nov 14. PMID:
29154769.
[8]
Embi AA,
Jacobson JI, Sahoo K, Scherlag BJ (2015)
Demonstration of Inherent Electromagnetic Energy Emanating from Isolated Human
Hairs. Journal of Nature and Science, 1(3): e55.
[9]
Abraham
A. Embi Bs
MBA. (2019). “INTRODUCING IN VITRO EXPERIMENTS OF OXYGEN BUBBLES SHOCKWAVES
TRIGGERING INTRACELLULAR LIPIDS LUMINESCENCE: IMPLICATIONS IN CANCER
ETIOLOGY.” https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2667714.
[11] Giannis Arnaoutis,
Stavros A. Kavouras, Nikolaos Stratakis,
Marita Likka, Asimina Mitrakou,
Christos Papamichael, Labros
S. Sidossis, Kimon
Stamatelopoulos. The effect of hypohydration on endothelial function in young
healthy adults. DOI: 10.1007/s00394-016-1170-8
[12] Grebe, A., & Latz, E. (2013). Cholesterol crystals and
inflammation. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-012-0313-z
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© Granthaalayah 2014-2020. All Rights Reserved.


