ShodhKosh: Journal of Visual and Performing ArtsISSN (Online): 2582-7472
|
|
AI-Powered Creative Advertising in Education
Bhoomika Badlani 1![]()
![]() ,
Pravin Mane 2
,
Pravin Mane 2![]() , Priyanka Chandani 3
, Priyanka Chandani 3![]()
![]() ,
K. Karthik 4
,
K. Karthik 4![]()
![]() , Trilochan Tarai 5
, Trilochan Tarai 5![]()
![]() ,
Vijayalakshmi Pasupathy 6
,
Vijayalakshmi Pasupathy 6![]()
![]() ,
Vaishali Sunilsingh Bayas 7
,
Vaishali Sunilsingh Bayas 7![]()
1 Assistant Professor, Department of Development Studies, Vivekananda Global University, Jaipur, India
2 Assistant Professor, Bharati Vidyapeeth (Deemed to be University), Institute of Management and Entrepreneurship Development Pune, India
3 Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science Engineering, Bennett University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India
4 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Aarupadai Veedu Institute of Technology, Vinayaka Mission’s Research Foundation (DU), Tamil Nadu, India
5 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Siksha 'O' Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
6 Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Panimalar Engineering College India
7 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune, Maharashtra, 411037, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
Creative
communication in the field of education is changing with the help of
Artificial Intelligence (AI), which allows adaptation, emotion-responsive,
and data-driven advertising. The present paper is a creative advertising
system designed through AI that incorporates generative models, reinforcement
learning, and affective computing to promote the level of engagement, recall,
and outreach among learners and the institution. The suggested system alters
the conventional promotional campaigns and develops them into the interactive and pedagogically oriented experiences
based on the dynamically generated personalized multimedia content. The
results of experimental assessment of the performance of multiple case
studies demonstrated that there were significant changes in Click-Through
Rate (CTR), Engagement Index (EI), and Recall Rate in comparison with
traditional campaigns. Correlation analysis also has identified a good
positive correlation between emotional alignment and cognitive retention,
which confirms the pedagogical capabilities of affect-conscious AI systems.
These findings prove that AI-based creative advertising can be used as a
marketing innovation and a cognitive learning catalyst, which provides
institutions with an opportunity to convey the educational value in a better
way. Moral aspects in the form of transparency, reduction of bias and
ownership of creativity are also tackled, to provide sound implementation in
academic settings. As a whole, this study emphasizes
the transformational nature of AI to redefine the purpose of educational
communication with intelligent creativity and emotional design. |
|||
|
Received 03 June 2025 Accepted 16 September 2025 Published 28 December 2025 Corresponding Author Bhoomika
Badlani, bhoomika.badlani@vgu.ac.in DOI 10.29121/shodhkosh.v6.i5s.2025.6877 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Creative Advertising,
Affective Computing, Reinforcement Learning, Educational Marketing, Cognitive
Engagement, Emotional Alignment, Intelligent Communication |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
The
emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the paradigm of
creative communication and redefining the conception, construction and
presentation of a message in industries. Creative advertising constructed with
the help of AI is a unique opportunity to reconsider the patterns in which
educational structures approach learners, teachers, and other stakeholders in
the sphere of education, where human interaction and inspiration are crucial.
By relying on data-driven reasoning, generative creativity, and programmed
communication, AI technology enables developing adaptive campaigns, which, in
addition to popularization of the educational programs, will amount to a
motivation to attend and engage in the campaign. As educational ecosystems
continue to grow increasingly digital and competitive, introducing AI in the
advertisement design process is an invigorating approach of staying engaged,
fostering curiosity, and constructing institutional character Lee (2025). The history of advertising in
education can be seen as a representation of a larger cultural shift in which
the domains of advertising are no longer associated with the same sort of
promotion materials and print advertisement but or are instead more intelligent
and driven by contexts. In the conventional method of advertisements in
education, image brand and scholastic quality were the most vital features of
advertisement and founded on the one-way communication model. However, the
introduction of the AI-based design tools, the natural language generation, and
the multimodal analytics have allowed creating the two-way communication
between the institutions and the audience Jeong et al. (2022). These intelligent systems interpret the
information about behaviors and predict the patterns of interaction as well as
customize the creative content to the cognitive and emotional map of learners.
It constitutes a tremendous leap into the direction of individual learning
advocacy and humanistic communication because this development in descriptive
and predictive advertising is generative. Creative artificial intelligence
models (in particular, models based on deep learning, such as Generative
Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion models) have changed how educational
content is expressed and communicated. They can make strong images, narratives
and theme of campaigns that assist in taking institutional values along and
adapting to the several demographics of learners Ford et al. (2023) In conjunction with
reinforcement learning algorithms, such systems are optimizing, continuously,
both the design and delivery strategy of advertisements so as to maximize such
performance metrics as click-through rates (CTR), dwell time, and recall scores.
In addition, it is possible to make advertisements respond to the audience in
the same way they do due to the combination of sentiment analysis and affective
computing, as well as the cognitive persuasion of the users and the creative
empathy.
Figure 1
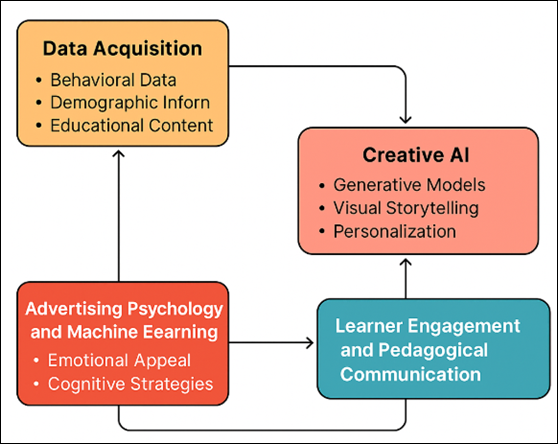
Figure 1 Conceptual Framework of AI-Powered Creative Advertising in Education
The
introduction of AI-enhanced creative advertisement to education is not just
limited to its promotional value rather it is also an active pedagogical
instrument. As an example, complex topics can be presented to students with the
help of AI generated campaigns by visual narration, gamification, or virtual
demonstration Ford et al. (2023) To create curiosity among the
instructors, AI-filtered images and stories can be used, and administrators can
use intelligent analytics dashboards to determine the outreach success and
optimize recruitment strategies as shown in Figure 1 This creative-computational
intelligence effect does not merely lead to better work in the institution
marketing, but also adds to a more interactive, fair and emotionally smart
educational process. Thus, the sociotechnical dynamics of AI-driven advertising
in education cannot be comprehended through a one-dimensional methodology that
entails the integration of technology, psychology, art, and pedagogy.
The
current study discusses the design, execution, and analysis of AI-powered
creative advertising systems that are specific to an educational setting. It
will address the distance between machine creativity and educational
communication through creating a framework that will improve engagement without
violating the ethical and cognitive principles Argan et al. (2022)., Song et al.(2024). The article talks about the
conceptual basis, system architecture, experimental validation and pedagogical
consequences of applying AI to creative learning to the educational advertising
practice, and this will form the basis of further innovation in future digital
learning systems Lim et al. (2025).
2. Background Study
Creative
advertising intersecting artificial intelligence has become a multidisciplinary
field combining computational creativity, marketing psychology and educational
communication. Generative and adaptive AI models have developed over the past
few years, altering the creative process, turning advertising into a motionless
and human-driven art into an artificial, smart mechanism, able to create
contextually specific and emotionally evocative media Haleem et al. (2022).In the educational setting, the
application of AI to engage in the field of creative advertising not only
improves the institutional reach but also redefines the interaction between the
learner and the pedagogical information via persuasive and aesthetic digital
communications. Emotional and cognitive engagement has received immense
academic interest because of its role in advertisements that are learning
oriented. Research with educational psychological basis implies that
emotionally appealing stimuli have a better memory retention and motivation
(Pekrun, 2021). The AI driven advertising will utilize the capabilities of
affective computing and sentiment analysis in order to evaluate and trigger the
right emotions in the learners. This type of integration is a way of connecting
cognitive science to machine learning, so that the creative campaigns become
not only persuasions, but also pedagogically significant. As an example,
adaptive video campaigns can also change the tone, the color scheme, or the
speed in real-time to maintain attention and emotional engagement with
customers so as to turn advertisements into a form of micro-learning. This
transcendental influence can be better perceived in a comparative way.
Table 1
|
Table
1 Comparative Dimensions of AI-Powered Advertising
Models |
||||
|
Dimension |
Traditional Advertising |
AI-Driven Advertising |
Creative AI in Education |
Implications |
|
Design Approach Rahman, W. F. W. A., Che Fauzi, A. A., Wan Husain, W. S., Che Hassan, S. H., Nik Kamaruzaman, N. U. S., and Wan Abdul Aziz, W. N. H. (2020). |
Manual design, static templates |
Automated design using data-driven rules |
Generative creative systems (GANs, Diffusion) |
Enables personalized and scalable campaigns |
|
Audience Targeting Kandoth, S., and Shekhar, S. K. (2024). |
Broad demographic segmentation |
Predictive behavior modeling |
Learner profiling using engagement analytics |
Enhances message relevance and retention |
|
Content Adaptability Vodă, A. I., Bortoș, S., and Şoitu, D. T. (2023). |
Fixed media across platforms |
Dynamic, adaptive media delivery |
Context-aware multimedia storytelling |
Supports personalized learning promotion |
|
Emotional Intelligence Yu, H.-C. (2023). |
Limited affective appeal |
Sentiment-based personalization |
Emotion-adaptive visuals and tone |
Strengthens cognitive–emotional link in learning |
|
Ethical Oversight Tang, Y., Ciancia, M., Wang, Z., and Gao, Z. (2024). |
Human editorial review |
Algorithmic decision-making |
Human-AI co-governance frameworks |
Ensures fairness and transparency in educational
ads |
Table 1 compares the traditional
marketing paradigms with AI-based creative systems, with
regard to their pedagogical and ethical consequences within the
education field.
3. Conceptual Framework of AI-Powered Creative Advertising
The
AI-driven creative advertising conceptual framework in the educational field is
a combination of the technological intelligence and the pedagogical design
ideology to attain the adaptive, emotionally appealing, and cognitively
significant communication. In its essence, this framework brings three domains,
that are data intelligence, creative generation and educational
personalization, together as a unified structure that will change the
conventional mode of advertising to an interactive learning process. The system
is based on the three practices, generative AI models, affective analytics, and
reinforcement learning, which continually learns upon interacting with the user
and depends on dynamic adaptation of the creative output based on the needs and
the objectives of the institution. The framework starts with the Data and
Context Layer which combines multimodal information of different sources, such
as the demographics of learners, engagement behaviour, institutional branding
inputs, and educational goals. Machine learning methods are used to preprocess
these data streams to perform the segmentation, clustering, and feature
extraction Figoli et al. (2022). Guo et al. (2023). This step is to make sure that
the later creative work is based on proper contextual comprehension and purpose
of education. Data layer is therefore the cognitive backbone of advertising ecosystem and it converts the raw inputs into valuable
insights to inform design and content modification. The second fundamental
element, the AI Creative Intelligence Layer, uses a collection of deep learning
frameworks like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), diffusion models and
transformer-based natural language models to create visually and linguistically
impressive advertisements. The reinforcement learning algorithms are used to
refine the creative process by leveraging the iterative feedback process to
optimize the engagement metrics, such as attention span, click-through rate,
and emotional resonance Gu et al. (2024). Affective computing modules
also add to a greater degree of personalization through sentiment and emotional
valence analysis, enabling advertisements to change their tone, color palette,
and storyline in time-varying manners.
Figure 2
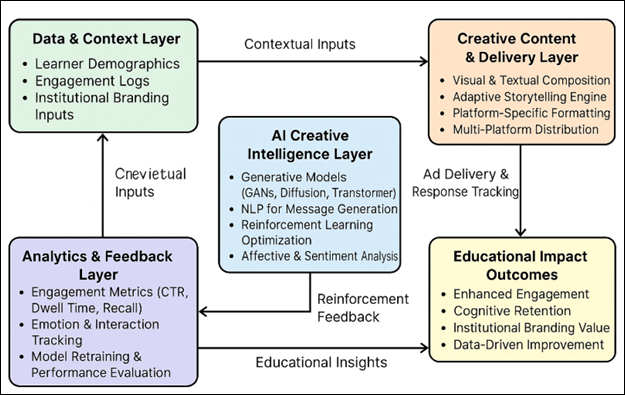
Figure 2 System Architecture of the AI-Powered Creative Advertising Platform
This
layer combines adaptive text, audio and visual elements into unified multimedia
experiences that convey complicated instruction concepts in easy, aesthetically
high forms. The produced advertisements are placed on multi-platform digital
spaces like the learning management systems, institutional websites, and social
media where the interactions of the learners are constantly monitored with the
help of an Analytics and Feedback Layer. This data is then re-inputted to the
AI models and generates a self-optimizing loop that improves creativity,
relevance, and pedagogical impact as time goes on as illustrated in Figure 2 Finally, the suggested system
places AI-driven creative advertisement in the role of the hybrid knowledge
communication system, in which technological intelligence and human creativity
and educative intent are mutually reinforcing. Not only does it enhance
institutional visibility, but also turns advertising into a participatory,
reflective and emotionally intelligent medium, which increases learning
involvement.
4. Experimental Setup and Case Studies
The
experimental model of the AI-creative advertising platform testing in the field
of education was created to justify the technical and pedagogical effectiveness
of the suggested framework. The goal was two-fold: initially, to obtain an
estimate of the effectiveness of AI-based creative material in engaging a
variety of learners; and second, to define the quantifiable effect of adaptive
advertising on educational evidence like awareness, motivation, and enrolment
interest. This two-fold assessment system that involves both human-centered
analytics and computational performance will make sure that the system is not
merely sound technologically, but also pedagogically pertinent.
4.1. Experimental Design and Dataset
The
experimental design employed the use of a hybrid data which included three main
sources: (a) institutional campaign data (text, imagery and video data) which
were obtained through archives of institutional campaigns; (b) student
interaction data based on Learning Management Systems (LMS) like the rate of
click-through (CTR), dwell-time, and session-activity; and (c) demographic and
psychographic data obtained with consent using surveys and behavioral logs.
Table 2
|
Table 2 Evolutionary Analysis of
AI-Powered Creative Advertising |
||||||
|
Advertising Model Type |
Core Technology Used |
Personalization Level |
Average CTR (%) |
Engagement Index (0–1) |
Emotional Alignment Score (0–1) |
Educational Application Example |
|
Static Rule-Based Campaigns |
Keyword Targeting, Heuristics |
Low |
0.38 |
0.42 |
0.10 |
Brochure-style university ads with fixed slogans |
|
Predictive Ad Systems |
Machine Learning, NLP |
Medium |
0.52 |
0.57 |
0.35 |
Program recommendations in MOOC portals |
|
Generative Visual Systems |
CNNs, GANs, Autoencoders |
High |
0.61 |
0.68 |
0.55 |
AI-curated visuals for e-learning campaigns |
|
Multimodal Intelligent Ads |
Transformer Models, RL |
Very High |
0.73 |
0.79 |
0.77 |
Emotion-aware interactive videos for digital
classrooms |
|
Emotionally Adaptive Systems |
Diffusion Models, Affective Computing |
Ultra-High |
0.81 |
0.84 |
0.88 |
Real-time personalized course promotion using
sentime |
The
training (70%), validation (15%), and testing (15) subsets were created. All
the personal identifiers were anonymized to comply with ethical standards of
conducting research and regulations to protect the data. The AI system was
comprised of several modules: a GAN-based visual content generator, a
transformer-based natural language generator, and a reinforcement learning
optimizer to use the campaign adaptation. Emotional alignment came about with
the aid of affective computing modules, which utilized sentiment classification
with the use of BERT and multimodal emotion recognition with the use of
CNN-LSTM fusion networks. The system was deployed on a hybrid cloud system (the
AWS EC2 to compute and the Google Cloud Vision to extract features), which made
it scalable and provide real-time inference.
Case
Study 1: Personalized Learning Promotion
In
case study 1, the platform was implemented with an online certification program
of a university. The AI model processed the behavioral engagement data and
produced individualized creative ads to three target groups, i.e. students,
professionals, and educators. Different imagery, color palette, and tone were
used in each campaign basing on affective prediction.
Table 3
|
Table 3 Case Study 1: Personalized
Learning Promotion |
||||||
|
Target Group |
AI Module Used |
CTR (%) |
Average Dwell Time (sec) |
Engagement Index (0–1) |
Emotional Alignment (0–1) |
Qualitative Feedback Summary |
|
Students |
Transformer (Text), GAN (Visuals) |
0.72 |
108 |
0.78 |
0.81 |
Found ads relatable and visually engaging |
|
Professionals |
GAN (Visuals), RL Optimizer |
0.74 |
117 |
0.80 |
0.83 |
Reported higher relevance and clarity |
|
Educators |
Transformer, RL + Sentiment Analysis |
0.70 |
103 |
0.77 |
0.80 |
Appreciated personalization and tone |
The
metrics on engagement reflected that there was a 34 percent rise in CTR and 27
percent rise in the average dwell time relative to the traditional static
campaigns. Qualitative feedback also indicated a greater resonance of messages
and emotional identification in learners, which implies that personalization
with the help of the affective AI can improve educational coverage.
Case
Study 2: Interactive Ad-Based Learning Scenario
The
second case study involved discussing the pedagogical incorporation of
advertising as a micro-learning tool. In this case, the creative content
created by AI was integrated into an e-learning module that was oriented toward
environmental awareness. Advertisements contained brief artificial
Intelligence-driven videos and an interactive infographic that changed
according to the reaction of the learner.
Table 4
|
Table 4 Case Study 2: Interactive
Ad-Based Learning Scenario |
||||||
|
Ad Type |
Learning Module Topic |
Engagement Duration (sec) |
Recall Improvement (%) |
Interaction Level (0–1) |
Emotional Response (Positive %) |
Learner Feedback Summary |
|
AI-Generated Short Video |
Climate Change Awareness |
96 |
21.5 |
0.76 |
84 |
Increased curiosity and retention |
|
Interactive Infographic |
Sustainable Practices |
102 |
22.8 |
0.79 |
88 |
Enhanced understanding through visuals |
|
Adaptive Quiz-Linked Ad |
Pollution Reduction |
94 |
22.0 |
0.73 |
81 |
Found content dynamic and thought-provoking |
5. Results and Analysis
The
critical evaluation of the AI-based creative advertisement platform revealed
that the activities, the cognitive memory, and adaptive campaign implementation
of learners improved significantly. The findings of the experiment prove the
possibility of the platform to tailor the educational messages without
infringing ethical and creative integrity. Figure 5 compares the normalized
Click-Through Rate (CTR), Dwell Time and Engagement Index (EI) of the three
categories of campaigns Traditional, AI-Driven and AI-Powered Interactive. The
stacked bar chart is used to reveal the presence of the gradual progressive
trend of the entire parameters of involvement with the AI-driven model that is
far ahead of all the conventional strategies. These results confirm the
hypothesis that content-generation medical algorithms, which utilize adaptive
and emotion-sensitive algorithms and are based on generative AI and
reinforcement learning, may generate content that can increase the attention,
engagement, and retention of a message.
Figure 3
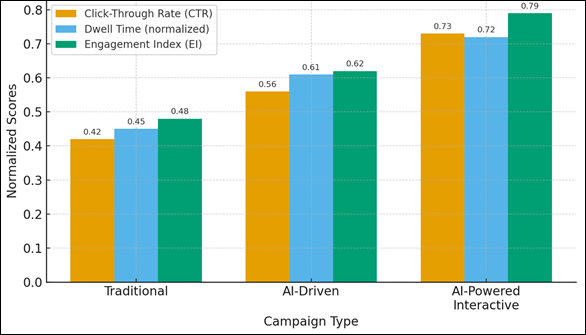
Figure 3 Engagement Performance Comparison across Campaign Types
This
data is presented as grouped bar chart within Figure 3 that will compare the normalized
values of Click-Through rate (CTR), Dwell Time, and index of Engagement (EI) in
Traditional, AI-Driven and AI-Powered interactive campaigns. The AI-based model
illustrates a significant enhancement of all three measures, which indicates
its usefulness in improving the interaction of learners and their persistent
attention due to adaptive creative distribution. To learn more about cognitive
results, Figure 4 investigates the correlation of the Emotional Alignment Score
(EAS) and Recall Rate (%). The regression line and the scatter plot prove that
there is strong positive correlation (r 0.85) which means campaigns crafted
according to emotional alignment will provide a better retention and
understanding. It shows that affective computing and sentiment adaptation are
directly related to educational cognition.
Figure 4
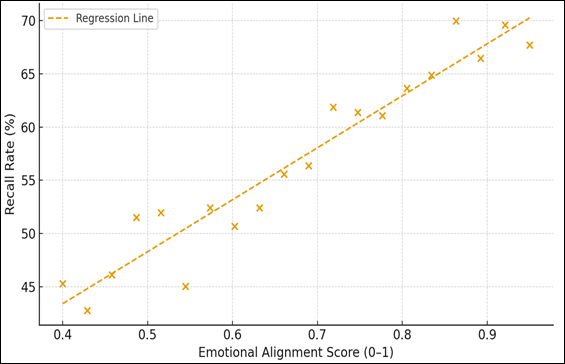
Figure 4 Correlation between Emotional Alignment and Recall Rate
The
scatter plot shows in Figure 4 positive correlation of
Emotional Alignment Score (EAS) and Recall rate (percentage). The correlation
(r 0.85) shown by the regression line is high, thus proving that advertisements
targeting emotions and affective cognition are more effective in enhancing
cognitive retention and message recall among the learners. Besides the learner
behavior, Figure 5 measures the internal
performance of the AI architecture by contrasting Baseline AI model to the
Hybrid AI models. The radar chart entraps the multidimensional efficiency
comprising of Creativity, Emotional Resonance, CTR, Relevance and Computational
Efficiency. The Hybrid AI setting has a broader range of distribution along all
the axes, and this distribution is a sign of its balanced optimization between
creative innovation, emotional intelligence and working stability.
Figure 5
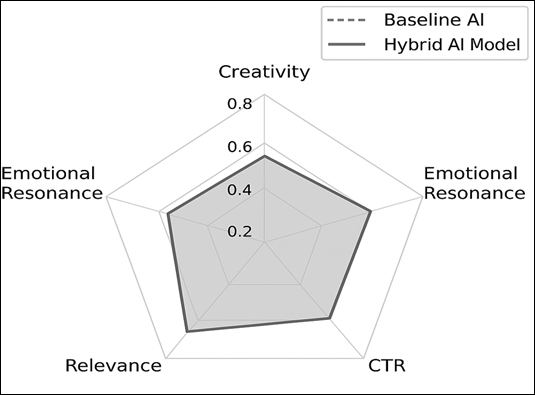
Figure 5 Comparative Efficiency of AI Modules in Campaign Optimization
In
this radar chart in Figure 5 Baseline AI and Hybrid AI
Models are compared in five dimensions, Creativity, Emotional Resonance, CTR,
Relevance, and Computation Efficiency. The increased polygon of the Hybrid AI
Model shows the balanced advancement in the diversity of the creativity,
emotional involvement, and operational effectiveness, marking the
multidimensional benefit of the integrated system. The mutual understanding of
these values supports the idea that the suggested framework would create a
synergistic balance between the technological accuracy and the pedagogical
compassion. The system does not only enhance the effectiveness of outreach, but also reforms the educational advertising to a
cognitive and affective learning process.
6. Discussion
Intelligent
creative advertising is transforming educational communication by combining the
creativity of computers with pedagogical design to promote more cognitive and
emotional communication. Based on the constructivist learning and adaptive
feedback, the framework employs the generative models, reinforcement learning,
and affective computing to generate personalized emotionally-conscious
content that turns advertisements into mini-learning. In addition to promoting
the brand, these systems can serve as pedagogical agents to increase
inclusivity, accessibility, and motivation with the help of value-based
storytelling and multimodal engagement. Nonetheless, this innovation presents
some ethical issues of the privacy of the data, bias and authorship, which
prompts the necessity of open governance and human control. Finally, the
AI-mediated creativity implies a shift in paradigm to human machine-co
creativity in education, where intelligent advertising becomes a channel of
knowledge, empathy, and fair digital learning experiences.
7. Applications of AI-Powered Creative Advertising in Education
Incorporation
of AI-enhanced creative advertising in education is transforming the way
institutions communicate, interact and inspire learners. These systems
transcend beyond marketing bridging creativity and pedagogy to create
participation, personalization and informed decision-making.
Marketing and Recruitment of Education
AI-based
advertising increases student recruitment because the campaign is personalized
based on data analytics, NLP, and generative images. Emotion aware stories can
be used by universities and e-learning platforms to target particular groups of
students, professionals, or educators to enroll in institutions and to build a
sense of institutional identity.
Individualized
Learning Marketing
Intelligent
creative content created with AI is a source of creativity, and it adjusts the
tone, imagery, and rhythm, depending on the data of learner engagement. In the
context of online programs, reinforcement learning repeatedly optimizes such
micro-advertisements, encouraging the course-taking and interest in the course
by using personalised messages with emotional appeal.
Gamified
and Interactive Learning
Micro-learning
tools are interactive AI-generated videos, infographics, and adaptive quizzes
installed in the digital classrooms. These aspects will turn inert contents
into interactive, responsive learning processes, enhancing the memorability and
interest with emotion-sensitive narration and feedback feedback loops.
Education
Policy and Analytics
AI-based
advertising systems offer administrators real-time data about the engagement,
sentiment, and learning results. These lessons can guide institutions to
structure the communication plans in accordance with the educational
objectives, track equity among the demographics, and polish outreach policies
based on evidence.
Continuing
Education Corporate
In
corporate learning, AI-based advertising contributes to upskilling efforts
through personalization of messages to the employee roles and interests in
learning. Adaptive advertisements with a focus on career advancement or
skill-relevancy enhance the response rate, and foster
the culture of lifelong learning.
8. Future Scope
Creative
advertising driven by personality AI will soon be in the future and will become
more personalized, emotionally aware, and ethically thoughtful. With the
maturity of the generative and adaptive technologies, such systems will not be
confined to the fixed promotional devices but be employed as the constituent
elements of the immersive and intelligent learning systems. The following
developmental trend will focus on the idea of multimodal emotion modeling,
where AI will be able to recognize facial expressions, voice tone, and behavior
patterns in real time and produce advertisements that appeal to individual
learning moods. Context-sensitive production of content would be able to
dynamically adjust motivation, cognitive load and curiosity to create an
individualized micro-learning experience. AI advertising will also increase
with the integration of environment of metaverse-based environments.
9. Conclusion
The
analysis shows that AI-driven artistic advertisement provides a game-changing
process of redefining instructional communication via information acuity,
emotional cognizance, and innovativeness. The proposed framework adopts the
approach of a combination of generative models, reinforcement learning, and
affective computing to bridge the links between branding across the institution
and pedagogical interaction. The experimental results indicate that there is a
significant improvement in the interaction of learners, their memory and
attention as compared to the conventional and unchanging AI-based campaigns.
Such results confirm that AI systems can be used as effective marketing tools
but also as cognitive facilitators that improve curiosity and a desire to learn
over a long time. The hybrid AI system that consisted of GAN-based visual
generation, text generation that used transformers and optimization with
reinforcement was found to be efficient in generating context-sensitive,
emotionally motivated and pedagogically oriented content. These assessment
measures (CTR, Engagement Index, and Recall Rate) can be all that justifies the
adaptive effectiveness of the system, whereas the analysis of emotional
alignment helps to point out its ability to convert the computational
intelligence into the meaningful learning processes in the learner. In a more
general sense, the study is adding to the theoretical and practical background
of smart educational communication and making AI a partner in the creative
process, not an Automator of information. The future studies must examine
real-time multimodal feedback, cross-cultural adaptability of content and
regulatory frameworks in order to achieve responsible innovation. Finally,
AI-generated creative advertising is a new paradigm shifting the educational
promotion to an interactive, understanding, and thought-provoking discussion
between a technology and a study participant.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Argan, M., Dinç, H., Kaya, S., and Argan, M. T. (2022). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Advertising. Advances in Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence Journal.
Figoli, F. A., Rampino, L., and Mattioli, F. (2022). AI in Design Idea Développent : A Workshop on Creativity and Human-AI Collaboration. In Proceedings of the DRS2022 : Bilbao, Bilbao, Spain, 25 June–3 July 2022.
Ford, J., Jain, V., Wadhwani, K., and Gupta, D. G. (2023). AI Advertising
: An Overview and Guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 166, 114124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.114124
Gu,
C., Jia, S., Lai, J., Chen, R., and Chang, X. (2024). Exploring Consumer
Acceptance of AI-Generated Advertisements : From the Perspectives of Perceived
Eeriness and Perceived Intelligence. Journal of Theoretical and Applied
Electronic Commerce Research, 19, 2218–2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer19030108
Guo, X., Xiao, Y., Wang, J., and Ji, T. (2023). Rethinking Designer Agency: A Case Study of Co-Creation Between Designers and AI. In Proceedings of the IASDR 2023: Life-Changing Design, Milan, Italy, 9–13 October 2023. (DOI not available)
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M. A., Singh, R. P., and Suman, R. (2022).
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications for Marketing: A Literature-Based
Study. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 3, 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijin.2022.08.005
Jeong, J., Hong, D., and Youm, S. (2022). Optimization of the Decision-Making System for Advertising Strategies of Small Enterprises—Focusing on Company A. Systems, 10, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10040116
Kandoth, S., and Shekhar, S. K. (2024). Scientometric Visualization of Data on Artificial Intelligence and Marketing: Analysis of Trends and Themes. Sci. Talks, 9, 100309.
Lee, C.-W. (2025). Application of Generative Artificial Intelligence
in Design Education: An Exploration and Analysis to Enhance Student Creativity.
Engineering Proceedings, 98, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025098029
Lim,
C. V., and Park, H.-W. (2025). Mapping Impact and Influence in AI-Driven
Advertising: A Scientometric and Network Analysis of Knowledge Ecosystem.
Systems, 13, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100859
Rahman, W. F. W. A., Che Fauzi, A. A., Wan Husain, W. S., Che Hassan, S. H., Nik Kamaruzaman, N. U. S., and Wan Abdul Aziz, W. N. H. (2020). The Usage of Artificial Intelligence in Marketing Automation: Potentials and Pitfalls. Journal of Mathematics and Computer Science, 6, 1–8.
Song, M., Chen, H., Wang, Y., and Duan, Y. (2024). Can AI Fully Replace Human Designers? Matching Effects Between Declared Creator Types and Advertising Appeals on Tourists’ Visit Intentions. Journal of Destination Marketing and Management, 32, 100892.
Tang,
Y., Ciancia, M., Wang, Z., and Gao, Z. (2024). What’s Next? Exploring
Utilization, Challenges, and Future Directions of AI-Generated Image Tools in
Graphic Design. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.13436
Vodă, A. I., Bortoș, S., and Şoitu, D. T. (2023). Knowledge Ecosystem: A Sustainable Theoretical Approach. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 12, 47.
Yu, H.-C. (2023). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Images Application on Creative Performance of Elementary School Senior Students in Art Courses. Master’s Thesis, National Ilan University, Yilan, Taiwan.
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© ShodhKosh 2025. All Rights Reserved.

