|
|
FUNDAMENTALS OF ART-IDr. Anima Jamwal 1 1 Assistant Professor, Isabella Thoburn College Lucknow, India |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Received 1 January 2021 Accepted 15 February 2021 Published 27 February 2021 Corresponding Author Dr. Anima Jamwal, animajamwal288@gmail.com DOI 10.29121/shodhkosh..v2.i1(SE).2021.20 Funding: This research received
no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or
not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2021 The Author(s).
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative
Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution,
and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are
credited.
|
ABSTRACT |
|
||
|
Art is like Nature. It is everywhere. As we all are a part of nature,
so are we all a part of Art. Like nature, we all see, perceive, and feel Art
in different and individual ways. For one person it can be superficial
ornamentation, whereas for someone else it can be ethos of life. For a
rambler artist, it becomes a soulful spiritual experience. |
|
|||
|
Keywords: Art, Fundamentals, Nature 1. INTRODUCTION
For most of us, Art is the
expression of human imagination involving creative skill and producing works
primarily for aesthetic power. Figure 1 Since the dawn of civilization man
was mesmerized by nature and tried to beautify his environment by copying
nature. Eventually he developed this sense of beauty as a skill and created
astonishing pieces of Art in several forms as painting, music, literature,
dance, sculpture, architecture etc. With the advancement of science and
technology, there seems to be a lot of advancement in creating designs. High
grade sophisticated software’s are now creating artistry that was once
considered the magic of human fingers alone. This also widened the areas of
practical application of the science of Art, ultimately emerging into various
professional fields of study like interior design, architecture, graphics,
animation, printing, photography etc. |
|
|||
Art is unparallel related to human and their culture. It communicates experiences of joy, sorrow, confusion, clarity and many more. It gives visual formation to ideas and feelings, connects us to past, reflects present and anticipates future. Webster’s New Collegiate Dictionary defines art as “the conscious use of skill and creative imagination especially in the production of aesthetic objects”.
Joseph Brodsky defines Art in his poem ‘NEW LIFE’ as….
“Ultimately one’s unbound/ curiosity about these empty zones/ about these objectless vistas/ is what art seems to be all about”
Art is absolutely individualistic and universal at the same time. It is impossible without high skills, hard work and talent. But all these essential and indispensable qualities are worthless if there is no artistic conception of the basic elements used for creation of a piece of art. These basic elements and the guidelines to be followed for application of these elements in a way to ensure a more successful and art piece which is pleasing to eyes and aesthetically appreciable are called the FUNDAMENTALS OF ART. Figure 2
|
|
|
Figure 2 Fundamental of Arts |
Thus, FUNDAMENTALS OF ART are the basic ingredients that are used to create a design and the rule or formulas to utilize these elements judiciously. For example if you are well versed with the alphabets and grammatical rules of English language, you are more likely to build more realistic words, sentences and paragraphs and eventually may create a great piece of literature, but if you don’t understand these alphabets and grammatical rules well, you might work tirelessly to write a paragraph but it might not come out anything more than meaningless jumbled letters. Thus, the fundamentals of art are the basic building blocks of a design.
2. ELEMENTS OF ART
The elements of art are basic ingredients that we use to create a design. It is like if we want to make a cup of tea, we need some basic ingredients (like tea leaves, milk, sugar, and water). By various combinations of these ingredients, we can make various types of teas like strong, light, more sweet, less sweet, and so on…When we combine these ingredients intelligently, we come up with a cup of tea that is satisfactory and cheering. Similarly, by combination of the elements of art we can create an art-piece that is pleasing and enlivening to our soul.
As nature is comprised of five basic elements, the Panch-Tatvas, so is art. There are Five basic elements of art (although some artists and scientists suggest Seven, Eight, Ten and even Fourteen elements of art, the following five are commonly accepted by most of them). Sometimes artworks contain only one or few elements and sometimes they have all the elements of art. One thing is certain however, that there would be absolutely no art without the five elements of art.
3. THE FIVE BASIC ELEMENTS
3.1. LINE
A line is a mark made upon a surface with its' length longer than its width. Lines can also be defined as the path of a moving point. They clarify the edges of shapes and structures. There are many different types of lines like Long, Short, Thick, Thin, Curved, Wavy, Broken, Dotted, horizontal, vertical, diagonal, Perpendicular, Parallel, Zigzag, Spiral, and more.
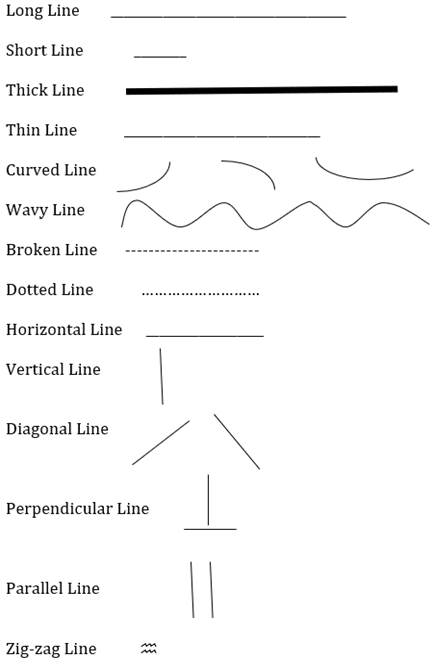
Every line has its own characteristic and feel. The impact of combination of lines can be very different from their individual character.
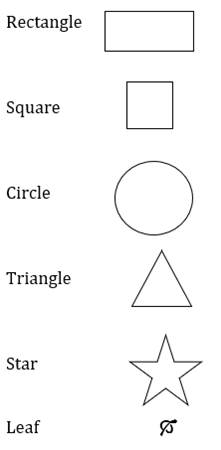
3.2. FORM OR SHAPE
When
a line connects to itself, it creates enclosure. These enclosures are transformed into an
element of art called shape. Shapes can be two-dimensional.it means that they
are flat and have height and width. Shapes can also be geometric and organic.
Geometric shapes are mathematical, like circles, triangles, rectangles
and squares. Organic shapes come from nature, like clouds, stars
and leaves.
Form is the next step up from shape. As we know that shape is two dimensional (Length and Width). When we add depth to it, it creates a three dimensional- form.
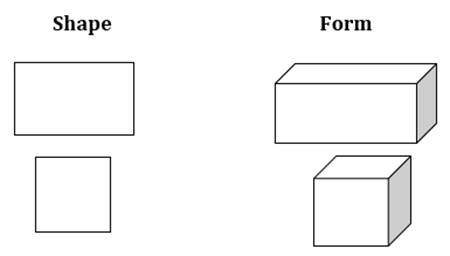
Form or shape can be Actual or Implied. Actual form is a shape that can be seen from all sides for example a statue whereas Implied form is created by shading and modelling.
3.3. SPACE
The element of space is used to vary the size and placement of lines and shapes. Space gives the viewer a reference for interpreting an artwork. Space deals with the illusion of depth on a flat surface but this element can be used for very effective results in three-dimensional art as well. Overlapping, placement, detailing and sizing are the most common methods of manipulating the element of space. Space can be either positive or negative. The object of attraction is the positive space whereas the space all around it is considered the negative space. To give the object of attention its full credit, it is very important to plan the negative space very carefully.
3.4. COLOUR
Colour is the most facilitating elements of art It has physical effect on us and also emotional. Children learn more easily is a colourful surrounding. Sick people recover more rapidly, in restful and pleasant surroundings. Colours also represent special feelings. E.g.: Red is symbol of love, action, enthusiasm and danger, green is the symbol of like and new beginnings. Sometimes green is also associated with every and jealousy, blue is the colour of calmness and white is the colour of purity. People related to aesthetics are concerned with beauty in the choice and combination of colour. Colour combination and choice of design play a dramatic look and enhance the beauty of the artifact immensely.
Dimensional
Qualities of the Colour
Colours have different various characteristics, there are 3 dimensional of colour:
1) Hue: Hue is the name of colour like blue, red, or green. Hue is like family name or surname which tells the root of the colour. A blue colour may be pure blue, green, blue, or violet blue. A pure group mix with green and will give a bright look of torquish blue. there are approximately 150 different hues
2) Value: Value is the amount of a lightness or darkness of the colour for e.g.: We say light blue dress and dark blue dress or light-yellow flower or dark yellow flower. If we mix white with a colour will produce a higher value of that colour and that is lonown as TINT of that colour. When we mix black with a colour, we produce a lower value of that colour, and it is lonown of SHADE of the colour.
3) Intensity: If refers to brilliance or purity of colour the other name or quality of colour
Warm and Cool
Colour
The term warm and cool are frequently used in connection with colour the warm hues are those which are associated with fire, heat, and the sun like real, yellow and orange. The cool hues are associated with water e.g., Blue, Green, Purple.
Classification
of colour
Colour may be classified as
·
Primary 10
·
Secondary 20
· Tertiary / Intermediate 3o
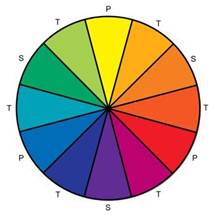
They are very simply depicted in form of a colour wheel. Figure 3
|
|
|
|
Figure 3 Colour Wheel |
|
Primary Colour
They are the most basic colour they cannot be broken down into other colour and no combination can produce them. Primary are red, blue and yellow.
Secondary Colour
These colours are created by mixing two equal parts of primary colour like yellow and red will produce orange and red and blue will produce violet and yellow + blue = green.
Tertiary colour
They are produce by mixing of primary colour with an adjacent secondary colour. The intermediate colours are e.g.:
Red + Orange = Red orange
Violet + Green = Red green
Red + Yellow = Red yellow.
Colour Schemes: Colour Schemes are actually Colour combination. They are developed from the colour wheel.
Types of Colour
Schemes
Colour schemes are divided into various groups –
1) Related Colour Scheme.
2) Contrasting Colour Scheme
3) Neutral Colour Scheme
3.5. TEXTURE
How something feels or looks like it would feel if you
could touch it is called its texture. It is the textile quality of any
material. It is the surface quality which basically describes the smoothness or
roughness of material. Texture is very dominating material it is used mainly to
create contrast in arrangement. Various material forms shiny to matte,
luxurious to dull smooth to rough are used in interior designing to make up the
furnishing and background of the room. Texture has gained more important in
modern art and designing where it often replaces the traditional pattern.
Texture is important in creating essence of a piece of art and can develop very
dramatic effect. There are two kinds of texture: Real (how something actually feels, such as a sculpture) and Implied (when an
artist paints or draws a texture but it is artificial).
The elements of art are important ingredients and tools for creation. They are not only the basic blocks but also a carrier of thoughts and imaginations of the artist. Elements of art also provide us the fundamental benchmark for judging a piece of art for its aesthetic value. Knowing these elements helps us to analyse, appreciate, write about art, and create ourselves. It is fun to play with elements of art and get magical results. We will study more about them in the chapters following
REFERENCES
Elements of Art & Principles of Design (n. d.). https://www.mayfieldschools.org/ElementsPrinciplesofDesign.aspx
Elements of design (n.d.). https://www.britannica.com/art/painting/Elements-of-design
Elements of design (n.d.). https://www.britannica.com/art/painting/Elements-of-design
Fundamentals of Art and Design (n.d.). http://ecoursesonline.iasri.res.in/mod/page/view.php?id=120905
What Are the Seven Elements of Art ? Definition & Examples (n. d.). https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-the-seven-elements-of-art-definition-examples.html
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© ShodhKosh 2021. All Rights Reserved.