ShodhKosh: Journal of Visual and Performing ArtsISSN (Online): 2582-7472
|
|
IMPACT ANALYSIS OF GARBHA MOBILE APPLICATION AMONG PREGNANT WOMEN IN CHENNAI
Dr. V. Jayalakshmi 1 ![]()
![]() ,
Dr. P. Sri Jothi 2
,
Dr. P. Sri Jothi 2![]()
![]()
1 Assistant
Professor, Department of Visual Communication, Asan Memorial College of Arts
and Science, Chennai, India
2 Associate
Professor & Head Department of Visual Communication, Vels Institute of
Science, Technology and Advanced Studies, Chennai, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
Information is
created and communications are exchanged through media. There have been
diverse forms of communication in the propagation of information, emerging as
a universal phenomenon. Digital media enable people to connect and enrich
their relationships with family and friends. As times become more difficult
in the modern age, digital media reduces the stress of many users. Through
the development of advanced technology, the study created a new platform for
developing mobile apps for pregnant women to gather information related to
maternity and childcare. To understand the importance of the health
communication through mobile application, experimental research design was
adopted among pregnant women to find the effective result. Participatory
communication adopted for the study. Respondents were exposed to the newly
developed mobile app and allowed to experience its usability and record their
observations. The study concludes that technology bridged the gap between
people in gaining their knowledge and power in accessing digital media. |
|||
|
Received 01 April 2023 Accepted 28 June 2023 Published 03 July 2023 Corresponding Author Dr. V.
Jayalakshmi, jaya_coolheart@rocketmail.com DOI 10.29121/shodhkosh.v4.i1SE.2023.394 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2023 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Health Communication, Pregnant Women, Parenting
Mother, Infant, Mobile Application, Information |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
Now a day’s our
communication systems are becoming more digital. In the modern world, digital
technology is becoming increasingly significant. The internet and other
electronic media allow people to communicate over long distances more
frequently. We are now surrounded by communication technology that once
intimidated many of us. Think of the introduction of the mobile phone into
everyday life, which we carry with us daily. And mobile phones are digitally
communicating with us today with more influencing technical factors. Digital
communications are not only changing our lives but also raising economic
issues.
Mobile phone usage became unlimited, and people started to
update every news and other events in a single tap before it reached television
or the radio. This new media called the internet, made people get an update
with technology. People are increasingly using mobile devices to complete most of their
activities, and healthcare couldn't be left out of the revolution. Mobile
devices have made it easier for people to access information, learn new things,
interact, and even transact with their mobile devices.
Digitalization of the health sector has been going on for a
long time. Different technologies have been adopted successfully in the sector.
Portable apps are one of the main reasons users and providers have embraced the
technology. A huge amount of mobile applications have been introduced in the
past few years, and some people are wondering why there are so many mobile
applications in medicine. Mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and
laptops have become widespread.
Women face distinctively many health problems like
menopause, menstrual cycle, pregnancy care, birth control and it’s the starting
stage in their life period. Men and Women come across several health issues,
but the symptoms may vary from one to one. For its cure, they require a diverse
treatment for specific concerns. We need to improve the health of women by
addressing issues such as reproductive health, maternal deaths, malnutrition,
and non-communicable diseases; through quality, affordable and accessible
health services. For women to have better health, women need a holistic,
life-course approach that extends beyond reproductive health. Pregnancy is just
the beginning and needs to be maintained throughout the new born, childhood,
adolescent and aging period. We need to empower women so that they can take care of their
own health.
2. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
According to the research, there are no
standards for providing evidence-based information to parents. It is common for
parents to access health information for their children through apps. The healthy
development and growth of infants can be supported by apps that promote
appropriate feeding and play. Information on infant feeding and activity was
incomplete or partially complete and covered few topics, as indicated by the
low quality of the information Cheng et al. (2019).
Quality and access to evidence-based resources and information were key
to women and their partners. Hay et al. (2022) noted that a variety of
information sources are available, but their usefulness to partners is
underappreciated during pregnancy and the early parenting period. For its
convenience, accessibility and timely access to information, the internet is
frequently chosen by women and their partners. It was important that women and
their partners directly communicated with health care professionals in order to
receive adequate information related to pregnancy and parenting.
In the study, pregnant women prefer to collect health
information in online forums. In these domains, unmet informational needs are
present in topics such as labour and miscarriage. Increasing public health
concerns make us to give more attention to peer-to-peer exchanges. Wexler et al. (2020)
in their study said the types of information pregnancies seek from their peers
during pregnancy are not well understood, despite the fact that pregnant women
rely on digital sources for their maternal healthcare.
3.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The goal of the study is to determine a cause-effect relationship, hence
the research adopts experimental design. The field research was carried out
using statistical methods.
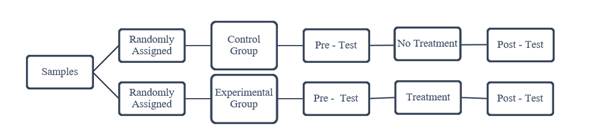
The study adopts
quasi-experimental designs. In Quasi-experiment, some subjects are managed
by one or more treatments that are also called treatment groups. However,
other subjects are not given such a stimulus called the control group.
Treatment may be considered successful if the subjects in the treatment group
are more constructively engaged in the outcome than the control group.
4. THEORETICAL STUDY
The research
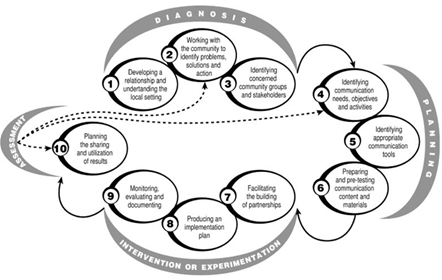
study applies Participatory communication research method. Participatory
communication is “the theory and
practices of communication used to involve people in the decision-making of the development process” Mody (1991).
According to the author Tufte & Mefalopulos
(2009), the participatory
communication is divided into four basic phases:
Phase
One – Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves
the initiation of dialogue between developers and communities.
Phase Two – Planning: Planning focuses on
creating a practical plan that incorporates these actions by specifying
methods, resources and timelines that will be used to accomplish the project.
Phase Three – Intervention or experimentation: A planned action for meeting the needs
of a community is called intervention/experimentation
Phase Four – Assessment: As part of
the participatory discourse, the assessment process is the most effective way
for participants to build knowledge and pride themselves on their contributions.
Figure 1
|
Figure 1 Participatory Communication Theory |
4.1. Theoretical FRAMEWORK of the study
The theory adopted for the
research is a simple process of participatory communication in five
stages.
1) Identifying the problem
At this stage, the research is
brainstormed to identify the relevant issues or problems. So, the problems are
grouped together and finalized with a single caption.
2) Planning the communication tool
Additionally, to setting up
the brainstorming process, the research determined the most effective tools for
the task. During this stage, the introduction; the body content; and the
conclusion were planned for further support.
3) Proceeding with test
During the third stage, the
resource identity will be established so that a pre-test and a post-test can be
conducted to test the reliability of the resource. Evaluating the resources
based on evidence collected through the survey.
4) Monitoring and evaluating
This stage of the research
focused on the analysis of the collected data; observation of the participants;
and the scoring of the samples based on the usage of the Garbha mobile
application.
5) Sharing and utilizing
Finally, in the concluding
stage of research, the title is acknowledged in a documented format; thoughts
and ideas are shared in a way that enhances their attraction and presented in
an appropriate manner for its appreciation.
5. HYPOTHESES
OF THE STUDY
H01: Age of the respondents do not influence accessing the mobile application on maternity among pregnant women.
H02: The age of the respondents do not influence the various media in communicating information to pregnant women through a mobile application.
H03: Age of the respondents do not influence the frequency of using mobile apps.
H04: The age of the respondents do not influence the overall effectiveness of mobile applications and their communication among pregnant women.
6. ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
The ANOVA is applied to test the factors with respect to
the impact of certain demographic variables on the study variables influencing
the usage of Garbha Mobile App.
6.1. ANOVA TEST – Age Vs Accessibility
Table 1
|
Table 1 ANOVA - Age Vs Accessibility |
|||||
|
User_Friendly_To_Access |
|||||
|
Sum of Squares |
Df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
|
Between Groups |
36.480 |
2 |
18.240 |
36.573 |
.000 |
|
Within Groups |
23.440 |
47 |
.499 |
||
|
Total |
59.920 |
49 |
|||
Table 1 explores the accessibility depending on the technical knowledge of the people and their age too. Hence, an attempt was made to check if age has really influenced the ease of access of mobile app.
Since P Value < 0.05, null hypothesis is proved.
Inferences: Age of the respondents influence the ease of usage of mobile applications among pregnant women is analyzed.
6.2. ANOVA TEST - Age Vs Time Saving, Value Addition to Next Gen & Necessary Information
Table 2
|
Table 2 Age Vs Time Saving, Value Addition to Next Gen & Necessary Information |
||||||
|
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
||
|
Time_Saving |
Between Groups |
40.042 |
2 |
20.021 |
50.979 |
.000 |
|
Within Groups |
18.458 |
47 |
.393 |
|||
|
Total |
58.500 |
49 |
||||
|
Value_Adding_To_Next_Gen |
Between Groups |
37.002 |
2 |
18.501 |
29.161 |
.000 |
|
Within Groups |
29.818 |
47 |
.634 |
|||
|
Total |
66.820 |
49 |
||||
|
Necessary_Information |
Between Groups |
41.465 |
2 |
20.733 |
29.075 |
.000 |
|
Within Groups |
33.515 |
47 |
.713 |
|||
|
Total |
74.980 |
49 |
||||
Table 2 reveals that the age in general has influence in time saving, value addition to next gen and in the quest of necessary information. Hence, the present study attempted to identify if age has really influenced time saving, value addition to next gen and in the quest of necessary information
Since P Value < 0.05, null hypothesis is proved.
Inference: Age of the respondents influenced in time saving, adding value to the next generation with necessary information among pregnant women.
6.3. ANOVA TEST - Age Vs Frequency of using mobile apps
Table 3
|
Table 3 Age vs Average_Amount_of_Time_Spent_on_Mobile_App |
|||||
|
Sum of Squares |
Df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
|
Between Groups |
21.969 |
2 |
10.985 |
25.146 |
.000 |
|
Within Groups |
20.531 |
47 |
.437 |
||
|
Total |
42.500 |
49 |
|||
Since P Value < 0.05, null hypothesis is proved.
Inference: Age of the respondents influence the frequency of using mobile apps.
6.4. ANOVA TEST – Overall Effectiveness
Table 4
|
Table 4 Overall_Effectiveness |
|||||
|
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
|
Between Groups |
36.756 |
2 |
18.378 |
52.786 |
.000 |
|
Within Groups |
16.364 |
47 |
.348 |
||
|
Total |
53.120 |
49 |
|||
The overall effectiveness is a yardstick to measure the reach of Garbha mobile app among the experimental group respondents. Hence, the present study attempted to understand the overall effectiveness of Garbha mobile app with regard to age as shown in the Table 4
Since P Value < 0.05, null hypothesis is proved.
Inference: Age of the respondents influence the overall effectiveness of mobile applications and their communication among pregnant women.
7. RESULTS AND FINDING
The findings of the study indicated that the age of the respondents influenced the use of the mobile app by pregnant women.
The respondents explored that the age, in general, has persuaded the mobile application to be time-saving, while gathering necessary information.
The study was co-related with the features, available in the Garbha App. The app is easy to access, which saves time and is more unique with significant information which has created a huge impact among the women respondents.
Based on the study of the relationship between the features available in the application, they are more relevant to each another.
8. CONCLUSION
There are a number of mobile applications that feature
information related to women's health issues. Pregnant women lack information
about their well-being, leading to an undefined pregnancy period. In order to
increase the effectiveness and efficiency of health care services for pregnant
women, a mobile application was developed, which improved their knowledge, gave
more information on health and enhanced their literacy level.
The app provides evidence-based information, which is provided by experts in their respective fields. Every module features high standard of information that is sourced from reliable sources. Smartphones were a breakthrough for the generation. Using their smartphones, pregnant women can make healthy lifestyle more feasible and effective. Modern life has become more connected through digital media.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Cheng, H., Tutt, A., Llewellyn, C., Size, D., Jones, J., Taki, S., Rossiter, C., & Denney-Wilson, E. (2019). Content and Quality of Infant Feeding Smartphone Apps : Five-Year Update on a Systematic Search and Evaluation. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 8(5), e17300. https://doi.org/10.2196/17300.
Hay, S. J., McLachlan, H.L., Newton, M., Forster, D.A., & Shafiei, T. (2022). Sources of Information During Pregnancy and the Early Parenting Period : Exploring the Views of Women and their Partners. Midwifery, 105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2021.103236.
Mody, B. (1991). Designing Messages For Development Communication : An Audience Participation Based Approach. Sage Publications, 211.
Tufte, T., & Mefalopulos, P. (2009). Participatory Communication : A Practical Guide. Applied Knowledge Services, Washington.
Wexler, A., Davoudi, A., Weissenbacher, D., Choi, R., O’Connor, K., Cummings, H. (2020). Pregnancy and Health in the Age of the Internet : A Content Analysis of Online “Birth Club” Forums. PLoS ONE, 15(4). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230947.
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© ShodhKosh 2023. All Rights Reserved.

