|
|
|
|
Article Citation: Chandan R Honavar, Krishna Bhargav K L, and Dr
Theresa Nithila Vincent. (2020). APPLICATION OF FRAMING IN LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION:
A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND RESEARCH AGENDA. International Journal of Engineering
Technologies and Management Research, 7(11), 39-49. https://doi.org/10.29121/ijetmr.v7.i11.2020.817
Published Date: 24 November 2020
Keywords:
Framing
Framing Effect
Framing Theory
Leadership Communication
Application of Framing
ABSTRACT
Under various fields of research, framing is a concept beautifully constructed by the diverse set of theories and notions. Framing is all about how an individual, a group, an organization or the society communicates and perceives a particular issue. Fields such as Media and communication, Health, Politics and law saw the advent of applications of framing. Due to increased burnout among employees and conflicts between leaders and employees, the need and importance of framing have raised in the area of Leadership communication. In any organization, leaders should be aware of the importance of framing for effective communication. This paper reflects the comprehensive review of the 'framing' concept and also the methodological procedures used in empirical studies of framing, leading to a discussion of how framing could be used in Leadership Communication. Researchers and Academicians can use this literature review to develop a model or frame policies to train individuals involved in leadership roles to use framing as a skill.
1. INTRODUCTION
Most successful people in the world
have mastered the art of communication. Human resource is the most valued
resource for an organization, but it is the most difficult to manage and
control. A superior form of communication strategy (Strategic Communication)
must be employed to harness the human mind and direct to elicit the desired action.
In the competitive corporate world, Individuals are ignorant about effective
communication. This article strives to analyze the applications of framing in
various fields and how it can be applied in Leadership communication to achieve
the benefits.Fairhurst

2. FRAMING: DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS
Applications of
framing have occurred in various other fields where communication plays a vital
role such as Marketing, Mass media, Health sector, Finance, Politics and Law.
However, this paper is focussed on five significant areas where framing
influences the way people process information. Framing can be used in forms of
a metaphor, stories with a specific focus, cultural traditions, value judgements
of positive or negative with inherent bias or even by presenting a concept with
contrast
For example, the
perceived gain effect is achieved through the display of nine-ending price in
the market. This led to findings that gain-framed messages are more likely to
increase the purchase likelihood of the product than a loss-framed message
along with a nine-ending price
Table 1: Definitions and Concepts
|
Author(s) |
Definition |
|
|
"To frame is to select some aspects of a perceived reality and make them more salient in a communicating text, in such a way as to promote a particular problem definition, causal interpretation, moral evaluation, and/or treatment recommendation for the item described" |
|
|
"framing is the selection of a restricted number of thematically related attributes for inclusion on the media agenda when a particular object is discussed." |
|
|
"framing incorporates a wider range of factors than priming and agenda-setting, which are both cognitive concepts,'' and that ''frames are tied in with culture as a macro societal structure." |
|
|
“draw attention to certain attributes of the objects of news coverage, as well as to the objects themselves" |
Though framing has a
broader range than just one issue; however, framing studies develop frames
related to a single point. Figurative framing includes metaphor, hyperbole and
irony, which help shape public discourse as they involve prominent conceptual and
linguistic content. Metaphor, hyperbole and irony are focused at societal
issues and then towards the complexity of the mentioned types of figurative
framing
Positive framing
highlights the benefits, while negative framing highlights the risk arising out
of products
Philosophical
arguments in social constructionism over relativism, essentialism, and agency
draw boundaries around that which is open to framing and that which is not.
According to O'Keefe's
• Uncertainty about an 'as if 'world
• Message Design Logics
For the purpose of our research, we have limited the concept of framing to just goal framing rather than agenda-setting, priming or evenprospect theory. From the above review, we can understand that Framing is more to do with how one communicates and how much information is contained in the message conveyed. It is a skill which can be honed just like any other by anyone over time with practice and application.
3. METHODOLOGICAL APPROACH
Literature Reviews primarily throw light on theoretical
concepts, the scope for further research and to present the list of sources
utilized
4. IDENTIFICATION AND SELECTION OF PAPERS TO REVIEW
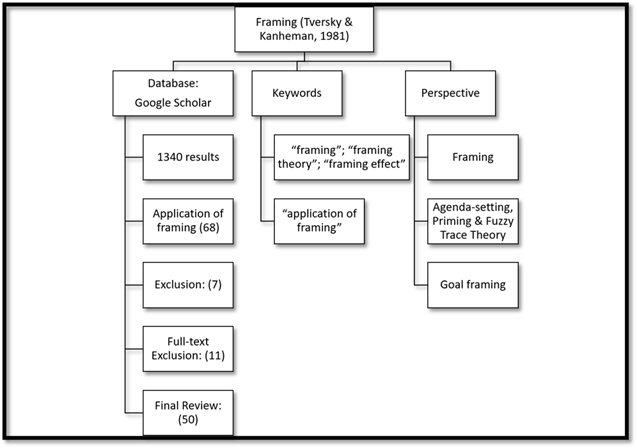
Figure 2: Methodological Approach
Tversky and Kanheman
Table 2: Perspectives on The Application of Framing
|
Category |
Author(s) |
Methodology |
Findings |
|
Health |
Dong Jenn Yang |
Structural Equation Modeling |
(1) Various driving sources, mental processes and excellent communication can be provoked by message framing, which also depends on agency thinking, (2) To promote the stoppage of smoking, a positively-framed message is tested to be effective. |
|
Health |
Adam D Koon, Benjamin Hawkins and Susannah H Mayhew |
Arksey and O'Malley framework for Scoping Review |
Not many studies are explicitly conducted on heath policy framing. Most of the studies commonly pointe out "constructivist epistemology". Homelessness, Injection drug use, assisted reproductive technologies may be reframed as "health issues". |
|
Health |
Chia-Yen Lin and Wei-Ju Yeh |
Two Factor Multivariate Analysis to test Hypotheses |
Regulatory Focus and Message framing were converged to identify attitude to health advertisements and behavioural intentions towards healthy eating. The direct publication is possible to persuade consumers to change their behaviour when message framing matches the regulatory focus of the recipient. |
|
Health |
Kang Li and Nora Rifon |
Structural Equation Modeling |
Message Framing: Loss vs Gain and Referencing Points (Self-other referencing and Other referencing experiment was conducted to find that Self-other referencing led to higher possibility in intentions of bystander intervention than a message with other referencing, Self-other referencing leads to students having more involvement with advertisements than public service announcements and Gender was a significant factor leading to engagement with ads. |
|
Marketing |
Punam Anand Keller, Isaac M. Lipkus and Barbara K. Rimer |
MANOVA |
Participants convinced to have a positive mood believe more in loss-framed messages, whereas the participants with a negative attitude are prompted with the gain-framed words. |
|
Marketing |
Ma. Criselda M. Tengco-Pacquing, Racquel N. Bustamante, Andrea Patricia E. Cabanban, Mary Bernadette M. Cesare Vince Andre Christopher C. Gamez |
Positive Framing Effect Survey |
A noteworthy distinction in the kind of positive framing effect states that Filipino millennials like decisive goal framing better. Themes identified frugality and instant gratification explain why positive goal framing is preferred while product truth and rationality states otherwise. |
|
Marketing |
Irwin P. Levin and Gary J. Gaeth |
ANOVA |
(1) The scope which differentiates the "label-only" condition of the 1987 Levin study and the "taste plus labelling" of the present-day research, (2) The scope which defines the difference between the "taste after labelling" and "taste before labelling" circumstances of the present-day study |
|
Marketing |
Stefan F. Bernritter, Iris van Ooijen and Barbara C.N. Müller |
Fourth-spread outlier test, Moderation Analysis |
Compared to direct persuasion, self-persuasion attempts will increase consumers' (customers with greater involvement) abundance. |
|
Mass Media |
Terence A. Shimp, Joel E. Urbany and Sarah E. Camlin |
Content Analysis based on Hypotheses tests |
The major part of the findings of this paper has implications on the research started by Edell and Staelin and Nelson's "Theory of advertising and information". In this paper, Magazine advertisements were studied for their structural characteristics being framed or unframed; the content available was analyzed by segregating them into characterized and non-characterized material. At the same time, the products advertised were differentiated based on search and experience goods. Findings suggest that most advertisements in magazines are framed and characterized. However, when the marked content is for experience goods, unframed ads are best suited. |
|
Mass Media |
Thomas E. Powell, Hajo G. Boomgaarden, Knut De Swert & Claes H. de Vreese |
Experiments using Cognition and Affect Scales |
Two separate political issues were tested using experiments, and the result stated that automatic and controlled processing favours the effects of visual and text media. While manipulations made in the experiments showed similar results, individual data gave a distinct result than expected out of multimodal effects. |
|
Mass Media |
BERTRAM SCHEUFELE |
Content Analysis with a specific focus on Definitions and Methods |
Field studies depend on the summation of data available, and Experiments make use of real impetus which is affected by other attributes, Researchers focussing on "agenda-setting" approach depict that they affect the victims aggressively; however, the issue being studied is essential. "Media-framing" first persuades the cognitions and later the behaviour of the recipients. |
|
Mass Media |
Vanessa G. Perry, Carol M. Motley and Robert L. Adams, Jr. |
Content Analysis |
(1) Actual content present in the message strategy and framing ads for lenders, like pricing or loan terms are comparatively rare, (2) Also, significant differences between informational and transformational themes are seen. |
|
Politics and Law |
Sophie Lechler, Andreas R. T. Schuck, Claes H. de Vreese |
Preacher and Hayes' INDIRECT Macro |
Effect on the opinion of the students was measured using enthusiasm, fear, contentment and anger as mediating variables. When the variables are not controlled, the result is higher than when directly, the opinion is measured without mediating variables. |
|
Leadership |
Sandra Honig-Haftel |
Narrative Review |
Framing increases the chances of achievement of purposive communication. Managers should develop sensitivity to the context as the interpretation of context occurs at a subconscious level. |
|
Leadership |
Amber L. Suthers |
Survey |
Officer responsible for communication within the hospitals stated that a plan is always in action. 93.8% of the employees mentioned that the internal communication system is key to timely notification about the hospital changes and the notice of hospital changes to all the employees. However, feedback systems in action were ineffective. More barriers to communication exist in urban hospitals. There is a link between employee stress and poor communication. |
|
Leadership |
Slaheddine Mnasri |
Theses |
Usually, the differences between words said, and they understood to go hand in hand with the failed framing attempts. |
|
Leadership |
Jolanta Aritz |
|
Discourse is crucial to communication as an expression of one's thoughts is limited by the social constructs/groups. Mental Models, however, can be developed with experience. |
|
Leadership |
Gail T. Fairhurst |
|
(1) Arguments in social constructionism over essentialism, agency and relativism are open for framing, (2) Managers use that logics to deliver and receive messages will impact framing ability, (3) Framing is a teachable skill |
5. DISCUSSION
One common and crucial
influencing tool which affects the consumer behaviour is 'Self persuasion'
which increases the tipping behaviour towards the arguments the consumer makes.
Provided with anti-smoking arguments, the consumer starts defending his/her
behaviour towards the act of smoking. Self-persuasion is better than planned
injunctive norms that are not more subjective to behaviour
For the enhancement
of consumer health, quite interesting marketing strategies have to be adopted.
By combining framed messages and regulatory focus, healthy advertisements can
be manipulated. Anticipating the viewer focus was not necessary and the
advertisements become effective when the message attracts the focus of the
audience. Direct advertisement is feasible for health-advocating messages
without the need to prompt viewers for the adoption of a specific focus
While framing the
information, it can be done in two ways. First, individual consumer's
experience is measured by alternately labelling the product (positive or
negatively attributing) after the consumers consume the product. Second, by
reducing the effect of framing or labelling when consumers get to check the
sample as compared to when they did not. At this point, the combined source of
information causes the effect of framing to decrease gradually
Along with positive
Communication (framing) agency thinking, appraisal efficacy and pathway
thinking help achieve this anti-smoking campaign
The respondents in the study felt that
internal communication is very much necessary and crucial for any medical
institution. Effective communication is a must, which enhances the internal
(organization and employee) relationship also. Feedback is a form of
communication that works well with any organization, as it is one of the best
practices to date
Leadership is not everybody's cup of tea, whereas some
embrace it as a skill. This is derived from the philosophical thoughts that
framing is drawn as a boundary here. This is the first argument, the second one
speaks about the manager's ability to frame the logics to frame, produce and
positively receive the messages. Expressiveusers speak their mind and are
indifferent towards framing skills. Conventional users perceive communication
as a challenge; therefore, framing is used to depict the context. Rhetorical
users are the most skilled framers because they see communication as the
construction and negotiation of social selves and situations. The third
argument is whether framing is a teachable skill or not. However, the result
was affirmative
6. FRAMING IN LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION
In an interview in
2015, Warren Buffet said, "A relatively modest improvement can make a
major difference in your future earning power, as well as in many other aspects
of your life". Effective communication can increase one's worth by 50% as
others must follow one's ideas or build on those ideas, especially in the case
of a management leader
Employers, Leaders,
Senior Executives, and Managers are people who engage in purposive
communication and act as the agents of the organization. Managers are expected
to motivate people towards achieving a common goal, more so an organizational
goal. Communication skills set an effective manager apart from the other
managers. The capability to frame the message in a way to give context
effectively is most critical
To train themselves
in such a task, Fairhurst
The five primary
functions of management have been: Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing,
and Controlling
7. CONCLUSION
We reviewed many articles and are aware of the fact that we
may have missed some articles. The focus of this paper was throwing light into
framing and how it can be a part of leadership training with regards to
leadership communication. There is a shift in focus from traditional functions
of a business process to applying many methodologies in each of the functions
like HR, finance, manufacturing and even implementations of ERP system
Under all the studies conducted with framing as the concept, we observed that each article first defines the concept for their research purpose. So, researchers in the field of communication can research for a standardized definition for framing as there is no standard meaning for this concept. Most studies conducted are either review papers or empirical studies, so framing can be studied with a broader perspective to apply in other functions of business processes concerning the study of social sciences. In totality, ethical framing without the indulgence in manipulative framing can arm the leaders with the greatest weapons of the 21st century in a dynamic organizational culture in a changing environment.
SOURCES OF FUNDING
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author have declared that no competing interests exist.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
None.
REFERENCES
[1]
Arowolo,
O. (2017). Understanding Framing Theory. ResearchGate.
[2]
Benjamin
A. Toll, P. S. (2008). Message framing for smoking cessation: The interaction
of risk perceptions and gender. Nicotine & Tobacco Research.
[3]
Burgers,
C., Konijn, E. A., & Steen, G. (2016). Figurative Framing: Shaping Public
Discourse Through Metaphor, Hyperbole, and Irony. Communication Theory,
410-430.
[4]
Carucci,
R. (2018). When Companies Should Invest in Training Their Employees — and When
They Shouldn’t. Harvard Business Review.
[5]
Casanova,
Dider; et al. (2019, August). Agile in enterprise resource planning: A myth no
more. Retrieved from McKinsey:
https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/agile-in-enterprise-resource-planning-a-myth-no-more#
[6]
Choi,
J., Lee, K., & Ji, Y.-Y. (2012). What type of framing message is more
appropriate with nine-ending pricing? Marketing Letters.
[7]
Conger,
J. A. (1998). The Necessary Art of Persuasion. Harvard Business Review.
[8]
Edson
Pinheiro de Lima, S. E. (2008). Framing Operations and Performance Strategic
Management System Design Process. Brazilian Journal of Operations &
Production Management.
[9]
Elkins,
K. (2019, August 30th). Warren Buffett: Developing this skill can make ‘a major
difference in your future earning power’.
[10] Entman, R. M. (1993). Framing: Toward
Clarification of a Fractured Paradigm. Journal of Communication.
[11] Fairhurst, G. T. (2005). Reframing the Art of
Framing: Problems and Prospects for Leadership. 21.
[12] Fairhurst, G. T. (2011). The Power of
Framing: Creating the Language of Leadership. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
[13] Fayol, H. (1916). Administration Industrielle
et Generale.
[14] Gaeth, I. P. (1998). How Consumers are
Affected by the Framing of Attribute Information Before and After Consuming the
Product. Journal of Consumer Research, 6.
[15] Gorp, B. V. (2007). The Constructionist
Approach to Framing: Bringing Culture Back In. Journal of Communication.
[16] Harrell, E. (2019, November-December).
Persuasion – and Resistance. Influence.
[17] Honig-Haftel, S. (1996). The Art of Framing:
Managing the Language of Leadership. Academy of Management.
[18] HRZone. (n.d.). What is Learning and
Development? Retrieved from HRZone:
https://www.hrzone.com/hr-glossary/what-is-learning-and-development
[19] Kahneman, D., & Frederick, S. (2002).
Representativeness revisited: Attribute substitution in intuitive judgment.
Heuristics and Biases: The Psychology of Intuitive Judgment. Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press., 49-81.
[20] Koon, A. D., Hawkins, B., & Mayhew, S. H.
(2015). Framing and the health policy process: a scoping review. Health Policy
and Planning, 16.
[21] Li, K., & Rifon, N. (2017). The Effects
of Message Framing and Reference Points of Public Service Announcements on
Bystander Intervention in College Students’ Binge-Drinking. Advances in
Advertising Research (Vol. VII), 215-229.
[22] Ma. Criselda M. Tengco-Pacquing, R. N.
(2019). Positive Framing Effect: A Mixed Method Study on the Buying Behavior of
Filipino Millennials. North American Journal of Psychology, 15.
[23] McCombs, M. (1997). Building Consensus: The
News Media’s Agenda-Setting Roles. Political Communication.
[24] Mnasri, S. (2008, June 05). Framing in
Leadership Communication: Strategies, Breakdowns and Outcomes. Framing in
Leadership Communication: Strategies, Breakdowns and Outcomes. South Florida,
Florida.
[25] O'Keefe, B. J. (1998). The logic of message
design: Individual differences in reasoning about communication. Communication
Monographs, 80-103.
[26] Pistrui, J., & Dimov, D. (2018). The Role
of a manager has to change in 5 key ways. Harvard Business Review.
[27] Punam Anand Keller, I. M. (2003). Affect,
Framing, and Persuasion. Journal of Marketing Research, 10.
[28] Punam Anand Keller, I. M. (2003). Affect,
Framing, and Persuasion. Journal of Marketing Research.
[29] Raffoni, M. (2009). How to Frame Your
Messages for Maximum Impact. Harvard Business Review.
[30] Ramsay, K., & Cask, J. (2018, March).
Influence: Communication Skills for Management & Leadership.
[31] Rowley, J., & Slack, F. (2004).
Conducting a literature review. Management Research News.
[32] Shimp, T. A., Urbany, J. E., & Camlin, S.
E. (2013). The Use of Framing and Characterization for Magazine Advertising of
Mass-Marketed Products. Journal of Advertising, 23-30.
[33] Sophie Lecheler, A. R. (2013). Dealing with
feelings: Positive and negative discrete emotions as mediators of news framing
effects. 20.
[34] StefanF. Bernritter, I. a. (2017).
Self-persuasion as marketing technique: the role of consumers’ involvement.
European Journal of Marketing, 15.
[35] Suthers, A. L. (2017). Evaluating Effective
Communication Methods: Improving Internal Communication. Evaluating Effective
Communication Methods: Improving Internal Communication. East Tennessee State
University.
[36] Terence A. Shimp, J. E. (1998). The Use of
Framing and Characterization for Magazine Advertising of Mass-Marketed
Products. Journal of Advertising, 07.
[37] Theory, M. C. (2011). Framing Theory.
Retrieved from Mass Communication Theory:
https://masscommtheory.com/theory-overviews/framing-theory/
[38] Thomas E. Powell, H. G. (2018). Framing fast
and slow: a dual processing account of multimodal framing effects. Media Psychology.
[39] Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1981). The
framing of decisions and the psychology of choice. Science Vol. 211, 453-458.
[40] Vanessa G. Perry, C. M. (2016). What’s the
Point(s)? Information Content and Messaging Strategies in Mortgage Loan
Advertisements. US Department of Housing and Urban Development, 21.
[41] Yang, D. J. (2018). Exploring the
communication effects of message framing of smoking cessation advertising on
smokers’ mental processes. International Review on Public and Nonprofit
Marketing, 18.
[42] Yeh, C.-Y. L.-J. (2017). How Does
Health-Related Advertising with a Regulatory Focus and Goal Framing Affect Attitudes
toward Ads and Healthy Behavior Intentions? International Journal of
Environmental Research and Public Health, 14.
[43] Younger, J. (2016). How learning and
development are becoming more agile. Harvard Business Review.
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© IJETMR 2014-2020. All Rights Reserved.


