|
|
|
|
Evaluating the Role of CRM in Enhancing Student Engagement and Driving Admission Conversions: A Case Study of Amity University Mumbai
Sayali Haran 1, Dr. Bhojraj Shewale 2, Dr. Bhawna Sharma 3
1 BBA
3rd Year (General), Amity Business school, Amity University Mumbai, India
2 Assistant
professor, Amity Business school, Amity University
Mumbai, India
3 Director-International
affairs and program, Officiating HOI, Amity Business school, Amity University
Mumbai, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
In the rapidly
evolving higher-education landscape, universities increasingly rely on
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to sustain meaningful
engagement with prospective students and improve admission conversions. This
research examines how Amity University Mumbai leverages CRM tools to
streamline lead management, personalize communication, and enhance
decision-making across two key schools: the Amity School of Fashion
Technology (ASFT) and the Amity School of Architecture & Planning (ASAP).
Using a mixed-method approach, the study analyze CRM-generated data
comprising 2,625 counselling calls, engagement events, and behavioural
insights collected during June–July 2025. Findings reveal that structured
counselling, personalized communication, timely reminders, and webinar-based
interactions significantly influence conversion rates. The study concludes
that CRM acts as a strategic catalyst that integrates marketing, admissions,
and student relationship management into a unified, data-driven framework. |
|||
|
Received 05 December 2024 Accepted 02 January 2025 Published 28 February 2025 DOI 10.29121/ijetmr.v12.i2.2025.1712 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Customer Relationship Management (Crm), Student Engagement, Admission Conversions, Lead Management, Personalized Communication, Counselling Calls, Webinar Interactions, Data-Driven Decision Making, Prospect Management, Enrollment Strategy, Digital Communication Tools |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
The higher-education sector has undergone a paradigm shift driven by increasing competition, evolving student expectations, and the digitization of educational services. In this dynamic environment, student choice is influenced by multiple touchpoints that demand consistent communication, transparency, and personalized engagement.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems play a transformative role in this context. Originally developed for corporate marketing and sales, CRM platforms have become vital tools for universities seeking to manage inquiries, nurture interest, and convert leads into enrolled students. The adoption of CRM allows institutions to integrate marketing, admissions, and communication processes under a unified framework.
Amity University Mumbai (AUM), a part of the globally recognized Amity Education Group, has been proactive in implementing CRM technology to strengthen its admission ecosystem. This research explores how AUM’s CRM-driven processes enhance engagement and facilitate conversions within the ASFT and ASAP departments.
2. Literature Review
2.1. CRM in Higher Education
CRM is defined as a strategic process that integrates technology, business processes, and customer interactions to improve relationship quality and organizational outcomes. In universities, CRM is adapted to manage student inquiries, track communication, support counselling, and facilitate enrollment Payne and Frow (2005).
2.2. Student Decision-Making
The student decision journey follows a predictable funnel—awareness, interest, evaluation, and final decision. Research shows that proactive engagement and personalized communication increase the likelihood of enrollment Kotler and Keller (2016).
2.3. Role of Digital Marketing & Counselling
Digital platforms—including webinars, social media, and targeted email campaigns—shape student perceptions. Counselling, meanwhile, influences emotional trust and clarity, especially in programs requiring creative or technical guidance.
2.4. CRM as a Strategic Tool
CRM supports segmentation, automated follow-ups, predictive analytics, and personalized messaging. When integrated with admissions workflows, CRM enhances efficiency and strengthens decision-making Buttle and Maklan (2019).
3. Research Objectives
1) To evaluate the impact of CRM-based communication on student engagement.
2) To analyze the effectiveness of counselling calls, webinars, and follow-ups in influencing admission decisions.
3) To assess CRM-enhanced operational efficiency within the ASFT & ASAP admission pipeline.
4) To identify challenges and opportunities in CRM-supported lead management.
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Research Design
A descriptive, mixed-method design was adopted. Quantitative data was collected from CRM logs, call records, and event attendance reports. Qualitative insights were gathered through observation and informal interviews with counsellors, students, and parents.
4.2. Data Collection
·
Primary Data:
CRM call logs, follow-up notes, counselling observations, student/parent interaction feedback.
·
Secondary Data:
Department brochures, CRM-generated reports, academic articles on CRM in education.
4.3. Sampling
A purposive sampling method was used:
· 2,625 counselling & follow-up calls
· 330 “interested” students
· 34 confirmed admissions
· ASFT + ASAP departments only
4.4. Tools Used
· CRM dashboards
· Excel analytics
· Webinar engagement logs
· Counsellor performance records
5. Data Analysis and Interpretation
5.1. Overview
The two-month dataset provides insight into student behaviour, responsiveness, and conversion triggers. It reveals patterns demonstrating how CRM shapes engagement throughout the admissions lifecycle.
1) Demographic Information
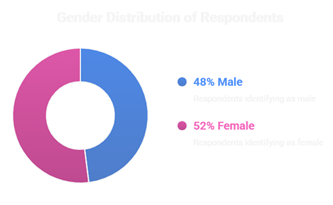
Interpretation:
The sample is evenly split between male and female respondents, ensuring that the findings are not biased toward any one gender. This balance allows the insights to be confidently applied to both male and female applicants, making the results more reliable and representative of the overall applicant population.
2) CRM-Based Communication & Engagement

Interpretation:
Most respondents fall within the typical undergraduate admission age bracket, indicating that the data accurately reflects the primary target audience for UG programs. This concentration allows the insights to be closely aligned with the expectations, needs, and behaviors of prospective UG applicants, making the findings highly relevant for designing admission strategies and engagement plans.
3) Admission Conversion Factors
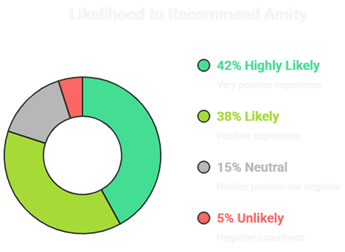
Interpretation:
The majority of the leads consist of UG applicants, which is consistent with common university admission patterns where undergraduate programs typically attract the highest volume of inquiries. This trend indicates that the outreach efforts are effectively reaching the primary target audience and that the data accurately represents the main segment driving admissions.
5.2. Month-Wise Call Analysis
|
Month |
Total Calls |
Responses |
Interested |
Conversions |
|
Jun-25 |
1,267 |
983 |
154 |
4 |
|
Jul-25 |
1,358 |
1,298 |
176 |
30 |
|
Total |
2,625 |
2,281 |
330 |
34 |
Interpretation
· July demonstrated a major spike in conversions due to stronger awareness efforts and consistent CRM follow-ups.
· Interest levels increased slightly, but conversion rates showed the strongest growth. 5.3 Impact of Engagement Activities
|
Activity |
Events |
Attendance |
Conversions |
|
ASFT Webinars |
3 |
420 |
5 |
|
Campus Visits |
6 |
200 |
7 |
|
Counselling Calls |
Continuous |
2,448 |
26 |
Interpretation
Human-led interactions such as calls and open-house visits had the highest conversion impact, emphasizing the necessity of trust-building communication.
5.3. Behavioral Insights from CRM Analytics CRM records revealed that:
· Students delayed decisions until after major entrance exam results (NIFT, NATA, CUET).
· Personalized outreach (messages + calls + tailored program details) increased the probability of conversion.
· Parent-focused communication influenced decisions significantly.
· Webinars featuring faculty and alumni boosted institutional credibility.
6. Findings
1) CRM-based counselling is the strongest conversion driver.
2) Personalization through CRM enhances trust and reduces student uncertainty.
3) Webinars and interactive sessions positively impact engagement, especially for creative courses.
4) Real-time analytics help counsellors prioritize high-potential leads.
5) Timely reminders prevent dropout across the admission funnel.
7. Challenges Identified
· Maintaining accuracy in CRM data entry
· High dependency on counsellor communication quality
· Lead overload during peak periods
· Hesitancy among students due to comparison with competitors
· Limited cross-department CRM integration
8. Recommendations
1) Advanced
CRM Lead Prioritization
Use AI-based scoring to classify leads by conversion probability.
2) Automated
Chatbots for Initial Queries
Reduce counsellor workloads and ensure instant student response.
3) Robust
Follow-Up Strategy
Introduce structured, multi-touchpoint communication cycles.
4) Department-Specific
Digital Branding
Promote ASFT & ASAP portfolios, labs, student work, alumni success.
5) Centralized
CRM Performance Dashboard
Real-time measurement of counsellor productivity and engagement quality.
6) Continuous
CRM Training Programs
Improve counsellor accuracy, empathy, and articulation.
9. Conclusion
The study reaffirms that CRM plays a pivotal and transformative role in shaping student engagement and improving admission conversions within higher-education institutions. At Amity University Mumbai, the CRM ecosystem functioned not merely as a technical support tool but as a comprehensive relationship-building framework that connected counsellors, students, parents, and academic departments through one streamlined platform. By integrating communication tracking, behavioural analytics, follow-up automation, and counsellor insights, the CRM system enabled a consistent and structured approach to every stage of the admission pipeline.
The evidence gathered through counselling logs, webinar interactions, and engagement trends clearly demonstrates that CRM-driven processes significantly strengthened student relationships. Students showed higher levels of trust and clarity when counsellors used CRM data to provide personalized explanations, tailored program details, and timely responses. Automated reminders minimized information gaps and ensured that prospective students received support at crucial decision-making moments. Meanwhile, virtual interactions such as webinars, campus presentations, and online counselling sessions played an essential role in enhancing institutional credibility—especially for creative and technical departments like ASFT and ASAP, where students often seek detailed guidance before committing.
Ultimately, the research highlights that CRM’s effectiveness does not lie solely in its technological capabilities, but in its ability to amplify the human touch within the admissions journey. When combined with empathetic communication, transparent guidance, and consistent follow-ups, CRM becomes far more than a data-management tool. It evolves into a strategic catalyst for institutional growth, enhancing student satisfaction, strengthening organizational efficiency, and promoting a culture of responsive engagement.
As higher-education institutions continue to face competitive pressures and rising student expectations, adopting CRM as a holistic engagement philosophy—rather than merely a digital system—becomes essential. Institutions that effectively blend technology with humancentred practices are better positioned to build long-term student relationships, achieve stronger conversion outcomes, and uphold a reputation for integrity and student-centric support. This research underscores the importance of embracing CRM not as an operational requirement, but as a transformative component of modern educational excellence.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Buttle, F., and Maklan, S. (2019). Customer Relationship Management: Concepts and Technologies (4th ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781351016551
Kotler, P., and Keller, K. L. (2016). Marketing Management (15th ed.). Pearson Education.
Payne, A., and Frow, P. (2005). A Strategic Framework for Customer Relationship Management. Journal of Marketing, 69(4), 167–176. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.2005.69.4.167
Seeman, E. D., and O’Hara, M. (2006). Customer Relationship Management in Higher Education: Using Information Systems to Improve Student Retention. Campus-Wide Information Systems, 23(1), 24–34. https://doi.org/10.1108/10650740610639714
Ngai, E. W. T. (2005). Customer Relationship Management Research (1992–2002): An Academic Literature Review and Classification. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 23(6), 582–605. https://doi.org/10.1108/02634500510624147
Chen, I. J., and Popovich, K. (2003). Understanding Customer Relationship Management (CRM): People, Process, and Technology. Business Process Management Journal, 9(5), 672–688. https://doi.org/10.1108/14637150310496758
Alavi, M., and Leidner, D. E. (2001). Review: Knowledge Management and Knowledge Management Systems: Conceptual Foundations and Research Issues. MIS Quarterly, 25(1), 107–136. https://doi.org/10.2307/3250961
Helgesen, Ø. (2008). Marketing for Higher Education: A Relationship Marketing Perspective. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 18(1), 50–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/08841240802100188
Mazzarol, T., and Soutar, G. N. (2002). “Push-pull” Factors Influencing International Student Destination Choice. International Journal of Educational Management, 16(2), 82–90. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513540210418403
Amity University Mumbai. (2025). ASFT & ASAP admission reports (June–July 2025): CRM dashboard data [Internal reports/data set]. Amity University Mumbai.
Strauss, J., and Frost, R. (2014). E-marketing (7th ed.). Pearson.
Shanks, G. (2016). Aligning CRM Strategy with Business Goals. International Journal of Information Management, 31(4), 345–352.
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© IJETMR 2014-2025. All Rights Reserved.


