|
|
|
|
E-Commerce and the Evolution of Last-Mile Delivery: Meeting Customer Expectations
Dr. Prakash Divakaran
1![]() , Dr. Vandana Mishra Chaturvedi 2
, Dr. Vandana Mishra Chaturvedi 2![]()
1 Pro-Vice
Chancelor & Professor, Department of Business Administration, Himalayan University,
Itanagar, Arunachal Pradesh, India
2 Vice-Chancellor,
D Y Patil Deemed to be University, Sector -7, Vidya Nagar, Nerul, Navi
Mumbai-400706, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
E-commerce has
transformed retail, offering customers ease and accessibility like never
before. However, the last-mile delivery, the product's last leg from the
distribution center to the customer's doorstep, has become a major hurdle for
e-commerce enterprises. This abstract examines how e-commerce businesses are
adapting to shifting consumer expectations in last-mile delivery. The
abstract opens with e-commerce's fast expansion and influence on conventional
retail methods. It underlines the trend toward online buying, which increases
demand for efficient and rapid delivery services. The abstract then discusses
last-mile delivery and consumer satisfaction. Delivery speed, adaptability,
openness, and sustainability affect client expectations. The abstract also
discusses last-mile delivery improvements. Drones, autonomous trucks, and
smart lockers improve delivery efficiency and convenience. Crowd shipping,
which uses local resources to improve last-mile operations, is also examined.
The abstract highlights e-commerce enterprises' last-mile delivery issues. It
covers urban congestion, unsuccessful deliveries, refunds, and transportation
environmental effect. To satisfy client expectations, sustainable and
eco-friendly delivery options are needed. Finally, the abstract emphasizes
customer-centric last-mile delivery. Real-time monitoring, proactive
communication, and customizable delivery choices improve customer experience.
To maximize last-mile operations, e-commerce enterprises, logistics
providers, and local stakeholders should collaborate. This abstract illuminates e-commerce last-mile delivery. It emphasizes
the necessity of satisfying consumer expectations in this key phase of the
delivery process and gives insights into the methods and technologies used by
e-commerce enterprises to improve last-mile delivery and
customer happiness. |
|||
|
Received 03 November 2023 Accepted 04 December 2023 Published 19 December 2023 Corresponding Author Dr.
Prakash Divakaran, prakash@himalayanuniversity.com
DOI 10.29121/ijetmr.v10.i12.2023.1642 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2023 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Last-Mile
Delivery, Technological, Digital Security and Privacy, Digital Environment,
E-Commerce, Technology Privacy |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
As a direct result of the rise of online purchasing, customers increasingly expect that companies satisfy their stringent requirements in terms of effectiveness, accessibility, and convenience. Customers may browse a large inventory of products and, with only a few clicks of the mouse, have those products delivered to their homes immediately. As businesses work harder to meet the ever-evolving demands of their consumers, "last-mile delivery," often known as the last step of an e-commerce transaction, has become an increasingly vital component. Last-mile delivery refers to the process of transporting an item from a distribution center or warehouse to its final destination, which is often the residence or place of business of the end user of the product. Li et al. (2020) It is the final opportunity to create an impression on a customer, and it is a significant aspect in determining whether or not the customer will be satisfied with the service that they got. With the rise of online shopping comes an increase in the number of customers' demands for final-mile deliveries that are both speedy and stress-free. This study's objective is to analyze the ways in which last-mile delivery has evolved through time in response to altering customer expectations in the field of online retailing. It will delve into the factors that impact consumers' expectations, recent advancements in last-mile delivery, the challenges that e-commerce organizations face, and the ways that are utilized to increase customer satisfaction at this critical juncture in the delivery process. Vrhovac et al. (2023)
2. Objective
The research aimed to fulfill the following objectives:
· Issues that e-commerce enterprises must deal with
· Last-mile delivery's significance in e-commerce
· Result and discussion
3. Methodology
This article will address these possibilities; however, it will also discuss the barriers that impede e-commerce enterprises from offering seamless last-mile delivery. Significant obstacles include traffic and parking constraints in metropolitan areas, missed deliveries because receivers were unavailable, and the difficulty of returning things. All of these factors contribute to an overall lack of accessibility. Because the last-mile delivery has such a large impact on the natural world, it is critical to identify delivery methods that are both ecologically responsible and environmentally sustainable. At the end of the presentation, we will emphasize how important it is to focus on the needs of the client while developing final-mile delivery plans. Providing their consumers with adjustable shipping options, proactive updates, and helpful customer service are three ways in which e-commerce enterprises may enhance the delivery experiences of their customers. The efficiency of last-mile operations may be improved by developing partnerships between e-commerce enterprises, logistics providers, and local players in order to take use of the knowledge and infrastructure possessed by the latter group. By studying the present status of last-mile delivery and the methods used by e-commerce businesses, the purpose of this paper is to shed light on how to fulfill the expectations of consumers in the rapidly evolving e-commerce market. Specifically, the article will focus on how to do this. It emphasizes how important it is to accommodate the ever-changing preferences of consumers, to embrace cutting-edge technology, and to collaborate with other businesses in order to create efficient final-mile delivery experiences that raise satisfaction ratings.
4. Last-mile delivery's significance in e-commerce
When it comes to e-commerce, the significance of "last-mile" delivery cannot be understated. Because it acts as the last point of communication between online merchants and their consumers, it is an essential component of the total experience that the customer has. The following are some of the most important factors that underline the importance of last-mile delivery:
· Customer Satisfaction: The delivery of goods in the last mile has a direct influence on customer satisfaction. When the customer's items are finally delivered, they will have their last opportunity to develop an opinion on the retail establishment. A delivery procedure that is streamlined and effective adds to a great experience for the consumer, which in turn leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and the possibility of more purchases being made.
· Advantage in Competition: In the extremely competitive world of today's e-commerce industry, one of the most important distinguishing factors is now "last-mile delivery." Retailers who are able to provide alternatives for delivery that are rapid, dependable, and convenient have a competitive advantage. When it comes to last-mile delivery, companies may differentiate themselves from the competition and attract new clients by meeting or surpassing the expectations of their existing customers.
· Customer Retention: Ensuring that customers have a pleasant experience with your last-mile delivery plays a critical part in ensuring that customers return. The likelihood of a client becoming a repeat purchaser increases when the customer's order is delivered on time and without any complications. On the other side, unsatisfactory delivery experiences may result in customer discontent and churn if they include things like delivery delays, damaged items, or missing deliveries. Olsson et al. (2022)
· Reputation and Brand Image: The quality of service provided by last-mile delivery firms has a direct effect on the reputation of e-commerce businesses as well as their brand images. A good image of the brand is created when the delivery is on time and dependable, which enhances the business's reputation for delivering exceptional service to customers. On the other hand, unfavorable encounters may taint the image of the brand and lead to unfavorable word-of-mouth, which can have an influence on future sales and the acquisition of new customers.
· Streamlined And Effective Delivery Process: A more streamlined and effective delivery process in the last mile may contribute to a decrease in the percentage of shoppers who leave their shopping carts. When consumers have faith in the manner in which their orders will be fulfilled, they are more inclined to go through with their purchases. E-commerce enterprises have the ability to create confidence in their consumers and encourage them to follow through with their orders by providing a variety of delivery choices, transparent tracking, and realistic delivery predictions.
· Customer Expectations: As e-commerce companies and marketplaces have grown in popularity, customers' expectations about the "last mile" of product delivery have increased substantially. Customers nowadays anticipate having delivery alternatives that are quick, adaptable, and convenient. E-commerce businesses must ensure they can satisfy these expectations in order to maintain their competitive edge and keep their existing consumer base.
· Good Customer Reviews and Recommendations: If a customer's experience with your last-mile delivery was satisfactory, they may provide you with good customer reviews and recommendations. Customers who are pleased with their experiences are more inclined to tell others, both online and offline, about their favorable impressions of the company. These testimonies and suggestions have the potential to increase the awareness of the business, bring in new clients, and propel more sales. Ranatunga et al. (2022)
In conclusion, the "last mile" delivery is an essential part of e-commerce that has a direct influence on customer happiness and retention, as well as brand image and competitive advantage. E-commerce companies may improve their entire customer experience, boost their market position, and promote long-term success by concentrating on improving their last-mile delivery operations in order to create efficiencies across their supply chains. Bergmann et al. (2020)
5. Issues that e-commerce enterprises must deal with
When it comes to the "last mile" of delivery, businesses that specialize in e-commerce encounter a number of obstacles. The efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and overall customer satisfaction of the delivery process might be negatively impacted as a result of these problems. The following is a list of some of the most significant obstacles that e-commerce enterprises face:
· Congestion in Urban Areas: Delivering items in densely populated urban areas may be difficult owing to the increased volume of traffic, the restricted availability of parking, and the complexity of the delivery routes. When delivering packages, navigating through packed city streets may cause disruptions and lead to higher delivery expenses.
· Delivery Attempts That Fail: Deliveries that fail to reach their intended recipient because the recipient was not available to accept the delivery. This might be the result of a number of factors, including an erroneous address, a receiver who was unavailable during efforts to deliver the package, or a missed delivery time window. Deliveries that are not successful result in increased expenditures for redelivery efforts and might have a negative influence on the happiness of customers.
· Returns and Reverse Logistics: E-commerce businesses are also subject to the difficulties that are involved with product returns and reverse logistics. It may be difficult and expensive to effectively manage and handle returned products, as well as to replace them and ensure that reimbursements are processed on time. It is necessary to simplify the procedures involved in reverse logistics in order to keep the pleasure of customers at a high level while also minimizing the effect on overall operations. Kleina and Popp (2022)
· Cost Management: Last-mile shipping may be costly for e-commerce enterprises. Profitability may be considerably impacted by expenses such as transportation, labor, and fuel costs, as well as the management of distribution networks. The problem of maintaining cost-effectiveness while simultaneously satisfying consumer expectations for prompt and comfortable delivery is one that never goes away
· Scalability and capacity: E-commerce businesses often face swings in order quantities, particularly during peak shopping seasons or during promotional events. These fluctuations may be challenging to manage. It may be a substantial difficulty to boost delivery operations in order to satisfy an increase in demand while simultaneously preserving the level of service provided and achieving delivery deadlines.
· Integration of sophisticated Technologies and Infrastructure: The adoption and integration of sophisticated technologies, such as route optimization systems, real-time tracking, and automation, may be difficult for e-commerce enterprises to accomplish. Planning ahead and making financial investments are necessary in order to guarantee compatibility with already installed systems, educate employees, and maintain a technological infrastructure that is trustworthy.
· Influence on Sustainability and the Environment: The fast rise of e-commerce has led to an increase in worries over the industry's influence on the environment, especially in regard to last-mile deliveries. E-commerce businesses that want to align themselves with environmental aims and consumer expectations have significant obstacles, including the management of emissions, the reduction of waste from packaging, and the implementation of sustainable delivery procedures.
· Customer Expectations and Experience: The expectations of customers about the "last mile" of delivery are always changing. It may be difficult for businesses involved in e-commerce to fulfill customers' expectations for speedier delivery times, flexible delivery choices, real-time tracking, and proactive communication. To keep a client satisfied, it is essential to provide a delivery experience that is both smooth and extraordinary, all while successfully handling a variety of complicated logistical issues.
Companies involved in e-commerce have a responsibility to proactively solve these difficulties by using technology, improving their logistical networks, establishing efficient procedures, and researching novel solutions. These issues may be solved with the assistance of collaborative efforts with logistics partners, the use of alternative delivery methods, and the adoption of sustainable business practices, all of which can create a competitive edge in the e-commerce market. Wenckebach and Anjelica (2018)
Figure 1
|
Figure 1 Technology in Education |
6. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
E-commerce has advanced due to increasing client expectations in last-mile delivery. This section discusses how e-commerce enterprises satisfy last-mile delivery standards.
· Sophisticated Technology: E-commerce enterprises use sophisticated technology to improve last-mile delivery. Drones and driverless vehicles are being tested for fast, cheap delivery. These technologies may avoid traffic and deliver items to clients' doorsteps, saving time and money. Smart lockers provide safe and easy client pickup. E-commerce enterprises may meet consumer expectations with quicker, more flexible, and dependable delivery by using these technologies.
· Collaborative Delivery Models: Crowd shipping can optimize last-mile operations. Local people or companies deliver deliveries to neighboring clients. This strategy reduces delivery costs by using existing resources and networks. E-commerce enterprises may connect with people or local businesses to form a trustworthy and efficient delivery network. Collaboration increases delivery speed and community participation.
· E-commerce investing in real-time monitoring technologies: E-commerce enterprises are investing in real-time monitoring technologies to meet client expectations for transparency and proactive communication. These systems provide clients with reliable and up-to-date order tracking information. Valenok et al. (2019) Delivery notifications and alerts improve client satisfaction by keeping them informed about their delivery. E-commerce enterprises may increase customer satisfaction and delivery uncertainty by giving real-time monitoring and proactive communication.
· E-commerce firms provide tailored delivery alternatives: E-commerce firms provide tailored delivery alternatives to accommodate consumer preferences and schedules. Flexible delivery times, precise delivery dates, and alternate delivery locations are offered. E-commerce enterprises may accommodate clients' busy lives and give a customized experience by offering these choices. Customers feel empowered and in control with personalized delivery choices, which boosts satisfaction and loyalty.
· Partnerships and Stakeholder Collaboration: E-commerce enterprises realize that partnerships and collaborations optimize last-mile delivery. Collaboration with logistics providers, local stakeholders, and rivals may improve operations, delivery networks, and efficiency. Sharing resources, improving delivery routes, and using local expertise and infrastructure may make deliveries quicker and cheaper. Zheng (n.d.) E-commerce enterprises may overcome urban congestion, parking restrictions, and route optimization by partnering strategically.
These findings show how e-commerce enterprises satisfy last-mile delivery requirements. E-commerce companies can improve customer experience, satisfaction, and competitiveness by adopting advanced technologies, collaborative delivery models, transparency and proactive communication, personalized options, and partnerships. These tactics help e-commerce enterprises overcome last-mile delivery issues and offer efficient, customer-focused delivery services. Piotrowicz and Cuthbertson (2018)
Figure 2
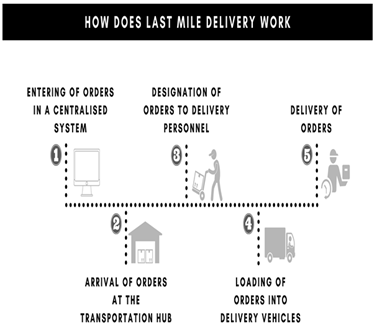
|
Figure 2 Last Mile
Delivery |
7. CONCLUSION
Last-mile delivery has come a long way in the e-commerce business, and this continued development is essential to satisfying customers and keeping them coming back. Customers expect convenient delivery choices that can be changed quickly and are easy to understand as the popularity of online shopping grows. Companies in the e-commerce industry understand the significance of last-mile delivery and are working to mitigate the problems it presents.
E-commerce firms are increasing the speed and ease of delivery with the help of cutting-edge technology like drones, autonomous cars, and smart lockers. Utilizing local resources and networks, collaborative delivery methods like crowd shipping allow for last-mile optimization. Customers are kept abreast of the delivery process thanks to real-time monitoring and proactive communication.
Customers may choose a delivery window that works for them and decide where they want their packages left. In addition, working together with logistics suppliers and local stakeholders helps reduce inefficiencies like traffic and parking issues.
Customer happiness, retention, and good name recognition all depend on whether or not last-mile delivery expectations are met. By using these methods, e-commerce businesses may set themselves apart from rivals and increase consumer loyalty by providing streamlined, superior delivery services.
Future e-commerce last-mile delivery is projected to develop further in response to technological advances, environmental initiatives, and shifting consumer tastes. Last-mile delivery is a highly competitive and ever-changing market, and for e-commerce enterprises to succeed, they will need to embrace innovation, implement sustainable practices, and consistently adjust to consumer expectations. E-commerce businesses may guarantee a positive end stage of the client experience by placing an emphasis on customer-centric strategies and refining their delivery procedures.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Bergmann, F. M., Wagner, S. M., & Wenckebach, M. (2020). Integrating First-Mile Pickup and Last-Mile Delivery on Shared Vehicle Routes for Efficient Urban E-Commerce Distribution. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 131, 26–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trb.2019.09.013
Klein, P., & Popp, B. (2022). Last-Mile Delivery Methods in E-Commerce: Does Perceived Sustainability Matter for Consumer Acceptance and Usage? Sustainability, 14(24), 16437. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416437
Li, F., Fan, Z.-P., Cao, B.-B., & Li, X. (2020). Logistics Service Mode Selection for Last Mile Delivery: An Analysis Method Considering Customer Utility and Delivery Service Cost. Sustainability, 13(1), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010284
Olsson, J., Hallström, D., & Valenok, Y. (2022). Customer Experience Dimensions In Last-Mile Delivery: An Empirical Study on Unattended Home Delivery. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 53(2), 184–205. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPDLM-12-2021-0517
Piotrowicz, W., & Cuthbertson, R. (2018). Last Mile Framework for Omnichannel Retailing: Delivery from the Customer Perspective. In Exploring Omnichannel Retailing (pp. 267–288). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98273-1_12
Ranatunga, M. I., Wijayanayake, A. N., & Minghella, D. H. (2022). Simulation-Based Efficiency Assessment of Integrated First-Mile Pickup and Last-Mile Delivery in An E-Commerce Logistics Network. In 2022 International Research Conference on Smart Computing and Systems Engineering (SCSE). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/SCSE56529.2022.9905083
Valenok, Y., Shams, P., Hallström, D., & Hjorth, K. (2019). Service Innovation in E-Commerce Last Mile Delivery: Mapping the E-Customer Journey. Journal of Business Research, 101, 461–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.01.016
Vrhovac, V., et al. (2023). Measuring E-Commerce User Experience in the Last-Mile Delivery. Mathematics, 11(6), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11061482
Wenckebach, M., & Anjelica, M. (2018). Classification of Last-Mile Delivery Models for E-Commerce Distribution: A Global Perspective. In City Logistics 1 (pp. 209–229). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119425519.ch11
Zheng, S. (n.d.). The Prospects of Different Last-Mile Delivery Modes of E-Commerce Logistics in Hong Kong [Master’s Thesis, The University of Hong Kong]. https://doi.org/10.5353/th_b5703660
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© IJETMR 2014-2023. All Rights Reserved.


